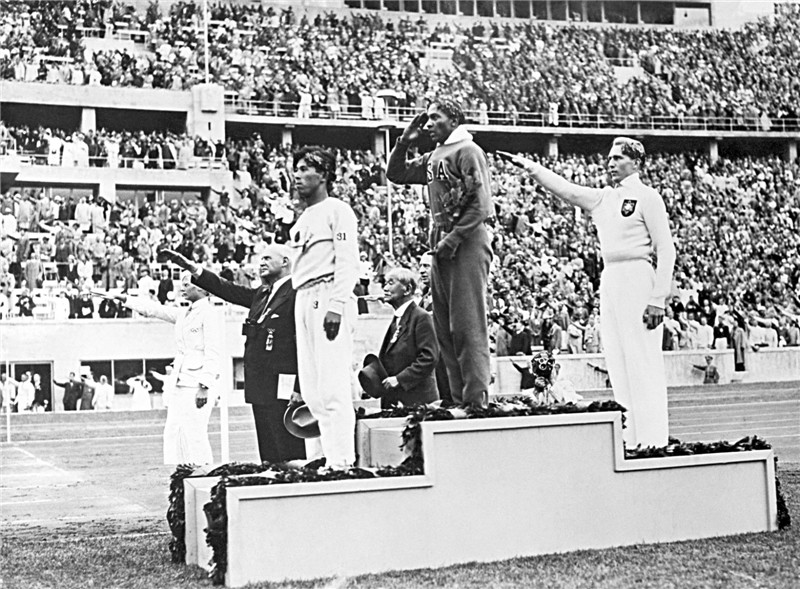
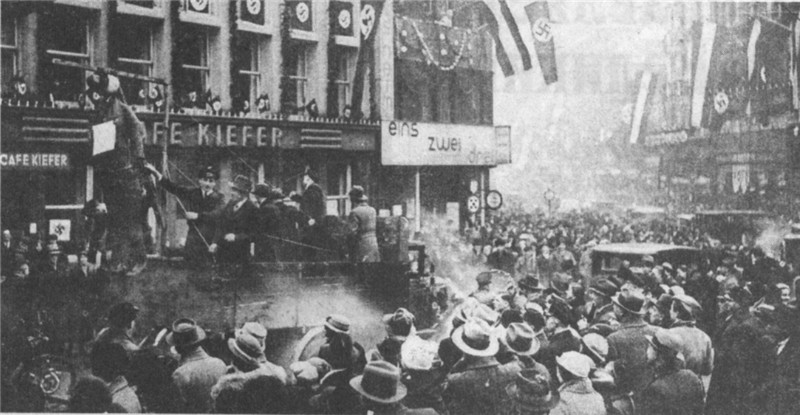
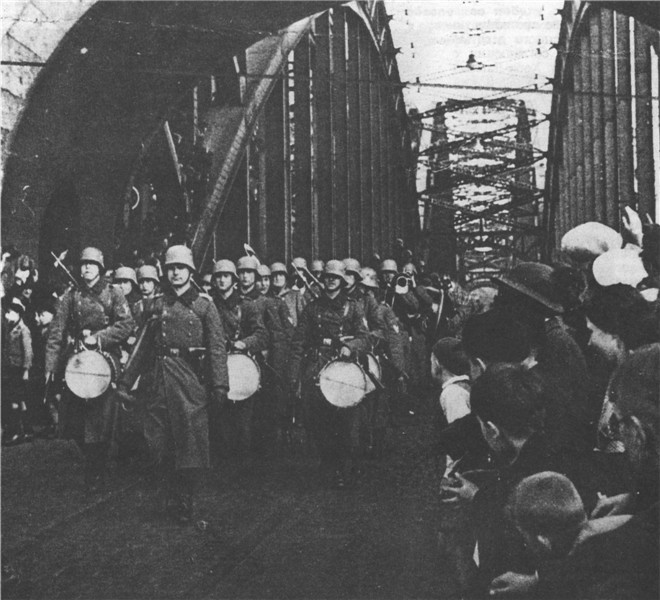
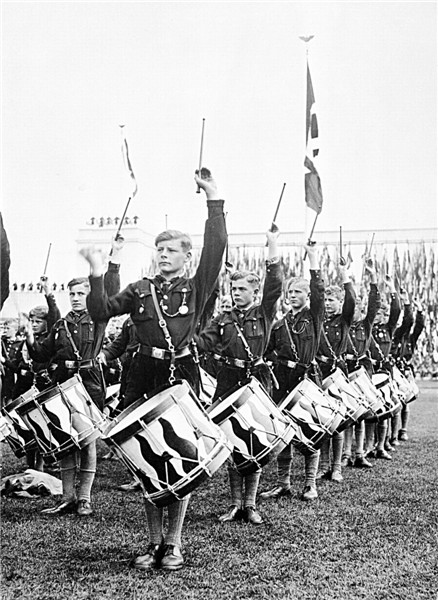
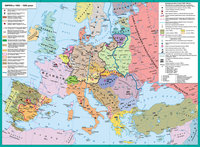
After the revolutionary events of 1917-1923 he was the political situation stabilized in the continent. Was overcome post-war economic crisis, some countries began a rapid growth, established borders, outlined a new peace dohovramy. Came to power new political forces.
first to a quiet life back Northern and Western Europe. Here after reformed, strengthened democratic institutions, economic development of States reached a new level. By the early 30's, these states have lived without major shocks except for the powerful miners' strike that gripped England in 1926
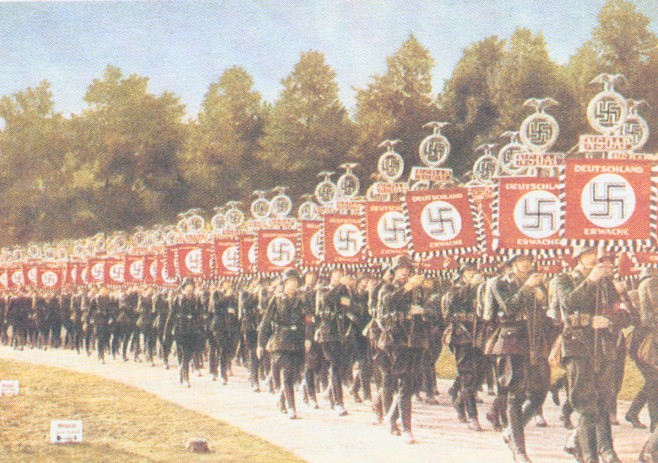
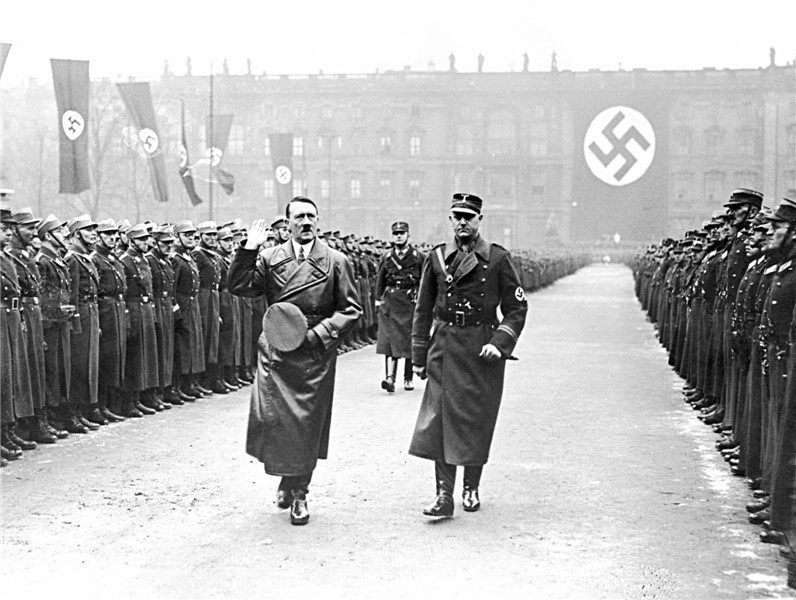
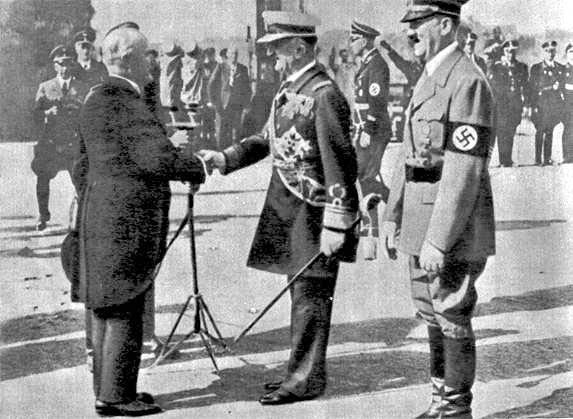
more complex processes taking place in Eastern and Southern Europe. These territories launched a sharp struggle between left and right movements, which ended not in favor of democracy. So in Hungary Horthy dictatorship established in Spain - Prima de Rivera, in Bulgaria - on June. Italy started fast fashyzatsiya country and strengthening government of Mussolini, who made it his goal to return the country the greatness of the Roman Empire.
In the mid 20's authoritarian regimes came to power in Albania (Zohu), the crisis parliamentary republics: in Portugal (Salazar), Poland (Pilsudski) and Lithuania (Smetona). However, in Greece as a result of military coup in 1924 had overthrown the monarchy. After all the blame for the defeat in the war with Turkey the public were supposed to King.
In 1929 as a result of worsening the national problem in the Kingdom of SHS, King Alexander established a royal dictatorship and renamed the country Yugoslavia.
island of stability in the region remained Austria and Czechoslovakia. Last 20-30's was a model of democratic development.
Authoritarian regimes that were established in Europe in 20 years, retained signs of democracy (representative authorities acted, there was no mass repression, there was a multi-visibility, the economy steadily went up).
In 1924-1932 he did not know Europe, and war, except for minor border incident between Greece and Bulgaria in 1925
important factor in the stability of international relations in Europe has become a wave of diplomatic vyznannnya USSR (1924). But relations between the West and the USSR were unequal. The Soviet Union tried removing the solution for European Affairs, isolate, creating a country that had a common border with it, "sanitary zone". This caused distrust and sometimes led to worsening relations. Thus, in 1927 Britain broke off diplomatic relations with the USSR, which almost led to armed conflict.
To end formed in 1922 Soviet-German alliance, the West German concessions. In 1924 they adopted the plan Dauesa that facilitated the payment of reparations for it. In 1925 withdrew from Ruru Franco-Belgian troops. That same year, the conference concluded at Locarno Pact Rhine guarantee that secured the inviolability of borders between France, Belgium and Germany. In 1926 Germany joined the League of Nations. And in 1929 the plan Jung reparatory it significantly reduced payments.
In 20-ies were made significant progress in the development of international law. For the first time at an international level discussed the problem of disarmament. However, it was doomed to failure because the Versailles-Washington system established inequality in inventory, so virtually all the talks were aimed at fixing this situation.
However, in 1925 signed the Geneva Convention on the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons, from which during the First World War affected about 1 million people. Also signed the Convention on the Prohibition of the use of barbaric weapons systems (bursting balloons, etc.) and on the rights of prisoners of war. The only European country that has not signed those conventions, was the Soviet Union.
the initiative of French Foreign Minister Briana and Secretary of State Kellogg in Paris on August 27, 1928 15 countries signed the Kellogg Pact, Briana, involving the renunciation of war as a means of solution of the inter-state disputes.
subsequently acceded to the Covenant of almost all European countries, including the USSR.
In September 1929 Briana gave to the League of Nations with the new political breakthrough. He proposed to create a united Europe ("pan-Europe"), that unite the leading European states by setting between "somewhat like the federal ties. Next year, Briana proposed specific plan for a "federal European Union, according to which European countries (except Turkey and the USSR) had gradually eliminate customs borders to create a" common market "and to strengthen guarantees of peace, adopted in Locarno. The "father of Europe" (this nickname later received Briana) critically met England, Italy, USA and other countries. Even Germany, which counted on the support of Briana, demanded the previous political settlement in Europe, ie the complete elimination of Versailles. So the idea of a united Europe should find support at that time.
late 20's economic crisis afflicting the U.S. and quickly overturned in Europe, which violates the stability on the continent. Germany were the first that was in financial dependence on the United States. Then the crisis spread to other European countries, the least touched France.
Each ideological force offered their recipes crisis. Slowly began to increase the authority of the extreme forces - communists and fascists, who advocated radical pereustriy Europe.
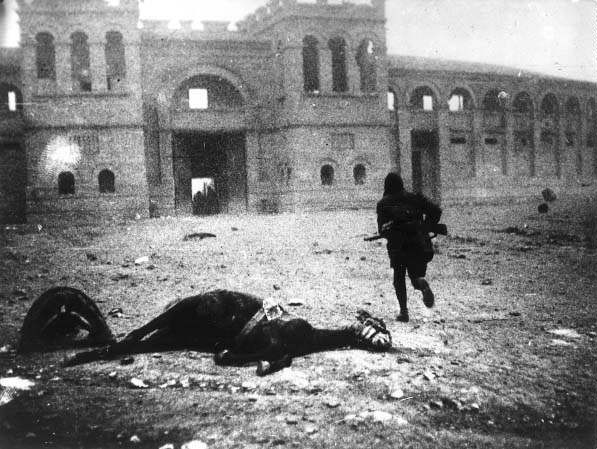
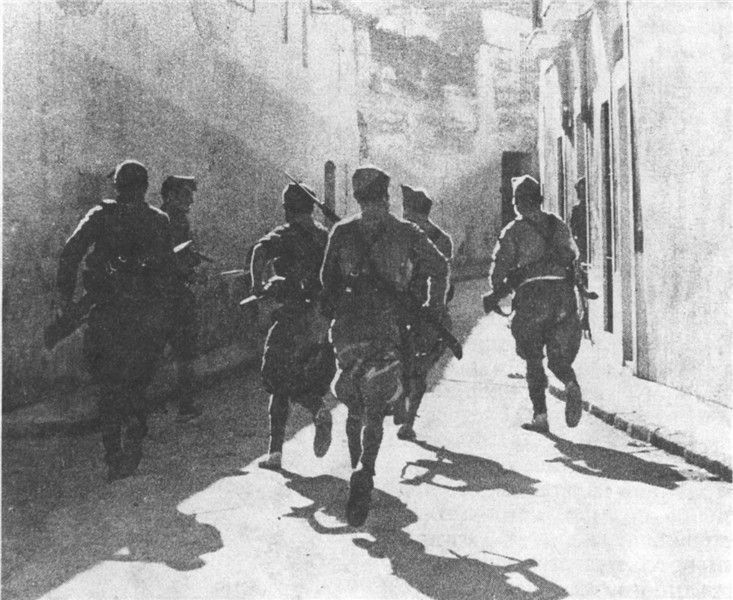
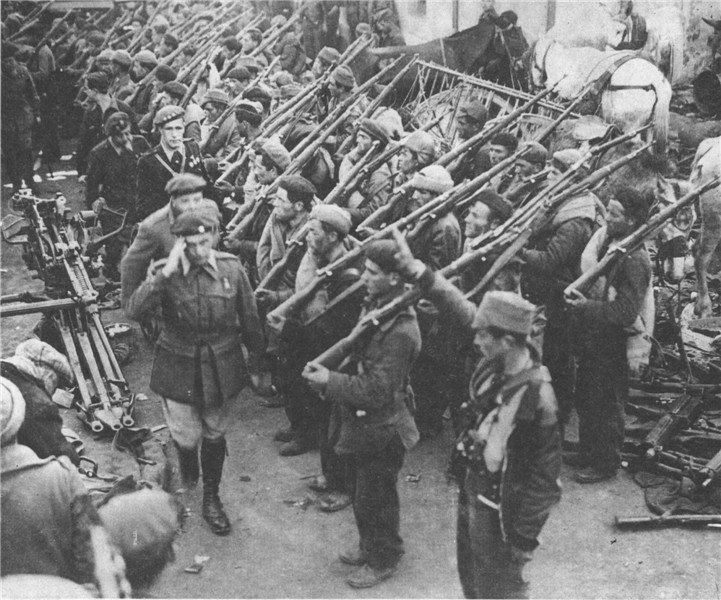
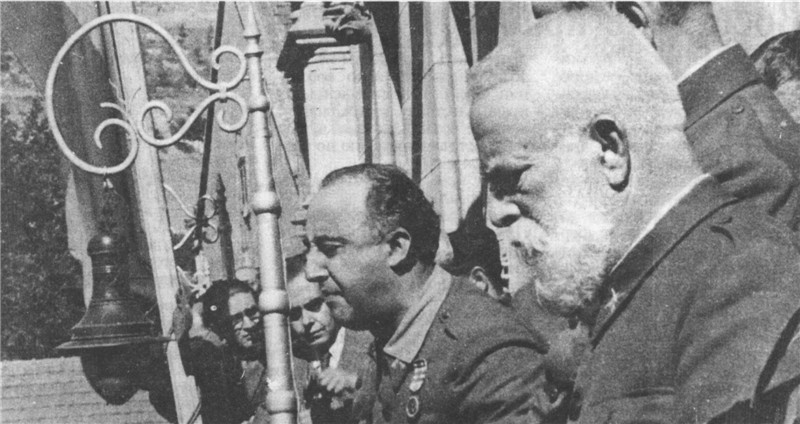
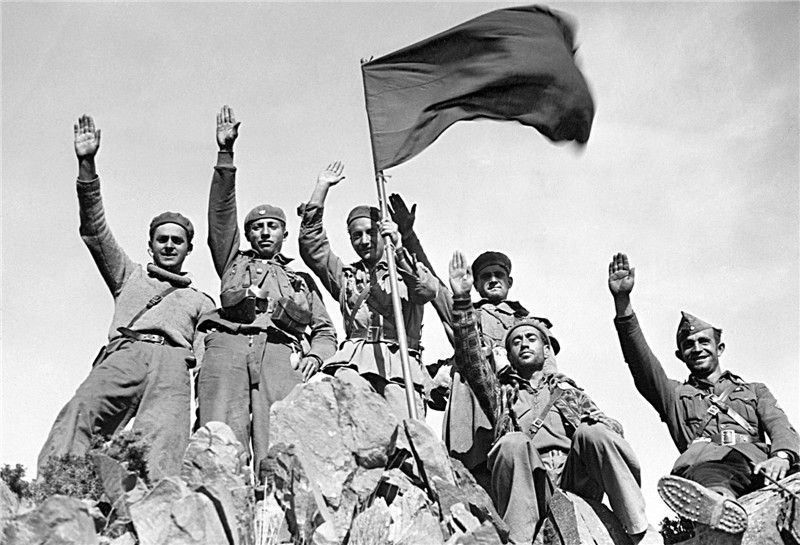
important event in the early 30's in Europe was the revolution in Spain. It was bloodless and brought down the monarchy to power dostupylysya Democrats. But the revolutionary camp was isolated. Hope naselennnya on radical changes for the better were improper. Every year the country's growing political struggle that eventually led to civil war years 1936-1939
 English
English