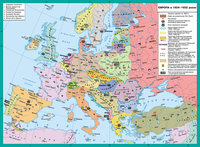
world economic crisis of 1929-1933 aggravated international relations and sparked threats of a new war. Unlike in 1914? in 30 years a few states wished to fight. This situation made a real opportunity to avoid war under conditions of joint action svtovoho community. But this did not happen.
first war there was a fire in the Far East. In autumn 1931 the Japanese troops occupied the territory of Manchuria - important in a strategic and economically part of China.
But Japan has not been condemned as an aggressor. League of Nations just declared that Manchuria is an integral part of China, and newly admitted states Manchu-Kuo on its territory. In response to Japan in 1933 defiantly withdrew from the League of Nations. Provided for in this case sanctions against Japan were not entered. Appeared first precedent of impunity for aggression.
In 1935 Italy took advantage of this precedent. She considered herself deprived the results of World War I, so concealed aggressive plans? which included the conquest of Ethiopia and intentions. In 1935-1936 he was the Italian army invaded this African country.
After Hitler came to power in Germany joined the group of aggressive states. By 1933 the situation in Germany within the Versailles system was much easier. She stopped paying reparations. In negotiations on disarmament in 1932 it promised equality in arms. At the official level, even discussed the issue of return of German colonies. An important step towards the further elimination of Versailles was signed in July 1933 at the suggestion of Mussolini Pact consent and cooperation "between Britain, France, Italy and Germany. This involved extensive cooperation pact countries on the revision of Versailles and Germany legally secured equality in armaments. However ratification the treaty failed. For Hitler's renegotiation of the Treaty of Versailles was only the first step towards world domination. The next step was to be the unification of all Germans in one State, as it involved the Austrian, German population areas of France, Belgium, Czechoslovakia, Poland and Lithuania. The third step was to gain a "living space" in the East. Possession and raw agricultural resources of Eastern Europe, Germany, according to Hitler, will win the struggle for world domination.
Thus, each set of steps meant that Hitler is not simply a revision of Versailles, but the way to its complete elimination and radical change in international relations? formed. This was the path to war.
evidence of Hitler's determination to become Germany's withdrawal from the League of Nations in October 1933
In 1934 the attempt was made to join Austria. To prevent this was Italy, which threatened direct military intervention. Hitler had backed down.
1935 was a turning point. After payment of compensation for the French coal mines in the Saarland plebiscite result went to Germany. And in turn rejected the Treaty of Versailles articles that forbade her to have a military aircraft, announced the introduction of general conscription and the formation of 36 army divisions.
between Britain and Germany concluded a naval agreement. Under this agreement allowed Germany to increase the tonnage of the fleet at 5,5 times and build submarines. Thus the German fleet had become bigger than the French. Bilateral agreement was a violation of Versailles.
This turn of events was to disturb the nearest neighbors of Germany. European diplomacy has been actively discussing the idea of creating a system of collective security. In 1934 the USSR was adopted by the League of Nations. In May 1935 the USSR and France signed an agreement on mutual assistance. A similar agreement was concluded between the USSR and CHSR. By contract the parties were obliged to provide mutual assistance. However, ratification of the treaty France relegated, using the fact of signing the contract as a means of pressure on Germany. Realizing this, Hitler dared to decisive action: the March 1936 German troops were put in Rhine demilitarized zone. Neither Britain nor France would not have applied in this case stipulated measures. And in Germany was preparing to open war.
Thus, established after World War imperfect system of European security have ceased to exist.
common interests of Japan, Italy and Germany have led to their convergence. November 25, 1936 Germany and Japan signed the Anti-Comintern Pact, and November 6, 1937 Italy joined him. Formed axis Berlin-Rome-Tokyo. The parties were obligated to inform each other about the activities of the Comintern and to lead a joint struggle against it. In addition to the contract promised in case of war by either side with the USSR did not do anything that might ease the situation of the USSR.
Germany Italy recognized the conquest of Ethiopia. In 1936 Germany and Italy supported the fascist rebellion in Spain, giving Gen. Frank direct and indirect assistance, by ensuring victory in the Civil War (1936-1939).
difficult relationship developed in Germany and Japan. Both countries were far apart and wanted to preserve freedom of action in its sphere of interest.
Under the terms of peace meant the preservation of Versailles-Washington system, which, despite its shortcomings, ensuring relative stability and recognized rule of law. This system included the principle of prevention of international crises by providing collective action against the aggressor through the League of Nations. However, the collective could not repel? mechanism failed.
reason for this is that the ability of Western countries to joint action against the aggressor fell through the aggravation of mutual rivalry in seeking ways to overcome the economic crisis. In addition, the economic situation and distract public attention to domestic political problems. Solving them was a priority. Also in the West continued hostile to the USSR and Hitler's anti-Soviet attacks were perceived positively in political circles.
collective resistance needed to use a variety of aggressors, including law enforcement techniques. Protecting peace in those conditions required the courage, commitment and willingness to certain losses. However, the very idea is for people who have just survived the war, seemed irrelevant. The public in England and France was set strongly against the use of force. China, Ethiopia seemed too far to view them as a threat to European security. Understanding the integrity and indivisibility of the world was not peculiar to the then public opinion. Such sentiments were reflected in the policy "appeasement" that led the country to inactivity and excessive caution.
Hitler coming to power was immediately taken to a landmark policy in Germany. Long time, it saw only a strong national leader who seeks to restore justice in Germany. Nazi plans for division of the world initially evaluated as a tribute to nationalist rhetoric and not taken seriously. The leaders of Britain and France saw no reason to change policy, which is actively implemented in the 20's and was designed to gradually reduce the burden of Versailles. It becomes clear lack of response to England and France of Germany, though they wore openly daring nature and violated a principle of international law: the contract must satisfy.
Nazism in Germany have not had time to show his predatory face. European countries have not suffered the horrors of occupation. Hitler seemed to be a politician with whom you agree.
Noteworthy to say about the U.S. position. The crisis there chained public attention to domestic issues. Increase of tension in the world has generated in the U.S. desire to protect themselves from just his "American fortress. Following the adoption in 1935, the law of neutrality world's richest country, with significant resources and ability to influence world politics as if it fell out. This dramatically increased the chances of aggressors.
Anti-Hitler rhetoric and his aggressive plans to address the Soviet Union pushed for the creation of collective security and deter aggressors. Leader of the course became the People's Commissar for Foreign Affairs of the USSR M. Litvinov. USSR managed to consolidate their position. In 1933, established diplomatic relations with the U.S. and the USSR in 1934 was adopted in the League of Nations as a member of the Council, which meant the recognition of his great power.
the success of a system of collective security was the conclusion in 1935, the Soviet-French agreement on mutual assistance. True, there were no war article, but in any case, the agreement opened the way for joint struggle against the aggressor. A similar agreement in 1935, concluded with Czechoslovakia.
attitude of Western countries to create a system of collective security was cool. Soviet-French agreement was ratified by France only a year. Doubts raised above all that the Soviet Union has no common border with Germany and to fulfill their obligations? Soviet troops would cross the territory of Poland and Romania. And these states fear the Soviet Union more? than Germany? and categorically refused to miss the Soviets. In French the impression that the USSR would drag France into conflict with Germany, but most stay away. When the West became known effects of repression in the Soviet Army, the military alliance with the USSR roztsinyuvavsya as meaningless.
most active supporter of policy "appeasement of the aggressor" was prime minister of Great Britain (1937-1940 biennium) N. Chamberlain. In his view, the danger was not in the aggressive intentions of Germany, and in the wrong estimation of the international crisis. He believed that the First World War started because the great powers for a time lost control of events resulting in a local conflict into a world war. To avert this danger, you want to keep contact with all parties to an international conflict and resolve existing problems through mutual concessions.
In fact, advanced by Hitler ever nahabnishi claim. They became the subject of discussion and is happy ending territorial claims in Germany.
culmination policy "appeasement" became "anshlyus" Austria and the Munich agreement of Czechoslovakia.
Accession of Austria was one of the important policy objectives in Germany. In February 1938 the Chancellor of Austria with Germany Shushnih signed a deal that put Austria under German control. March 12, 1938 German troops with the support of Austrian Nazis occupied Austria. No great powers, neither the League of Nations did not reacted to it. Only the Soviet Union protested.
next victim of Nazi aggression became Czechoslovakia, from which Germany demanded the Sudetenland, inhabited by three million Germans. But at first the correlation of forces was not in favor of Germany. Czechoslovakia was well armed and prepared an army of 45 divisions and border fortifications. Germany had 47 divisions insufficiently armed. In addition, the government invited the Soviet Union Czechoslovakia under the contract of 1935 overall assistance.
An international crisis. For its solution Chamberlain met Hitler twice. They agreed that the conflict will be resolved in Munich.
during the Munich meeting, Hitler said that the Sudetenland - the last territorial demand in Germany in Europe. This, and the Anglo-French ultimatum to the Czechoslovak government on immediate transfer of Germany CHSR territories inhabited by Germans, clearing the way to the Munich Agreement. It was concluded at the back of Czechoslovakia heads of governments of Britain, France, Germany, Italy, September 29-30, 1938
result was the rejection of the agreement CHSR to Germany all the border areas. CHSR lost 20% of the population and almost 50% of heavy industry. The border with Germany was held at 40 km from Prague.
Munich agreement CHSR obliged to satisfy the claims of Poland and Hungary. Poland was assigned Cieszyn Silesia, Hungary - part of Slovakia and Carpathian Ukraine. Czechoslovakia became a federal state.
Munich agreement - one of the most shameful pages of Western diplomacy. England and France betrayed Czechoslovakia, a country of which it was linked to the Versailles system, one of the few real democracies in Europe. Was cynical reference to the right of nations to self-determination, the right of Germans, Hungarians, Poles to unite with their motherland, because in 1919 in Paris, this right was sacrificed and antyuhorskym antynimetskym strategic interests, as in 1938 in a sacrifice policy of "appeasement".
Munich Agreement meant the transformation of Germany into the strongest country in Central Europe. All the small countries of the region understand that neither the League of Nations nor the United Kingdom with France can not guarantee their sovereignty and went to the rapprochement with Germany. In this sense the Munich agreement was a strategic defeat in London and Paris, approached the outbreak of war.
But while the West plot were received with relief. Chamberlain said, returning to London he brought peace to this generation.
These thoughts dominated long. For winter 1938/1939 he was British and French leaders understood the fallacy of their reasoning. Meanwhile, Hitler did not leave time for reflection. March 15, 1939 German troops occupied Bohemia and Moravia, Slovakia was declared an independent and Hungary occupied the entire Carpathian Ukraine.
Besides England and France recognized the Franco government in Spain F., which opened his way to victory in the Civil War.
Then Germany began to seek consent from Poland to Danzig and transfer it to build through the Polish corridor exterritorial road which would unite Germany with Prussia. German troops entered the region Memelsku (Klaipeda), which belonged to Lithuania. In April 1939 Italy invaded Albania.
collapse policy of appeasement "became apparent. In the public consciousness fracture occurred. From the government demanded rigidity in attitude and determination to Germany. England and France have exchanged notes on mutual assistance in case of aggression and provided appropriate safeguards States that have a common border with Germany. Began preparing for war.
a person's war demanded from the government of Great Britain and France's rapprochement with the USSR.
Munich fully demonstrated inability of the Soviet leadership to create a system of collective security. Soviet-French and Soviet-Czechoslovak treaties were simple piece of paper. For the Soviet leadership, Munich was a signal that it wants to eliminate from participation in European politics.
Soon France and Germany concluded an agreement, equivalent non-aggression pact. USSR is assessed as an attempt to send the West German aggression eastward.
defeat the USSR in the European diplomatic front was held against the backdrop of deteriorating relations with Japan, which resulted in a conflict near Lake Hassan in July 1938 According to the Soviet leadership? Soviet Union was the prospect of aggression from the East and West.
Once their isolation and distrust proynyavshys to England and France, the Soviet leadership began searching for ways of rapprochement with Germany. An important feature changes of foreign policy orientation of the USSR was replaced Litvinov as Commissar for Foreign Affairs. Became the new Commissar Molotov, which meant that Stalin was set to guide foreign policy.
turning point in Soviet foreign policy coincided with the beginning of a policy of Western countries. USSR moved from England to Germany and France, and they sought rapprochement with the USSR.
London and Paris, are concerned about unforeseen developments, issued a statement on guarantees help several European states - Poland, Romania, Belgium, Netherlands and Switzerland. Guarantees resulted in the situation in Europe. Germany could not carry out aggression against the USSR, without violating the sovereignty of Poland and Romania and, accordingly, risking not find itself at war with England and France.
In March 1939 the UK proposed to sign the USSR together with France and Poland general declaration on interaction. In April 1939 the Western powers turned to the Soviet Union with a proposal to guarantee Poland and Romania.
In response, the USSR proposed the pact of mutual assistance between England, France and the USSR, while providing safeguards to the border with the Soviet Union states. However, negotiations that began in this case proved difficult because of mutual distrust between the parties and the parties' unwillingness to compromise. Parties failed to overcome differences in the case of indirect aggression. England and France saw in formulating Soviet threat to the sovereignty of its neighboring states. Because any change in the border states of the Soviet Union Soviet leadership would qualify as aggression , which allowed him to enter their territory troops. Besides England considered these talks as a means of pressure on Germany and did not want an agreement.
Along with political talks Britain, France and USSR agreed to start negotiations for the conclusion of military missions joint convention. They also performed poorly.
formal obstacle to signing the convention was reluctant to miss Poland and Romania through its territory to the Soviets. The Soviet government studied the question of rapprochement with Germany.
In August 1939 the USSR was in the center of world politics. His commitment to England as demanded by France and Germany. Soviet leaders faced a choice before the final landmark that had become crucial to the events in the world.
According to Stalin's alliance with Britain and France, at best, could bring tensions with Germany and at worst, a war with Hezbollah. But the Union with Germany would leave the world aside USSR conflict. One would expect a cessation of hostilities with Japan on the River Halhin-Chief (there were from May to August 1939 on the territory of Mongolia), which would affect only Germany and the territorial gains at the expense of Poland, the Baltic States, Finland and Romania.
Germany agreed to this, if only to bring the Soviet Union from the game, solving a hand for aggression against Poland, which was scheduled for August 26 and then on September 1.
August 21 from Hitler, Stalin received a telegram in which he stated that seeks to conclude non-aggression pact with the Soviet Union and is ready to sign any additional agreement which applies to all controversial issues. Hitler asked for Germany's Foreign Minister Ribbentrop to sign the relevant documents.
the same day, Stalin gave the order to suspend the negotiations with England and France. He directed the telegram to Hitler, in which he expressed hope for a significant turnaround in the Soviet-German relations, and agreed to accept Ribbentrop during this period.
After brief negotiations, Ribbentrop and Molotov signed in the Kremlin August 23, 1939 non-aggression pact and a secret protocol to it.
The minutes of the sides agreed on the delimitation of "spheres of interest 'in Eastern Europe. Germany recognized the Soviet sphere of interests of Finland, Latvia, Estonia and Becsarabiyu. Lithuania declared to the German sphere of interest. The protocol involved the division of Poland, the line which had held about Narew, Vistula, Sian.
signing the protocol, the USSR was actually among the states - "incendiary war".
direct result of the signing of these documents was that the German troops the morning of September 1, 1939 attack against Poland. September 3 Britain and France declared war on Germany. Outbreak of World War II.
Spanish Civil War
In April 1931, in Spain was bloodless revolution, which resulted in the monarchy was overthrown. But delays in the new government in reform extremely worsen the situation in the country. Sharp confrontation broke out between leftist and rightist political forces. In 1933 the return of law and fully rolled reforms. Basque refused to grant autonomy. Against opponents of the government used military force.
In 1934 the government began the policy of massive public appearances. Catalonia declared its independence in Asturias flared armed uprising led by anarchists . Because of the lack of unity of left forces all these performances was suppressed.
zmyryvshys not a defeat, left in January 1936 formed the Popular Front, which made a broad program of reforms. In February 1936 the Popular Front won the election.
Based on the army, right-wing forces began to prepare a revolt. At the head of the conspirators were Jose Antonio de Rivera Prima, General Sanhurno, directly preparing a revolt, and General Franco.
Mutiny began July 17, 1936 in Spanish Morocco. The next day it spread to other parts of Spain. On the side of rebels took over 80% of the Spanish army (20 thousand officers on the side of the republic there are only 500), but the air force and navy remained loyal to the republic. The country began a civil war. In the rebels once had trouble: Prima de Rivero was arrested and executed, Sanhurno killed in plane crash in French Moroccan troops had blocked the Republican fleet in Morocco. Riot threatened to defeat, but came to the aid frankistam Italy and Germany, on airplanes threw the Moroccan army in Spain.
Thus the internal conflict in Spain was to gain international znachennnya, becoming fascist and anti-fascist resistance forces.
Franco, who in September 1936 led rebels, proclaimed goal of rebellion: a "totalitarian state, social peace and common prosperity».
Republican government was hoping for help from England, France and USA. But the leadership of these states posylalosya on international law, prohibiting interference in internal affairs of other countries. They take into account and their experience in Russia, where armed intervention and support anti-Bolshevik forces had the reverse result.
27 countries signed an agreement on non-intervention in Spanish affairs. But Italy and Germany did not pay attention to it and actively supplied weapons frankistam. In October 1936 the USSR announced that it would not comply with an agreement to send military advisers to Republican supply them weapons. In defense of the republic came to Spain by various estimates from 35 to 42 thousand people who wanted to fight against fascism. Of these teams were established internationally.
in September 1936 formed a new republican government headed by Largo Caballero. On the territory controlled by him had a pretty radical social and economic reforms. Catalans and Basques have autonomy. But the political regime gradually evolved in the direction of democracy, protection of which was the main objective of the war. This is partly explained by time of war, the main reason was the growing influence of Communists, who relied on the support of the USSR. Thus, the Spanish democracy ceased to exist before the Spanish republic was lost.
In 1936-1937 he was the main fighting there were around Madrid, but all were repulsed frankistiv offensives. Did not help them and "fifth column" (secret supporters of the rebels) in the same city. After failing to capture Madrid frankistiv Germany and Italy began to openly intervene by entering the country its troops (German Legion Condor, an Italian expeditionary force, the Portuguese troops, etc., total about 200 thousand). Italians attempt to strike from the northwest to the Republican troops that defended Madrid, was unsuccessful. In the town of Guadalajara in March 1937 an Italian building was destroyed.
After this defeat frankisty focused their main efforts in Catalonia, trying to use the conflict between the Trotskyists and communists. 03/06 May 1937 Trotskyites? Largo Caballero supported, made in Barcelona armed speech to protest the policies of the communists. In April 1938 the army frankistiv Catalonia cut off from the rest of the country. Trying to break the blockade of the Republican army offensive in July 1938 had no success. In early 1939 French troops occupied Catalonia. The territory controlled by Republicans, was cut off from France.
February 27, 1939 England and France broke diplomatic relations with the Republican government and recognized the Franco government. Once in the international isolation (USSR almost stopped arms supplies, 1938 Spain abandoned internationally CDR), March 6, 1939 Madrid defense commander Colonel Kasado down republican government and entered into negotiations with Franco. Trying communists suppressed the uprising. On the territory controlled by Republicans, joined Franco's troops. In Spain, established the dictatorship of General Franco (March 1939 - November 1975).
Spaniards costly war: killing 1 million people, 500 thousand left the country, lying in ruins.
 English
English