§ 33. Middle East conflict and attempts to its solution
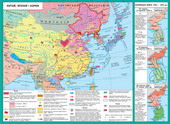
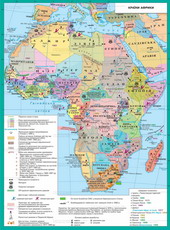
Most of the Middle East regionare Arab countries. The Arab world extends to 20 stateslocated in North Africa, Arabian PeninsulaMiddle East. These countries are united by common ethnic composition and language.Culture and traditions. In 1945 was formed League of Arab States (LAS).The main wealth of the Arab countries - oil (90% of world reserves). MajorityArab members of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC), which seeksprotect the interests of oil exporters. Arab countries differ in terms ofdevelopment and political system. Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, are united ArabEmirates, Qatar highest in the worldrate of per capita income. They have advanced technology, freeeducation, developed social security system combined with strongIslamic traditions, the monarchic regime (absolute theocraticmonarchy), traditional relics. Democratic traditions are not available. OtherArab countries (Algeria, Libya, Egypt, Syria) have a republican system andpostwar period tried to build"Arab socialism."
In the postwar years, Arab countriesthe main problem was the Arab-Israeli conflict.
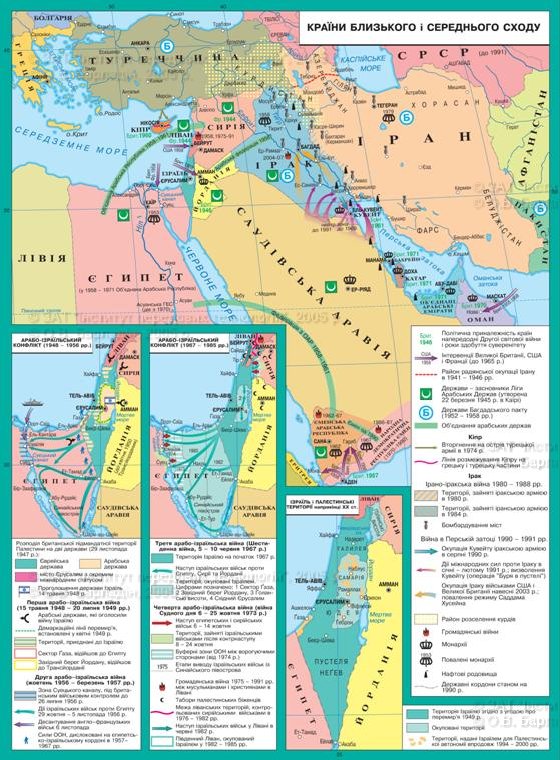
1. Create state of Israel. The first Arab-Israeliwar
In World War II at the hands ofNazis killed 6 million Jews. The tragedy of European Jewry encouraged toactivation of the Zionist movement which developed under the slogan: "Only inJews own country can feel safe. "
November 29, 1947 GeneralUN Assembly majority - 33 in favor, against 13adopted a resolution on division of Palestine into Jewish and Palestinian state.Jews welcomed this decision, the Arab world categorically denied the UN resolution.May 14, 1948 State of Israel was proclaimed. Not passed and 24 hoursas the armies of Egypt, Jordan, Syria, Lebanon and Iraq began military action againstyoung state. BillPanel bloody war that lasted from May1948 on July 20, 1949 (Israelis call it a war forindependence). Receiving weapons from the USSR, Czechoslovakia and financial assistanceU.S., thanks to unprecedented courage of soldiers and officers (many of them were activefighters with the Nazis in Europe), all the people of Israel defeated. Inresult of this war, territory that predicted by Palestinian Statewas distributed as follows: Galilee and the Negev all went to Israel;Judea, Samaria, part of Jerusalem to Jordan, Gaza strip to Egypt. Thisway, the Palestinian state was created. The war laid the basis for conflictsolution is not pegged to the present.

BronechastynyArab Legion before the attack on Israel. 1948
Late 40's - early50 years of Arab-Israeli conflict became part of the Cold War. USSRstood in the way of open support of Arab countries in their conflict with Israel. U.S.and on the West side of Israel. Based on such support sidetried to force to prove their right to the land of Palestine. Repeatedlybloody wars broke out between Jews and Arabs: War on Sinai1956, 1967 Six-Day War, War of attrition1967-1970,, Yom Kippur War in 1973, Israeli military operationsLebanon against the military forces of the Union of Palestine and SyriaFrom 1982-1983 *
* Learn more aboutWar, see next paragraph.
Arab-Israeli War
|
War
|
Titles
|
Major participants
|
Result
|
|
1948-1949 biennium
|
Home Arab-Israeli (Israeli War of Independence)
|
Israel
Egypt Transjordan, Syria, Iraq, Palestinians
|
Israel defended the independence.
Not established Palestinian state.
The emergence of problems Palestinian refugees.
Distribution Palestinian territories between Israel and neighboring Arab states.
|
|
1956
|
Anglo-French-Israeli aggression against Egypt (Sinai war)
|
Israel France, England.
Egypt, Syria
|
The defeat of Egypt.
Termination Navigation of the Suez Canal.
Close Cooperation between the USSR and the Arab states.
Defeat Anglo-French colonial adventure.
|
|
1967
|
Six-Day war
|
Israel
Egypt, Jordan, Syria, Iraq, Palestinians
|
Defeat Israeli armies of neighboring Arab states.
Occupation Israel West Bank, Gaza Strip, Sinai Peninsula, Golan Heights.
Gap Diplomatic relations between the USSR and other socialist countries with Israel.
|
|
1967-1969 biennium
|
The war on depletion
|
Israel
Egypt Jordan, Syria, Iraq, Palestinians
|
Failure Israeli Arab drain power and thereby secure the safety.
Strengthening defense of Egypt and Syria.
|
|
1973
|
Seven war (Yom Kippur War)
|
|
Showed hopelessness of further military action against Israel's Arab countries.
Debunked myth invincibility of the Israeli army.
Gave rise to peace process that ended with the signing of Camp David agreement between Israel and Egypt.
|
|
1978
|
Aggression against Lebanon (Operation Litani)
|
Israel.
Lebanon, AFP, Syria
|
Creation Israel's "security zone" in southern Lebanon.
Israel delivered the final defeat of the Christians in the civil war.
Introduction to Syrian troops in Lebanese territory, which actually should control the country.
|
|
1982-1983 he
|
Israeli Aggression against Lebanon (Operation Peace Galilee)
|
Israel.
U.S., France, England and Italy.
Lebanon, Syria, ORP, extremist Islamic groups
|
Were Base ORP defeated in Lebanon, Palestinian troops were withdrawn from country.
Israel did not could defeat Syria and ensure security of their northern border attacks from Islamic militants. Also failed to achieve peace with Lebanon.
Lebanon has suffered aggression of the USA, France, Britain, Italy, which intervened in the course of civil War.
Even more strengthened the position of Syria in Lebanon.
|
|
1987-1996 biennium
|
The first intifada
|
Israel.
Palestinians
|
Israel was forced to give the Palestinians limited autonomy.
|
|
Of 2000-2004
|
Second intifada
|
Israel.
Extremist Palestinian groups
|
BillPanel implementation plan for the peaceful settlement of the Palestinian-Israeli conflict "Road Map".
|
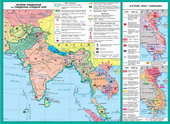
2. The Palestinian problem
The first Arab-war izrayilskabare the problem of Palestinian refugees who settled in various Arabcountries. This dealt a major blow to Palestinian national consciousness:Missing independent Palestinian organizations, rescue vbachavsya only
in uniting the Arab states for the Liberation of Palestine.
In 50 years the Palestinians blamedhope for unions Arab Republic, which united to bring Egypt and Syria, butAnglo-French-Israeli aggression (1956) and decay SAR (1961) dispelled thisexpectations.
In the late 50's there in KuwaitNational Movement for the Liberation of Palestine (Fatah), headed by Arafat Yasyr. Thisorganization launches a new program to fight for the Palestinians: 1. "NoArabic voyage to Palestine, Palestine - the path to ArabUnity 2. Non-interference in internal affairs of Arab states.

Yasyr Arafat
This ideology provided Fatahsupport from the monarchy Arabian Peninsula. Victorynational liberation struggle in Algeria (1962) contributed to the spreadFatah ideology. (Algeria gave the example of the liberation of Arab countries on their ownwith the support of Arab States).
Some Arab countries were notinterested in the Palestinian independence movement. To control it in1964 lawyer Shukeyri established the Palestine Liberation Organization(AFP).
To get out of control Arabcountries begins to self-Fatah struggle against Israel. The first armed action washeld January 1, 1965 This day became the birthday of the PalestinianResistance Movement (ABM). For a short time turns into a powerful Fatahmilitary-political force that establishes control over the AFP. In February1969 Yasyr Arafat was elected presiding Board ORP. In 1970he became chief of the armed forces of the Palestinian revolution.
Limited area centered wherehostilities, the terrain is not given opportunities to create areas in the liberationPalestine, which would have become bases for combat. All armed action(Terrorist attacks) were carried from the territory of neighboring States, which led to2 major problems: Israel carried out the attacks on these states, causing up todissatisfaction with governments and their population Palestinians; ABOUT been getting independence on the Arab states. The first problem has led to armed conflictbetween Israel and Jordan in 1966 and the Jordanian-Palestinian conflict1970 The Palestinians had to leave the country and move in Lebanon.
I wonder
In order to reach the worldpublic to achieve transparency of their actions Fatah militants have carried out carefullyplanned terrorist act. In September 1970 Palestinians werecaptured three civil aircraft - English, Swiss and American(Israel could not capture because he, unlike other aircraftguarded) and forced their crews pryzemlyty in Jordan. The terrorists demandedrelease those arrested in Europe Palestinian militants in exchange forhostages. Terrorists and hostages were released aircraft blown up.
In 1972, Palestinian group"Black September" made a daring attack. During the Olympics in Munichgunmen burst into the room where the Israeli athletes and livingcold-bloodedly shot them. Killing 11 people.
But the Palestinians in Lebanon destroyedfragile balance of power in the Lebanese society, causingcivil war and Israeli intervention in 1978 and1982-1983 he
After the bloody battles in the SouthLebanon and Beirut in 1982 Palestinian fighters and had headquarters ORPmove into Tunisia. But here in October 1985 Israeli aircraftattempted bomb attacks kill nerve center ORP.
The second problem has led toORP transformation in conglomerate groups of kraynolivyh to right thatclaim to leadership in the AFP.
The October 1973 War changedviews Yasyra Arafat. He begins to speak for a Palestinian statenot instead of Israel, along with him for a change of armed struggle by peaceful meanssolution problems. This turnORP rescued from isolation and death. In 1974 ORP has been recognized onlylegal representative of the Palestinian people. In 70 to 80 years Arafat ledactive diplomatic activities under the slogan: "No day without movement,maintaining friendly relations as possible with everyone.
December 9, 1987 on the leftRiver Jordan and the Gaza Strip began a popular uprising("Intifada" - the war of stones) performed without weapons.November 15, 1988 Palestine National Council (parliament in exile)decides on the proclamation of independence of Palestine. All parties to the conflictunderstand that this can not continue further. The efforts of U.S. and USSR aggressionIraq against Kuwait contributed to the beginning of the Middle East peace settlement.
3. Middle East peace process.
The first attempt to settle the peaceArab-Israeli conflict was made in 1951 King of Jordan. Butafter his murder by the end of 70 years to resolve everything on the battlefield.
In September 1978 the meetingPresidents of Egypt and Israel at Camp David, U.S. President's ResidenceD. Carter, was prepared historic agreement between the two countries to startpeace negotiations.
March 26, 1979 WashingtonIsrael and Egypt signed a peace treaty. Egyptian President Sadat and A.Israeli Prime Minister Begin was awarded the M. Nobel Prize forpeace and cessation of hostility between the two countries. Trying to makesimilar agreement with Lebanon (1983) failed.
Summer 1994 such agreementIsrael signed with Jordan.
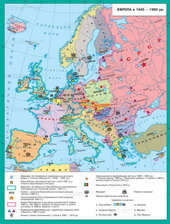
The collapse of the USSR,changes in power relations in the world, weakening the influence of radical Arab(After the defeat in the war with Iraq Multinational Force (BNS)), economicinterest of Arab countries and Israel further understandinginability to hold captured territory that did not guarantee himSecurity (Israeli shelling of Iraqi ballistic missiles, Palestinian Intifadaetc.) prompted the warring parties to participate in the Madrid Peace Conferencein October, 1991 The conference was the structure of negotiations,necessary to achieve total peace in the Middle East.This structure provided for two separate and parallel negotiationprocesses. The first was the bilateral talks aimed at resolvingthe conflict between Israel and its neighbors: Syria, Lebanon, Jordan. And alsobetween Israel and the AFP. The second process consisted of multilateral negotiations aimedto build the future of the region. These negotiations include fiveseparate forums on key issues for the region. Such as water resourcesthe environment, arms control, the problem of refugees, economicdevelopment. They participated in all Middle Eastern countries and representatives of worldcommunity.
The Israeli government, formedLabour Party in 1992, went on to direct talks with AFP, which at that timeabandoned many of his positions on Israel, not perception. In September1993 as a result of secret negotiations in Oslo (Norway) between Israel andORP was signed declaration on principles of mutual relations. Agreement providesgranting autonomy to Palestinians in the West Bank was Jordan and GazaStrip for 5 years.
Implementation of the Declaration of Principles inlife began in 1994 with the introduction of autonomy in Gaza and IyerihonStrip. The Palestinians were given powers in education, culture, healthhealth, social welfare, taxation and tourism. Autumn1995 agreement was signed on the second stage of putting the Palestinianautonomy. The agreement identified the future of Israeli settlements,boundaries and structure of the Palestinian Authority. The capital of autonomy was electedcity of Ramallah.
However, the process of becomingPalestinian Authority is difficult and controversial. It is connected with manyfactors:
- On both sidesis the mutual distrust of the peace settlement plans;
- Extremistfaction Hamas, Hezbollah, IslamicJihad and others are actively terrorist activities against IsraelOften this is the territory of the Palestinian (terroristsmostly kill civilians, arrange transport bombings and otherpublic places). Israel also claims that Arafat is involved interrorist attacks in Israel. In turn, the Palestinians launchedSecond Intifada (2000). As a result, the failure of negotiations, beginninga general war between Israel and the Palestinian Authority (particularly tensesituation happened in winter 2002-2003);
- Actuallyabandoned plans for armed resistance against Israel, Syria, Iraq, Iran,some other Arab states, who actively support terrorist activitiesgroups;
- Not acceptedIsraeli peace, and radicals who killed Israeli Prime Minister YitzhakRabin - developer of the Arab-Israeli dialogue.
The situation in the Middle Eastremains a difficult and controversial. At any time or place escalationconfrontation whose consequences can not be predicted.
Despite the opposition of hostile forces asin the Arab world and Israel in the Middle East peace process continuesdevelop. The important result was the signing of its peace treaty betweenIsrael and Jordan. As a result of the agreement were settled border issues:Israel is turning part of the border area, but which were keptIsraeli settlements available for 25years. Also, Israel agreed to transfer 50 million cubic meters of Jordan wateryear of its resources. The peace treaty also meant the restoration of the fullvolume of international relations.
Difficult negotiations developingprocess with Syria, which promise to be lengthy. The main problem in bilateralrelations is the return of Israel's Golan Heights, captured in war1967
Also essential outcomeMiddle East crisis is the cancellation of the Arab oil producing countries inOctober 1, 1995 boycott of companies that have trade relations withIsrael (boycott was introduced in 1947).
The overthrow of the Saddam Hussein regime(2003) opens new prospects for settlement of the Palestinian problem.Persistent diplomacy to solve this problem, the U.S. deployed. InJune 2002 they proposed a peace plan parties, whichcalled "Road Map" (or "Route guidance"). Unlike allpreliminary plans for each subsequent step was only afterprevious, recognized the existence of a Palestinian state.
According to the plan intended to resolvePalestinian-Israeli conflict by 2005 main aim of the planproclaiming a Palestinian state. The implementation plan wasoccur in three stages. In the first phase expected to restore the situation thatexisted before the Second Intifada (September 28, 2000) and choose the firstPrime Minister of the Palestinian Authority, which was Mahmid Abbas (Abu Mazen).
The second stage (approximately toend of 2003) decided to conduct free elections in Palestine andcreate a Palestinian state with provisional borders and attributes of somesovereignty. " Meanwhile, international mediators should organize an internationalconference on economic assistance the new state.
The third stage was completed moreone international conference that would announce the solvingconflict. Will be concluded agreements on permanent borders, Jerusalem, refugees,Israeli settlements in Palestinian territories. Syria and Lebanon will agreeto conclude peace with Israel.
At present, the parties can notdecides on the first phase. The Palestinians continue terrorist attacks inIsrael makes a response action retribution (assassinated leaders of Hamas, killed400, wounded 20 thousand Palestinians), began building a wall that would separate thehim from the Palestinian territory. Prime Minister Sharon of Israel offered fullwithdraw Israeli settlements from the Gaza Strip. In Palestine has changedseveral prime interiors.
I wonder
Shynaz Amur (or Wafa Idris)(1980-2002). Palestinian student who turned himself first to the live bomb.January 29, 2002 girl blew himself in Jerusalem, killing one person andinjuring about 150. Saddam Hussein ordered her to put a monument in Baghdad. Itsinflated example of widespread among terrorists. "Shahid, as they werename have become commonplace.
Results
After the Second World War wasThe process of decolonization of Arab East. Independent path of developmentthe region was difficult. Economic and political experiments withconstruction of "Arab socialism, bloody war, political instability,terrorism turned the region into the most painful point on the planet. At the same time, somecountries in the region based on huge profits from oil exports have managedachieve the living standards of the leading countries of the world, but it was accompaniedconservation relations in the political sphere, culture, morality.
Most significant progress in upgradingMiddle East has reached Turkey, which at the present day is a candidate forjoining the European Union.
Questions and tasks:
1. What is the essence of the Middle East conflict?
2. The heart of the Middle East conflict is the Arab-Israeli conflict. Whatcauses of this conflict?
3. Why Middle East conflict has become part of the Cold War?
4. How did the Palestinian problem and developed?
5. Describe the Middle East peace process. Why the conflict in the MiddleEast to date no solution pegged?
6. Define the milestones of the Middle East conflict and peace process. Makeanswer table.
 English
English