To prepare peace treaties with the defeated countries, it was decided to convene a peace conference. France succeeded in holding her in his capital.
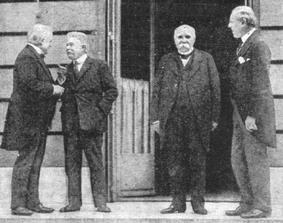
January 18, 1919 Paris Peace Conference was opened by French Prime Minister Jean Clemenceau. In it was attended by 27 countries, but the dominant role played by France (J. Clemenceau), UK (D. Lloyd George) and the USA (B. Wilson). At the conference were not invited representatives of the vanquished nations and Russia, where there was civil war.
main issues at the conference resolved to narrow the meetings: first to "Council of Nine", and from March 1919 - to "Council of Four.
Treaty of Versailles
In April, has been developed text of the treaty with Germany. Her delegation was summoned to Paris for his presentation. Attempts by German diplomats to make at least some changes to the document rejected, and 28 June 1919 in Versailles, signed a peace which became the basis of the postwar settlement. The text of the treaty at the insistence of Wilson was placed Charter of the League of Nations (text vmistyly statute and treaties with allies, Germany).
Under the contract
France returned her land - Alsace and Lorraine, and passed Saar coal mines, however the area for 15 years passed under control of the League of Nations. Germany passed Poznan Poland, part of Upper Silesia, Pomerania and parts of East Prussia, which is separated from the territory of Germany Polish (Dantsyzkyy) corridor, the opening has access to the Baltic Sea to Poland. Belgium received Eypen counties, and Moreno Malmedi after plebiscite , Denmark - northern Schleswig, Memel (Klaipeda) gone to the Ministry of winners ( 1923 connected to Lithuania) and Danzig (Gdansk) proclaimed a free city under the protection of the League of Nations.
Over Treaty of Versailles Germany lost 1 / 7 of its territory. She completely lost colony - they divided among the conquerors. She was forbidden to keep the army more than 100 thousand soldiers, have air and submarine fleets, likvidovuvavsya general staff, skasovuvalasya general conscription. Foreseen that 15-year occupation of the Entente troops left bank of the Rhine and demilitarization 50-kilometer area on its right bank.
By decision of the special commission had Germany pay reparations . Their total amount determined by the Special Conference of 1921 in the amount of 132 billion gold marks, of which 52% was to get France, 22% - UK and 10 percent - Italy.
formation of the League of Nations
Paris Peace Conference adopted the Charter produced by a special commission of the League of Nations, which became part of the Versailles and other treaties.
main organ of the international organization had annual Assembly, comprising all members of the organization, and the Council of the League, which had represented the United States, Britain, France, Japan, Italy, and five non-permanent members. Decisions on all matters be brought had unanimously. The losers in the war state, and Soviet Russia, not up to the League of Nations. League declared the development of cooperation between peoples and guarantee the security of post-war world. U.S. Senate, after reviewing the terms of Versailles peace treaty and, therefore, the Charter of the League of Nations, rejected it, and the U.S., being the initiator of this international organization is not included in it.
General Assembly LF performed the role of international parliament and had the right to make decisions on all international political issues, including measures to preserve peace.
belonged to the LF of two areas: City of Danzig and the Saar. Colonial possession of Germany and the Ottoman Empire were given the mandate by LF UK, France, Belgium and Japan.
LF Statute entered into force January 10, 1920 on 16 January in Paris held its first meeting of the LF, and 15 November in Geneva (which became the permanent seat of the headquarters organization) held its first session of the Assembly .
Saint-Germain Treaty
September 10, 1919 was signed by St. Germain Treaty of Peace with Austria, which fixed the recognition of new frontiers, formed after the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian monarchy.
Former Austrian possession - the province of Bohemia, Moravia and Silesia became part of Czechoslovakia. Italy won the South Tyrol, Julian extreme, almost all of Istria, in addition to the city of Fiume (Rijeka). Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes received Bosnia and Herzegovina, Dalmatia, extreme, Slovenia. Romania got the Bukovina and Poland invaded Galicia.
Austria allowed to have 30-thousand army. Austria also had to pay reparations, although the amount has not been defined. She was forbidden to join Germany.
Neyyiskyy peace treaty
November 27, 1919 in Paris suburb Neyyi-sur-Seine signed a peace treaty with Bulgaria. She lost western Thrace, Greece has passed, and get rid of the exit to the Aegean Sea. South Dobruja remained in Romania. Part of Macedonia was handed Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. Bulgarian army was forbidden to keep more than 20 thousand soldiers. The amount of reparations was determined in 2.25 billion gold francs, which had to pay for 37 years.
Trianon peace treaty
peace treaty with Hungary was named Trianon. He was only signed June 4, 1920 This was due to the existence of the Hungarian Soviet republic. Hungary is under contract declined by 77% and the population - by 59%. Romania received Transylvania and Banat, the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes - Vojvodina and Croatia. Hungary lost access to the Adriatic Sea. Slovakia and Transcarpathian Ukraine moved to Czecho-Slovakia. Hungary refused all rights in the former Austro-Hungarian Monarchy, including in Transcarpathian Ukraine.
Hungary also passed Burgenland (border zone inhabited by the German population).
prohibited general conscription, the army was limited to 35 thousand soldiers. The victorious Hungary paid reparations.
Sevrskyy peace treaty
August 10, 1920 Turkish sultan's government signed a peace treaty Sevrskyy, so there was division of the former Ottoman Empire. Turkey refused the Arab lands, recognized the British protectorate over Egypt and France - over Morocco and Tunisia. Turkey was deprived of rights to Sudan, recognized the annexation Cyprus, lost possession on the Arabian peninsula and Europe. Islands of the Aegean city of Izmir and transferred Greece. The army was limited to 50 thousand soldiers. Throughout the country remained surrender mode that actually mean Turkey's semi.
Lausanne Peace Treaty and Turkey's agreement with Soviet Russia
Sevrskyy contract never became effective. Thanks to the national liberation movement Turkey managed to expose their sovereignty and to win back some territory. By agreement with Soviet Russia (1921) Turkey has received a city of Kars and the surrounding area.
for solving problems circle around Turkey and the Straits convened an international conference in Lausanne, Switzerland November 20, 1922 and continued intermittently up to July 24, 1923 The conference was attended by representatives from the UK France, Italy, Japan, Greece, Romania, the Kingdom of SHS, Turkey and the Soviet republics (Russia, Ukraine, Georgia) and Bulgaria.
The Conference adopted the Convention on the Regime of the Black Sea Straits, which was based on the principle of free passage of ships, both military and civilian, under any flag.
July 24, 1923 Lausanne Treaty was signed, so legally fitted decay of the Ottoman Empire and defined new borders of Turkey. Turkey returned to the territory, which were previously transferred to Greece. France subsequently lost part of Syria in favor of Turkey.
In the 20's of the Arab Ottoman possession was handed over by the League of Nations mandates of Great Britain (Iraq, Transjordan, Palestine) and France (Syria, Lebanon).
signed peace treaties with Germany and its allies after the First World War, not vhamuvalo aroused by war and revolution to Europe. Armed conflicts, revolutions, riots, political crisis continued to shake the European continent has for several years.
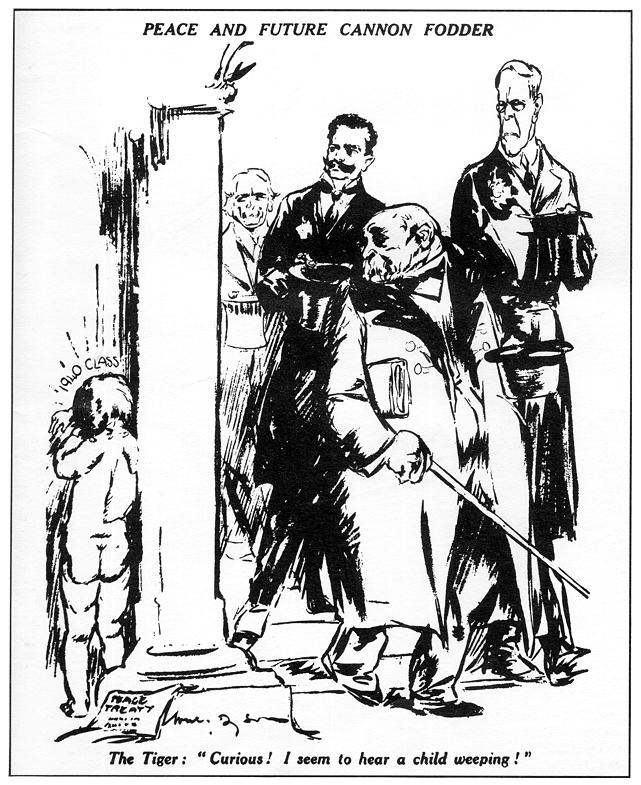
main root cause of acute political struggle and confrontation was in the formation of Versailles, which was the first attempt in history to achieve harmony between our countries and the world community, but it was unfair, especially to the vanquished countries.
Also new European borders, carried out on the map as a result of a long diplomatic bargaining, not always take into account the will of the people of areas subject to territorial redistribution. Especially evident disparity of state borders and ethnic boundaries of the settlement reflects the map "The nations of Central and Eastern Europe in the interwar period. In 1923 the majority of interstate conflict connected with the territorial problem was solved solution, some have postponed for the future. Yes, Italy in its favor solved the problem of Fiume. Went to the armed conflict with Greece on the island of Corfu, but this time unsuccessfully (1923). Poland, using any means, managed to achieve the joining of the Silesia region of Vilnius, Riga and for peace in 1921 with Soviet republics - in Western Ukraine and Western Belarus. In 1923, the new eastern border of Poland was considered the Entente countries. Remained unresolved dispute between the Soviet republics and Romania of Bessarabia.
instability of the situation adding new attempts by leaders of the Comintern and Soviet Russia ignite a global revolution in Europe after the defeat of the socialist revolution in Germany, Hungary and Slovakia in 1919 Thus, during the Soviet-Polish War of 1920-1921 Red Army tried to bring their bayonets revolution in Europe. But the better-armed Polish army managed to stop the "red invasion". The next attempt occurred in 1923, while in Bulgaria, Poland and Germany were also organized armed appearances driven Communist Party. But these revolts were brutally suppressed by government troops, the Communist Party suffered police harassment and lost for a long time a significant number of his supporters.
war and postwar instability had a great influence on the internal political situation in Europe, even those who escaped the revolution. In England the situation was stabilized by broad social reforms. In France, social tensions could translate into a state of waiting for the moment when Germany will pay reparations. In Spain vstanovyvsya authoritarian mode Prima de Rivera (push to the Spanish army were defeated in war with the Republic of Rif in Morocco). Post-war problems of Italy, whom they called "vanquished among the winners," resulted in "red biennium" (1920-1921 biennium), when the workers took power in factories vyhanyayuchy owners. Italy fell into chaos, the government was in complete inaction. In such circumstances the ruling elite scared "red danger" to appoint the prime minister the leader of Italy's fascist movement B. Mussolini. October 30, 1922 he led troops entered Rome blackshirt. Mussolini activelyat fashyzatsiyi took to the country and transform Italy into a powerful empire of the Mediterranean.
the early 20's in the leading countries of the Entente to power who did not want to pin responsibility for the injustice of Versailles, at the same time trying to improve it. As a result, the 20-ties was a series of measures to remedy the defects of post-war settlement in Europe.
One of the weaknesses of the new system was the exclusion of her Russia. Trying to isolate Russia because of the commitment of its leaders to the idea of world revolution and the dictatorship of the proletariat had no success, but has made a destructive element in international relations. In the early 20-ies became clear that the Bolsheviks were firmly established in power, and plans for world revolution - impracticable. In 1922, Russia invited the delegation to the Genoa conference on the search of "economic recovery of Central and Eastern Europe, where, among other issues, an attempt was made to develop common terms for normalizing relations with Soviet Russia and other Soviet republics. But problems paying debts royal party could not overcome. Entente countries put in by $ 18 billion rubles. In response to Soviet Russia demanded that it pay 39 billion rubles. for losses from intervention of the Entente. In addition, the delegation of Soviet Russia flatly refused to pay the debts of the Provisional Government.
Appearing at a conference in critical condition, April 16, 1922 Soviet Russia and Germany in the town of Rapallo signed an agreement to restore diplomatic relations in full and to refuse any claims. This agreement initiated fruitful cooperation between Russia and Germany in economic, political and military spheres. Under this agreement Russia Germany forgave her debt -10,000,000,000 rubles. The contract was a breakthrough on the diplomatic front, which brought Russia and Germany from international isolation. Treaty of Rapallo has created a fundamentally new situation in Europe. Two "insulted" the state made a contract, effectively jeopardizing elaborated winners post-war security system. The one that saved the Versailles system was that Germany remained weak conditions of peace, and Russia - Revolution and civil war.
In 1924 rolling wave of diplomatic recognitions from other Western countries who were concerned about the possibility of establishing a strong German-Soviet bloc antyversalskoho. Exceptions were only the United States. But relations between the West and the USSR were unequal. The Soviet Union tried removing the solution for European Affairs, to isolate it, a country that had a common border with it, "sanitary zone". This resulted in mistrust of the Soviet leadership in the West and contributed to even greater rapprochement of Russia with Germany and Turkey.
same time it was faster solution of problems connected with fulfillment of the Treaty of Versailles and restore Germany to the world community as a full member.
remained most acute issue of reparations. Established in 1921 amount (123 billion marks) was not capable of Germany. France is demanding full payment and to make the Germany before, along with Belgium occupied the Ruhr region, where heavy industry was concentrated in Germany (1923).
An international crisis. To solve the difficult situation in London in 1924 an international conference was convened, which adopted a plan developed by the commission of experts led by American banker Dauesa. According to the plan envisaged the withdrawal of French and Belgian troops from the Ruhr and Germany commit yazuvalasya in the next 4 years to pay 1-1,75 billion marks a year and in subsequent years - to 2 billion of 6 years of this plan, Germany has paid in July , 5 billion marks. The plan involved the provision of German and American English credits in the amount of $ 2 billion. How to guarantee implementation of the plan installed allied control of the railways and the State Bank of Germany. The implementation plan Dauesa helped restore the German economy, but put it in dependence on the U.S..
In 1929, they adopted a new plan for American businessmen and bankers Jung, followed by reparations volume decreased to 113.9 billion marks, and annual payments were established in the amount of 2.5 billion marks. The payments were spread for 55 years. According to the plan all types of control over Germany and its economy and finances were canceled. To receive reparations and their distribution was established Bank for International Settlements. The bank played a leading role in financing the leading sectors of German economy and helped to further ownership ed Germany to the economy in the U.S..
 English
English