§ 27. Features of the East.
Medieval India
You know
·
What are the main features of the East in the Middle Ages?
·
What's new in the development of medieval India?
·
Why North India underwent Islamization? What is Delhi
Sultanate?
·
What are the achievements of the medieval culture of India?
1. Features of the East.
The term "east" in Historical Studies accepted
understand the society is not only Asia but also Africa and Oceania. Below
become familiar with the development of civilizations most typical East: Indo-South Asianand Sino-Far East (about the origin and development
Middle Eastern-Muslim you learned from the preceding paragraph). Although these
civilization in many respects different, and they have some common features that give
to evaluate them as belonging to one type - the east, which
different from the West.
Characteristic features of the civilizations of the East:
·
state is the supreme owner of the land.
·
who is in power, he has property;
·
basis of society and the state - rural communities;
·
private property plays only a supporting role as dominant
is the state;
·
presence of large cities, which first played the role of
administrative, religious centers and the centers of international trade.
On
Unlike Europe, the clear distinction of transition from the era of the ancient East
medieval world to spend almost impossible. They had such enormous
changes in Europe. Orient have developed, as in the previous century, in their
traditional boundaries.
In all states east of management system was
organized under the scheme. Those who cultivated the land were united in
communities that have a guaranteed right and obligation to handle it and
used for farming all the necessary resources: water, wood,
suburbs and more. However, the right to own and dispose of land and its resources
in the hands of the state apparatus. Between communities and the state apparatus
there was a clear connection. Made redundant product community as conveyed
tax state, which transferred most of its staff and for the benefit of society
whole (built canals, roads, bridges, churches, etc.). So, those who belonged
the state apparatus, had access to the distribution of manufactured products and
respectively, received their share of the property. What a man held a higher position in
state apparatus, the greater the share it receives. Therefore we say that
feature of Eastern civilization was the presence of government - owned.
What
effectively served the state apparatus, so regularly and in sufficient
collected taxes. The state was strong and powerful. Its power has grown from
productivity peasant or artisan. But if this clear mechanism
failures occurred, the whole society was raised: rebellion, famine,
destruction of others. Failures of this system took place through two main reasons:
when the amount of taxes due to reckless policy of rulers exceeded
possible after production or external invasion, which eroded
traditional system of life.
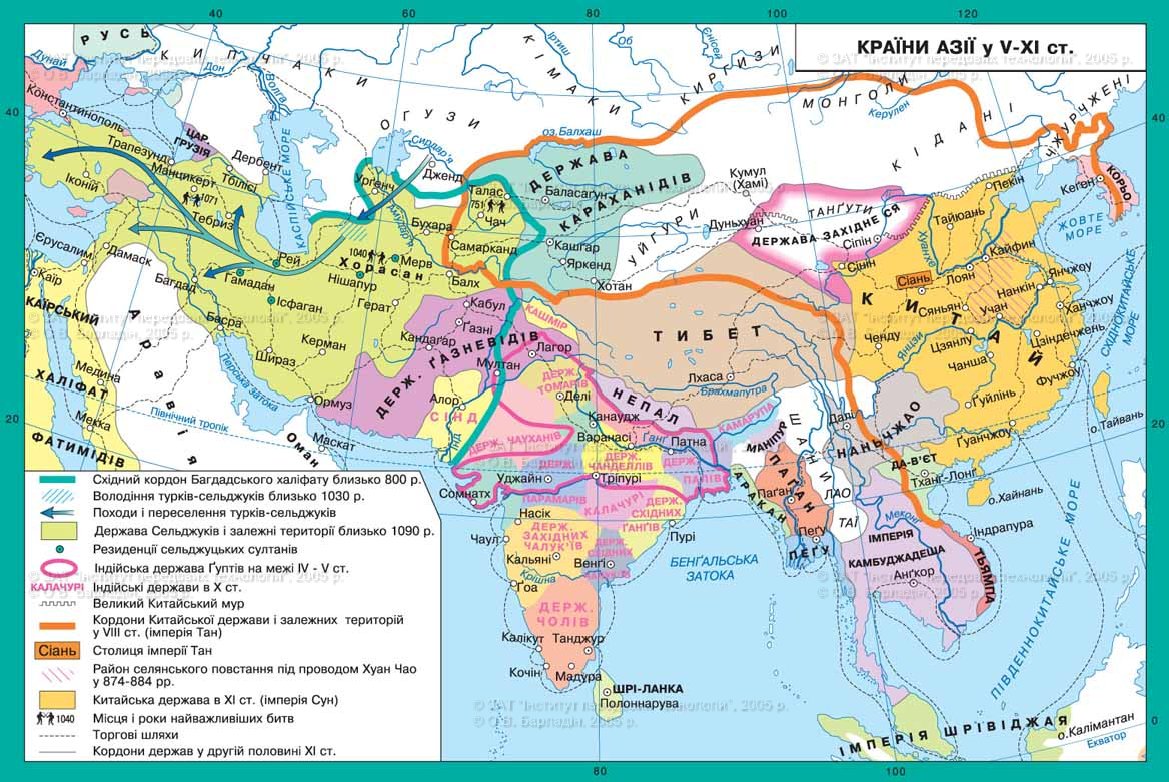
Countries in Asia V-XIArt.
2. Indian society in the era
Middle Ages
In
history of India, as mentioned, it is difficult to draw the line between ancient
history and Middle Ages. When in Europe, major changes occurred related
with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the formation of feudalism, India
continued to grow in their own script. Many small states
fought among themselves, while the principles of life of most people remained
inviolable.
More
of Indian society during ancient times shared on four major groups - Varna. Higher Varna (Brahmin and Kshatriya) Continued to operate and fight, and lower (vayshi and Shudra) Work on
fields and workshops. In the Middle Ages this ancient division changes.
Varna were split into smaller groups of people united by professions or
occupation. Thus, for example, among the Brahmins vydilylysya pharmacists, doctors,
teachers and others. Among Kshatriya - Soldiers, officials and others.
The Europeans called these groups of castes. By the tenth century. number of castes has increased to
several thousand. Each caste has its own special symbols, rituals, ornaments, rules
behavior. Bride or groom can find was only in their caste and
only to educate children according to tradition and customs of caste. As Varna, Shared the lower caste and higher. There was also
the special caste of "untouchables".
Representatives
higher castes could not even be near the lower, the more washed
food or water with their hands. It was considered higher can "desecrate" even a shadow
"Untouchable." Only representatives of higher could read and listen to the sacred
texts. Those who violated those customs and traditions suffered cruel punishments.
From
Chinese travel notes Xuan Tszan (VII century)..
Soft yasnyky, fishing, garbage cleaners,
healers, laundress, traveling artists, gravedigger, butchers and others like them living outside the
city. On the streets of these people or do does not appear, or hold the left
side until you reach the desired location. Their home is surrounded by walls and
located outside the city.
1. Which castes include the above
groups of city dwellers: higher or lower?
2. Limitations experienced representatives
these professions?
3. Why are they subjected to such restrictions?
Despite
existence of caste division from different castes objects yednuvalysya in communities
were organized as small self-sufficient state, which acted as a unit
of government. Communities are the foundation of Indian society. They
it provided internal stability. While state power was
weak and limited to collecting taxes from the communities.
Between
different castes in the community has developed a system of mutual services - exchange
products and services. Almost all the community decide the question itself: elected
counsel, judges, taxes, people allocated for public works. Those who
violated the rules of life in the community, could be punished. The worst punishment -
expulsion from the community.
In
medieval India there were several religions. Based on ancient religion
in the first millennium AD Hinduism emerged. In first place came the worship three gods:
Vishnu, Shiva and Brahmi. In their honor built temples and offered rich
offerings.

Figure Shiva.
India, Article XI.
Hindus
believed in rebirth after death. If a person lives by not doing anything.
What disturbed the caste tradition, he is in the next life could be reborn in
higher caste. If the departed, then pererodzhuvavsya in below or in animals, plants,
stones.
Hindus
obozhestvlyaly animals. Especially cows. They are forbidden
kill. Hindus also worship the sacred river Ganges.
The second
Indian religion was Buddhism, which originated here in the VI century. BC The Buddha taught that
all human life - is tuhist and suffering and therefore his soul must
rid of all the earth and strive for a higher peace. He called forget
of wealth. Pleasure to speak only the truth and not to kill living things.

Figure of Buddha. India
From
V cent. Buddhism declined in India, but spread rapidly in China, Japan,
Korea, Mongolia, South-East Asia. Buddhism became one of the world
religion alongside Christianity and Islam.
From
the arrival of Muslim conquerors in India Islam penetrated. He most widely
acquired in the north of the peninsula.
Except
these religions in India was spread hundreds of local cults.
|
According to the Russian orientalist L.Olena: Medieval India was characterized by almost
persistent instability of political power ... This instability reflected in
korotkochasnosti and sincere weakness dynasties and states, the existence
constant internecine fighting several equally weak political
formations ... structure of society, she remained in medieval India
that which was before ... "
|
3. Delhi
sultanate
As
noted in Hindustan by
thousands of history, there was no strong government. Sometimes that one
distinguished from other states and sought to subjugate others. However,
exhausted its potential in wars against their neighbors, and she was dying again
split. It happened with the state GuptaThat
faced in 320 years because of the Raj Chandragupta.
But his successors failed to preserve the unity of the state and stand against raids
Hun, and the late VI century. it ceased to exist. In the VII century.
estimated the Chinese traveler Xuan Cyanogen in
India were about 70 principalities whose owners were Raj and
Maharaja, who fought among themselves.
Significant changes in the lives of India began in the XII century.,
when its northern region was conquered by Muslims. They wanted to conquer
India with Article VIII. But their actions were unsuccessful. Finally, the governor
neighboring states of India HaznevidivThat
followed the collapse of the caliphate Baghdad, Mahmoud Ghazni(998-1030 years) carried out systematic predatory trips to India. He
17 times rozoryuvav it, moving each time further in the inland. Through
stolen wealth and captured slaves he transformed his capital Ghazni one of the most beautiful cities of the East.
On
his death in 1206 governor Qutb-ud-Din Aybek separated from Ghazni and
established an independent state in northern India from the center in Delhi. New
state known as Delhi Sultanate. At the end of the XIII century. sultanate
quickly increased its territory and to the XIV century. captured almost
the entire peninsula Hindustan. The largest amount of Sultanate
reached by Mohammed Tuhlaka(1325-1351), who even cherished plans of aggressive
journeys to Persia and China. This aggressive policy has undermined the internal
state power, which began to collapse. At the end of the XIV century.
Delhi sultanate occupied territory smaller than that in the XIII century. Him
already had to reflect the intrusion of powerful neighbors, that arose after the collapse
sultanate. Constant war weakened and destroyed Sultanate and its neighbors. This
advantage of the Mongols, who began to make regular raids in North India
plundering of the city and population. In 1398 in India has directed his campaign Timur.
The main purpose of his trip was robbery, not the accession of India to their
possessions. 120,000th Timur army fire and sword held cities in North
India. Although Timur was a Muslim, he did not particularly rozbyrav that occurred on
his journey - Hindu or Muslim. Daly City, which seemed to favor
winners, also became the object of robbery and murder. In 1399 Timur
returned to his Samarkand, where prisoners were gathered together artisans in India
to build a mosque to commemorate the victory.
After Timur's campaigns and internecine fighting between the two
dozens of countries that emerged after the collapse of the Delhi sultanate, India
was weak and vulnerable in the face of European penetration, which
started in the XVI century. and Mughal invasion led by Babur(1526).
Among the reasons that
prompted widespread success of invaders in India are the following:
·
significant natural wealth;
·
lack of ethnic and religious unity;
·
internal wars of rulers;
·
traditional strength of the peasant community.
4. Culture of India
In the Middle Ages in the culture of India held
significant changes. Continued assimilation of cultures north and south of the peninsula,
followed by the formation of religions of Hinduism and Buddhism.
During the XIII-XV centuries. Development in India were the two
significant moments. First, in northern India continued the process of combining elements
Islamic and Indian civilizations. Secondly, during the rather intensive
developing urban life, which was associated with development of various residences
rulers of India and involvement in international trade through
Arab merchants. Rapidly growing cities like Goa, Calicut,
Kambay, Agra, Panipat,
Lahore, Multan, New Delhi.
Building on previous achievements, the culture of India
evolved, enriching their achievements world culture. Yes
at the beginning of our era in India used the decimal system of numbers, which
now used worldwide. Indian mathematicians were able to calculate
Square shapes and volumes of bodies operate on fractions, relatively accurately determine
number p
An important achievements were in medicine. Indian doctors
perfectly know the internal structure of the body, doing complex operations using
about 200 surgical instruments, medicine prepared from different diseases. They
were known for their knowledge and skills in all countries of the East.
To this day preserved many buildings during the
Middle Ages. Architectural masterpieces of this period are Buddhist temples, hewn in rocks:
Ajanta, Ellora, Fr.Elefant.
Temple in Ajanta - This is a
complex of buildings, caves that were built over nine centuries. 30 rooms of the house
were painted with frescoes (murals preserved only in 16 caves), reflecting
life of the then India, scenes from Buddha's life. Paints and painted murals that are not
brightness and still lost. Its main feature is that they
glow in the dark.
In addition to churches in
rocks, temples were built as towers. In Orissa was
built the whole temple town and surrounded by mighty walls. Inside the temples
almost not decorated, but outside they are continuously covered with reliefs, statues
and skillfully executed stone carvings. Sculptors depicted scenes from
legends and stories. They could well depict people and animals in motion.
Since the XIII century. the architecture of India considerable
made an impact of Muslim culture. Most impressive was the huge
minaret Qutb Minar in Delhi. Its height reaches 70
meters.
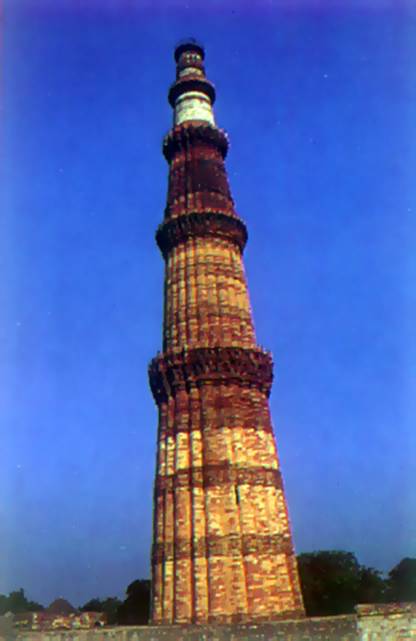

Minaret
in Delhi. XIII.
Literature of medieval India created mainly
Sanskrit (ancient language that Aryans). This language served the same
role as Latin in Europe. Most famous poets and playwrights of contemporary India
was Kalidas. After the Muslim conquests
Indian poets began using folk language, Arabic and Persian.
The Indians loved music and dancing. But they were dancing
ritual - the language of dance, they told stories of life goals of gods and heroes.
In Indian dance every movement of the body, arms, legs, especially the fingers, every gesture of something
mean. Art of Dance equaled to craft. It opanovuvalosyayears.
Indians love to games and entertainment. Favored were
Chess, which are spread around the world. In the popular Adrenaline
was dice.
Check how to remember
Which division
existed in Indian society? What's new in this division emerged in the Middle
ever?
What
religion had spread within the Indyi in the Middle
ever?
Who from
conquerors left the most visible mark in India: the Huns or the Arabs?
When
Delhi Sultanate was established?
How many years have existed Delhi Sultanate?
Give reasons
death of Delhi sultanate.
Specify the purpose and
Timur effects hike in India.
What was the contribution of Indian culture
valued?
On telling the Indians dance?
Think and answer
How different from the caste Varna?
What are the existing rules of relations between strata and caste?
1.
What we mean by the term "east"?
2.
What characteristics are typical for the eastern
civilizations?
3.
Name the factors of stability in Eastern
civilizations.
4.
Why India has been attacked many
invaders?
5.
What were the consequences of gains for India?
Why and how India was conquered by Muslims? To what consequences this led?
Perform the task
6.
Specify the masterpieces of medieval Indian culture.
For the curious
- Make chronologically.
- Using additional
literature, make a story: "Polovtsian raids on Russia"
- Fill in the table:
|
Period
|
Grand Duke
|
Major events
|
|
|
|
|
- Prepare detailed
story of life
- Make a plan for response to
theme: "
- With `yasuyte
positive and negative sides
- Specify
key moments in history
- Define
main features of. Answer Just as a table.
 English
English



