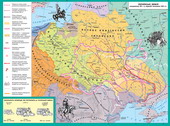
Union of Lublin. HOME Polish domination ON UKRAINIAN LANDS
Principal PROCEEDINGS
- Ukrainian nobility XIV-XVI century. - A bridge between the two periods of the Ukrainian state - princes and Cossacks.
Vasily Konstantin - -Ostrog - Ukrainian prince "uncrowned king of Rus-Ukraine", defender of Orthodoxy.
- Lublin Union - an intergovernmental agreement to merge the Polish Kingdom and Grand Duchy of Lithuania into one state - the Commonwealth.
Outside the Union of Lublin - not contradict the laws of the then and was as a voluntary decision of the representatives of Ukrainian lands, in substance, but actually it was an act of usurpation of Poland Ukrainian lands.
- Union of Lublin, on the one hand, contributed to the Polish expansion to Ukrainian lands, devastating attack Catholicism, the rise of social tension, the then Polish influence the Ukrainian elite, on the other - caused the outbreak powerful national liberation and cultural-educational movement.
CHRONOLOGY OF EVENTS
|
1558-1583 he |
Livonsk war. Moscow's war against the Livonian Order of German Knights, and after its collapse (of 1561) - against the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Poland (from 1569 - the Commonwealth) of Denmark and Sweden for access to the Baltic Sea. |
|
1569 |
Union of Lublin. Association of Polish Kingdom and Grand Duchy of Lithuania in the Commonwealth. Poland's accession Kyiv, Bratslavshchina, Volyn, and Podlasie. |
|
1582 |
introduction in the Commonwealth's new - the Gregorian calendar. |
|
1587-1632 he |
Board in the Commonwealth, Sigismund III. |
|
1596 years . |
Orthodox and Uniate Cathedral in Brest. The establishment of the Uniate Greek Catholic Cathedral Church. |
PERSON
Prince Vasily (Constantine) Ostrozky (1526-1608) - is one of the most influential political figures of the time . From 1559 Kiev was the palatine and winner of Ukrainian border. Outstanding cultural and educational activist. In late 16 th century. - The largest landowner after the King of the Commonwealth. Annual Duke researchers estimate earnings of 10 million zlotys. Konstantin Ostrog was able to put naystyhlishyy time 15-20000th army. Telling is the fact that at princely courts continually on about 2 thousand noble youths-young men who served here knightly training.
After the death of Polish King Stefan Batory (1586 City), Vasily Konstantin Ostrog was considered one of the possible contenders to the throne. General, Ambassador Pope in Warsaw Enrico Spanokkyo stressed that on the side of Prince two advantages: first, he richest person in the state, and second, it all hold a prudent and decent man, the only thing standing in the way - the prince was "Rusin, and leader of the schismatics".
BACKGROUND
Polish State in the XVI century., especially during the reign of Sigismund II Augusta (1548-1572 biennium), experienced a period of economic and cultural development. At that time it has become the main supplier of agricultural products to European markets. At this time Poland seemed to be the only island of internal harmony against the backdrop of bloody religious conflict that raged in Europe: religious wars in France, the arbitrariness of the Inquisition in Spain, brutal persecution of Protestants in Mary Tudor England, reform economy of war in Germany, in Moscow's bloody oprichnina ...
In XV-XVI centuries. Poland became a kingdom gentry republic with an elected monarch at the head. A huge role, especially in 1573, belonged to the Diet - is-representative body, which had legislative powers. It consisted of a king, senate, which sat magnates and representatives of royal administration and the Chamber Ambassadors, envoys dietines that united the provinces or territories. Unless the general (ted) Diet King could not legislate, set taxes, to convene a feudal militia - the levy en masse, to marry others. Throughout the gentry guaranteed equal rights.
UKRAINIAN LAND UNDER THE RULE OF FOREIGN COUNTRIES AT THE BEGINNING of the XVI century.
|
Ukrainian lands |
State under the authority of which were |
|
Galicia (from 1387) West Podolia (from 1430) |
Poland |
|
Bukovina (from the middle of the XVI century.) |
Moldavia |
|
Transcarpathia (from the XIII century.) |
Hungary |
|
Kyiv region, Volyn, Bratslavshchina (Eastern Podolia), Chernihiv-Siverschyna |
Grand Duchy of Lithuania |
|
Black and Azov Sea region |
Crimean Khanate |
changes that have occurred during the first half XVI century. position in the Ukrainian lands
|
Chernihiv-Siverschyna |
Home XVI century. - Muscovy |
|
Transcarpathia |
1526 - Hungary and Transylvania under the rule of Austria |
|
Bukovina |
1538 - Moldovan principality ruled by the Ottoman Empire |
BACKGROUND OF ASSOCIATION Duchy of Lithuania and Polish Kingdom. Lublin Seim 1569
-
interest of the Ukrainian, Belarusian and Lithuanian gentry in the Polish model of the state with its political rights and is a privilege for the nobility.
-
Awareness of Ukrainian in the second half of XVI century. search of reliable protection of their land, because the powers opposition Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the devastating raids of the Tatar hordes Noghay was ineffective.
-
Loss
Grand Duchy of Lithuania during the Livonian War, vast territories, destruction of farms, loss of life, threatening the absolute absorption Muscovy.
-
desire Polish nobility to expand their holdings in a situation where in Poland itself almost free land was not.
July 1, 1569 Diet ruled on the union of two states: the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Poland. The new state called the Commonwealth .
-
new state managed only zahalnoobranyy King who crowned in Krakow as the Polish King and Grand Duke of Lithuania and the Sejm and Senate joint.
-
between Lithuania and Poland likvidovuvalysya customs borders; in the new state introduced a single currency.
-
though Lithuania has lost the right to own diet and external relations, but retained some independence - and in particular their right to trial, a treasure.
SOCIAL AND POLITICAL CHANGES IN UKRAINIAN LANDS After the Lublin Union
-
After the Lublin Union of Podlasie, Volhynia, Bratslavshchina (Eastern skirts) and Kyiv region passed to Poland, which included already were Western Galicia and Podolia.
-
on Ukrainian lands ceded to the Commonwealth, zaprovadzhuvavsya administrative division under Polish model.
in the Commonwealth of Ukrainian lands was six provinces:
| old |
new |
|
Ruske (centered in Lviv) Belz (Belz) Podolsk (Kamianets) |
Volyn (Lutsk) Bratslav (Bratslav) Kiev (Kyiv) |
implications Lublin Union
implications Lublin Union had the character of the distant future, as soon as the union any significant changes in the Ukrainian situation did not happen.
-
Since the fate of Ukrainian land entirely dependent on external circumstances: while the direct owners of estates remained princes who ruled them and the union until the country was ruled a king who belonged to the understanding of local customs and faith, so long and Ukrainian life if not experienced significant changes.
-
However, the result of the union
Polish magnates and nobles took great opportunities for misappropriation of Ukrainian lands, ruthless exploitation of peasants and townsmen, and spiritual enslavement Ukrainian.
-
Soon after the Union of Lublin in the lands of Kyiv, Bratslavshchina, Zadniprov'ya began to show new owners - Polish gentry, and with them spread filvarkova management system of serfdom and enslavement.
-
acute after the Union of Lublin became the problem of faith and language. The Catholic Church wanted to increase the number of its supporters. Therefore, Ukraine introduced in Jesuit schools and colleges. They contributed to the spread of education: many Ukrainian had the opportunity to study at Western universities. However, payment for education is often become abdication of parental native language and faith. Because for the XVI century. representatives of the lower strata have limited opportunities for education, nobility of Polish influence Ukraine a loss of power, capable of leading the struggle for restoration of statehood.
loss of statehood, which although in a very limited form, but still remained in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania - the most dramatic consequence for Ukraine Union of Lublin.
 English
English