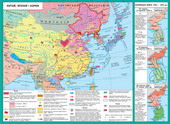
§ 36. Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia tend tocalled a wide area: Peninsula Indochina and the Malay IslandsPhilippine archipelago. This region is inhabited by various peoples whoprofess different religions. From the first years of European colonialexpansion, he became the object of their invasion. Attracted to natural colonizersWealth: spices, rubber, wood valuable, and tin, petroleum and more. Onlate nineteenth century. region is divided between England, France and Holland. InWorld War II the region attempted to subdue Japan under the slogan"Asia for Asians".
1. National Liberation Movement in the Region(Indonesia, Indochina, Malaya). The emergence of new states
At the end of World War IIIndochina, Indonesia, Malaya turned mass national liberation movementagainst Japanese invaders and colonizers.
|
Factors that influenced the course of national-liberation movement in the region
|
|
1.
|
The fight against Japanese occupation during the Second World War.
|
|
2.
|
Civil War China, the Communist victory in it.
|
|
3.
|
Start the Cold War.
|
|
4.
|
The desire of the former parent to resume their colonial possessions in the region (France, England. The Netherlands).
|
At the Potsdam Conference(1945) it was decided to divide the region by occupying the zone betweenEngland, USA and China in order to disarm the Japanese troops.Taking advantage of the defeat of Japan and the lack of colonial troops, leadersnational liberation struggle in Indonesia and Vietnam declared independencetheir countries. This dramatically changed the situation in the region. Great Powers werefaced the necessity to recognize or not recognize the new state. Mountain Innovationsdesire to restore power to the former European colonizers. However, the returnFrench, British and Dutch colonialists turned colonialwars, worst of which lasted in Indochina, especially in Vietnam(1946-1954 biennium) and Indonesia (1946-1949 biennium).
Events In Vietnam unfolded as follows. Yes, September 2, 1945proclaimed the Democratic Republic of Vietnam, President andPrime Minister of which was Ho Chi Minh. In September 1945 the southFrench troops landed in Vietnam. France is working towards rebuilding theircolonial authorities in the south first, and then - in the whole country.
After announcing the formation of the DemocraticRepublic of Vietnam, Ho Chi Minh government held a series of reforms:
- Vidminyalysformer taxes;
- Decreasingrent by 25% and land tax at 25%;
-konfiskovuvalasya tenure of French colonialists and distributedamong peasants;
- Installedeight-hour working day;
- The process beganelimination of illiteracy.
1946 held a generalElections to the National Assembly. Confidently won the elections Vetmin -National Front, initiated by the Communist Party of Indochina. November 91946 DRV Constitution was adopted.
In March 1946 France and the DRVsigned a preliminary agreement by which France recognized the DRV componentpart of the Indochina Federation and the French Union. In southern Vietnamplanned to hold a referendum on the future destiny, and on DRV territory temporarilyintroduced, the French armies.
However, despite France subsequently Agreementproclaimed the establishment in the Republic of South Vietnam and the north KohinhineVietnam's two autonomous states. November 23, 1946 was carried outbarbarian bombing of Haiphong port (killed 20 thousand people). This wasTop of armed intervention against the DRV. Vietnam's self-defense forces didstubborn resistance coming colonizers. Major battles ensued in the districtscities of Hanoi, Hyuye, Namdin. In the jungle and mountain areas were base resistance.France, trying to consolidate its power in Vietnam, created in the northpuppet government headed by Emperor Bao give, which has signedestablishment of military bases and control of foreign policy. Butend DRV failed.
The victory gave the Communists in Chinanew impetus to anti-colonial struggle v'yetnamskoho people. USSR regardedDRV as the best line of the fight against "imperialism" and gave itmilitary assistance. 1950 was a turning point. Vietnam People's Army(VNA) passed in counterattack. A decisive battle took place near the village Denb'yenfu(March-May 1954), in which French troops were defeated.
July 21, 1954 Francewas forced to sign the Geneva agreement. Before the general elections(July 1956) the country was divided into two zones parallel to 17. French troopsdeduced from northern DRV and stop fighting. However, temporarily kept theirtroops in the south. In colonial adventures France lost its 92 thousandsoldiers.
Having beaten went to DRVdevelop the socialist path with all the inherent features:industrialization, collectivization, the cultural revolution. However, the countryfaced another important task: joining South and North. But the unityIn Vietnam have been through a bloody war (1960-1975 biennium), which waspart of the Cold War between the USSR and the USA.
Difficult path to independencehad to go Indonesia. August 171945 was proclaimed
independence, which set out the following basic principles: equalityfreedom of all religions and faiths, unity of the state, democracy on the basisconsultation and representation, social justice.
August 29 in the country was createdCentral National Committee (the interim parliament), in which all includedpolitical forces that fought for liberation.
August 29, 1945 was electedfirst President of independent Republic of Indonesia. They became the leadernational liberation movement, Sukarno. Also, the Constitution was adopted. 28September Japanese troops (280 thousand people) capitulated to the IndonesianArmy.
Spring 1945 pretextdisarmament of Japanese troops landed on the islands of Java and Sumatra, the British, andthen they changed the Dutch troops. The return was accompanied by Dutchrestoration of the colonial administration. This led to armed clashes betweenDutch and Indonesian army, which escalated into a real war.Indonesian army was defeated. January 17, 1948 The Netherlands has imposedIndonesia Renvilsku agreement which limited its sovereignty and the countryturned into a federation (United States of Indonesia).
Defeat in the war led to sharppolitical struggle in the Indonesian leadership: all wine was placed onCommunists and the Defence Minister Sharifuddina (KPI member). Used thisDutch and launched a second war. Indonesian army suffered a new defeatbut the population moves to the partisan fighting that vymotuvala forceDutch. November 2, 1948 SSHI were recognized as independent.However, completely rid of the colonialists managed the country in early60 years of joining the Western Irinamu.
The first years of independence were held inseeking development. Trying to establish parliamentary democracy in the country notfailed and in 1957 Sukarno enters the country and declares martial lawnew public course - democracy that goes. " Indonesia isunitary state. In fact, all the fullness of power ended up in the hands of Sukarno.Soon in the economic sphere was taken a course, called -"The economy goes." BillPanel nationalization of largeforeign ownership of industrial facilities (up to 1965 was nationalized70% of the industry) is being actively carried out agrarian reform (was limited to largeland ownership). But the new course guide is not led to improvementcountry's economic situation. Nationalisation caused bureaucratizationstate apparatus and chaos in manufacturing (used 30 - 40%capacity). Rapidly falling living standards. All thatoccurred against the backdrop of undue enrichment of the top, led by the father of the nation. "
In the face of imminent collapseSukarno resorted to a dangerous political game: the fight to push the maintheir rivals - the army and the Communists. However, the events in September 1965 gaveadvantage of the army led by General Suharto, who in March 1968 becomespresident. Suharto is profoundly changing internal and external policy of Ukraine.Now the policy of the state were targeted Western countries were organizedMassacre of Communists. In 70 to 80 years in Indonesia was carried denationalizationin industry and agriculture, foreign capital was providedfavorable conditions for investment. In the political sphere kept authoritarian formpolitical regime. All this, as well as significant natural resources, became the basisfor rapid economic growth.
However, neither economics nor politicalsystem of the country were unprepared for the challenges that have befallencountry due to economic crisis in the late 90 th century. Economiccollapse led to the fall of Suharto, which in turn drew on the surfacenational and religious problems that postponed brute force.
Otherwise, events unfolded in Maize breadWhere the British tried to returntheir power. To this end, they totally changed the management system, which object yednavshyformer principality subject only to Malayan Union, the power of local sultansabolished, and the Indonesians were deprived of privileges. This situation causedresistance from the Malay community. At the same time opened a guerilla struggleLeft parties, which consisted mainly of Chinese. To contain the situationBritish launched a tough anti-partisan struggle, at once, turningprivileges of the Malay community. Sultan restored power, and the British protectorate.February 1, 1948 proclaimed the Malaysian Federation. In the early 50'sthree years of community leaders of the country (Malay, Chinese and Indian) havea treaty creating a union party to fight for independence by peacefulway. In 1955 British allowed to hold elections to the LegislativeMeeting Malaya, on which the Federal Party won an absolute victory. After the elections startedpreparation for independence. Sultan received a guarantee of their rights andprivileges. In 1957 England provided the political independence of Malaya. In1963 proclaimed the establishment of the Federation of Malaysia. In 1965, withSingapore left the federation, becoming the path of independent development. The compositionfederation refused to sign the Sultan of Brunei, who up to 1984 wasunder British protectorate.
For a long time remained in Malaysiaunstable political situation, was conducted guerrilla supporters ideasMao. But eventually the situation has stabilized. Attracting Japanese experience in the country were carried out reformsensure the gradual economic
exaltation. У developing country mining, electricaland other industry.
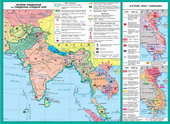
2. The war in Vietnam
"War in Vietnam" - a conventional namea series of conflicts that continued in the countries of Indochina in 40 or 70 yearsTwentieth century. The key conflict was against U.S. aggression in Vietnam. Conflict inIndochina was a key in the "cold war". Defeat U.S. in the regionUSSR was the greatest success in the Cold War. "
Shnma: Development of Indochina
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
Civic War (early 60's - 1975).
American and pivdennov`yetnamska intervention years 1970-1975
|
|
|
Civil War (Early 60's - 1975).
American and pivdennov`yetnamska intervention years 1964-1973
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
Civic War in RO, interference DRV (1960-1975 biennium).
American intervention (1964-1973 biennium)
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
1975 - proclamation of the Lao People's Democratic Republic
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
1975 - on`In connection`Vietnam, from 1976 - Socialist Republic inVietnam (Vietnam)
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
1991 - elimination of trans`yetnamskoho regime. Return the name of Cambodia.
1994 - restoration of the monarchy.
Continuation Civil War to the end of 90 years before his death, Paul sweats.
|
|
|
The defeat of France's colonial warprompted the U.S. to actively penetrate the south of Vietnam. Such U.S. actionswere motivated by fear of the spread of communism in Southeast Asia. U.S. hasteSEATO bloc created here in the U.S., Britain, France, Australia, NewZealand, Thailand, Philippines, Pakistan.
In 1956, in South Vietnamelections were held in the National Assembly and adopted the Constitution, one ofArticles by reinforcing anti-communism as a state policy. USA, England,France recognized this state, and gave her economic and military assistance. In Vietnamwas sent to three thousand American advisers. USA 1955 on1961 allocated 2 billion 118 million dollars in addition to militaryneeds 571.3 million. The use of these funds was located in sightmission to monitor the use of American aid. Much ofassistance went to infrastructure - roads, ports, airfields andothers. Was carried out agrarian reform, agricultural settlements were built,created consumer cooperatives, provided soft loans, but storedlandlordism. In the political sphere limited political rights andfreedom, created concentration camps, and from 1959 wereField military tribunals.
In 1960 Congress heldPatriotic Forces, which was created by the National Liberation FrontSouth Vietnam (NFOJUV). Organizational design of the front was completed1962 It brought together 20 political parties and organizations of variouspolitical orientation - communists, socialists, radicals. Basedin support of the DRV, he opened active hostilities against sayhonivskoho regime.Government troops suffered defeat.
To save his henchmen, USAinvolved in the Vietnam War. Since coming to power in the U.S. President Kennedyappeared doctrine of "flexible response" and "strategyprotypovstanskoyi fight. "Washington believed that the SouthVietnam is the front anti-communism and the victory of the partisan movementcould mean that "the Pacific Ocean becomes sea of red" and the U.S.defense will have to take on its coast.
In 1962 established in SaigonAmerican commanders. Aircraft bombed the U.S. controlled territoriespartisans. October 1, 1963 was established in the country's militarydictatorship. However, the guerrilla movement continued to spread and in the summer1964 2 / 3 of South Vietnam was located under his control.
In 1964, became U.S. presidentL. Johnson. With his name associated escalation of the Vietnam War and spread it onDRV. The U.S. developed a plan of attacks on the DRV, because without the supportDRV guerrilla movement would not acquired such scope. The reason for the aggression againstDRV was the Tonkin incident. March 8, 1965 American troopslanded on the coast of South Vietnam and came into active hostilitiesagainst the guerrillas.
Gradually the number of Americantroops increased to 550 But suppress guerrilla movement they failed.DRV bombing also gave nothing. With the help of Soviet air defenseVietnam gave the United States respond to aviation.
Since 1968 war in Vietnam allresembled less partisan and more resembled a battle of two regulararmies. After the New Year offensive "guerrilla and loss of American troopsimportant strategic base Khesan (January - June 1968) inpublic opinion of the U.S. population come the break. 77% of American citizensapproved of government policy. Americans were too long to conclude thatVietnam war with them not Vietnameses communists and nationalists Vietnameses. Hardimagine a person more distant from politics than the Vietnamese peasant. Butpeople of this country is practically in its history not only fought for the opportunitysurvive, but for the right to have their own state, fighting for it with foreigninvaders, being the wonders of heroism and brilliant organization.Communists only skillfully used these circumstances, and war, in which foreigners were killedv'yetnamtsiv, was for most local residents for the next warindependence. For the U.S., the war that threatened to go to the total of allv'yetnamskym people was futile.
May 13, 1968 in Parisbegan negotiations with the DRV on a political solution, and from November 1U.S. aircraft bombing stopped DRV. Since then, the collapse startedAmerican participation in war. In November 1969 was announcedexercise program v'yetnamizatsiyi "War and the withdrawal of Americansthe country.
To reach the breaking point in the war, the U.S.developed the operation, designed to cut paths (paths Ho ChiMine "), which was help the partisans of Southern Vietnam.US-Saigon troops for this purpose in 1970-1971 biennium committed aggressionagainst Laos and Cambodia, but the operation failed.
March 30, 1972 PeopleLiberation Forces (NZSV) were third and delivered a strategic offensivelarge areas of the country. In response, the U.S. established a blockade the coast andrenewed bombing of DRV. Were carried out two air-offensive operations,which caused considerable damage to farm DRV. The new escalation of the war has caused a stormprotest in the U.S. and in August 1972 The U.S. Senate has decided to withdrawall American troops from Vietnam. January 27, 1973 U.S. signedThe Paris agreement ending the war and restoring peace in Vietnam.
However, the withdrawal of U.S. troopsdid not stop the war. In 1973 sayhonivskyy mode, receiving significantU.S. assistance, has begun a wide offensive against NZSV, but failed. InOctober 1973 NZSV begin counteroffensive, which ended April 301975 partisan victory. It was completed unification of Vietnam. 2July 1976 National Assembly proclaimed the creation of a socialistRepublic of Vietnam (SRV).
The war in Vietnam was the mostbloody local wars among the twentieth century. Total in war deaths and5 million injured v'yetnamtsiv, U.S. lost 58 thousand people, 304 thousandbecame disabled and 2500 Americans found themselves in captivity. Since 1961 over allacross the country shot down American planes 3744 and 4888 helicopters. U.S.This war has cost 130 billion dollars.
The main winner in this war wasSoviet Union.
In December 1976 held on 4 thCongress of Vietnam's Labor Party, which approved the program of socialistconstruction throughout the country. BPS was renamed the CommunistParty of Vietnam (CPV). In December 1980 Vietnam constitution was adopted.
Defeat U.S. significantly changedcorrelation of forces in Southeast Asia. Joint Vietnam, havingnumerous, well armed and trained army and relying on governments to obeyLaos and Cambodia, became a kind of a regional superpower. In addition,1975 SEATO bloc collapsed. Hastened to restore disturbed equilibrium Chinacommencing hostilities against Vietnam in 1979 Together with China almost U.S. isolatedVietnam in the international arena. Besides Vietnam proved inability to beareconomic burden superpowers: the country was destroyed, she was threatened by famine, andchief patron - the USSR was no longer able to help.
In the late 80's Vietnam broughttroops from Cambodia and Laos, normalizuvav relations with China. Since 1986Vietnam has decided to follow the example of China's market reforms and held atmaintaining the Communist Party monopoly on power.
Vietnam is currently before a numberproblems: the need for restructuring the economy (priority developmentlight and food industries), placed the economy on market rails;the problem of employment, reduction of the army; solutionfood problem.
In August 1995 between the U.S. andVietnam restored diplomatic relations.
3. Khmer Rouge. Their model of communism
After World War II Cambodiareceived limited sovereignty within the French Union, and in 1947was proclaimed a constitutional monarchy. (April 25, 1941 by Crownwas approved by King Norodom Sihanouk).
In 40 years in Cambodia rozhortavsyanational liberation movement against French colonialists. Norodom, toprevent disruption of military performances and achieve liberation of the country by peaceful meansattempts to lead the anti-colonial movement. (In early 1953 Norodomsent to an overseas tour to rally support from otherStates, but failed). The defeat of French troops in Vietnam, signingGeneva agreement in 1954 granted independence to countries of Indochina.
The conquest of the country independenceled to the collapse of one of the front anti-French political parties and tostart addressing various parties against the monarchy.
To maintain its influence Norodom 2March 1955was abdicates in favor of his father and formsPeople's Socialist Community Sanhkum to do away withmulti and strengthen the monarchy. Norodom develops the idea of "Khmer,Buddhist, Royal socialism, "which attracted various stratasociety. In the elections of 1955 Norodom and his party win andget all the cities in parliament. Norodom becomes prime minister and strengthensregime of personal power.
In the fieldForeign Policy Norodom hold back the policy of neutrality. Maintainedgood relations with the Soviet Union, Vietnam, China, USA and France.
Despite the success of politicalNorodom course, in the early 60's the country's guerrilla movement unfoldsorganized communist groups.But the split in the communist movement gave the opportunity to hold fast to the Norodompower.
In the early 60's leading partpositions in the communist movement took a group of Cambodia led by Pol Pot. In1963 he became secretary of the Communist Party and deploys combatNorodom against the regime. The views of Paul wore sweats bright national-chauvinistic,Antivietnamese character. The main ideological borrowed frommaoyizmu.
In the early 70's Norodomdeparting overseas trip to find the necessary support to itspolitical course. This used the right political forces that were dissatisfiedpolicy "Buddhist socialism", and in March 1970made military coup led by Gen. Lon NOL. The new regimebet on the U.S. and South Vietnam.
This orientation gave the new regimeimpetus to the deployment of a powerful guerrilla movement led byKhmer Rouge (led - Pol Pot). In the early 70's wasnational united front formed Cambodia (NYEFK) after agreement betweenNorodom and supporters of the Khmer Rouge on joint fight againstLon NOL regime.
After a lengthy guerrillacombat troops Lon NOL and South v'yetnamskymy redRouge in April 1975 came to power and declare aDemocratic Republic of Kampuchea. Formally, the power in the state belonged Norodom,but actually belonged to Paul sweats. April 2, 1976 Norodom presents inretired and getting under home confinement.
Once in power, "redRouge started to build a "communist society." The firstexperiments begun in the early 70's. One of the first actionsof the new regime was the elimination of cities and their residents in resettlementrural areas where created communes. Crop grown in municipalitieskonfiskovuvavsya and the food seemed to be according to established norms. Along with the immigrationconducted purges, repression, znyschuvalas intelligentsia. The victims of the regime was3 million people to 7 million population. Doing redRouge "caused dissatisfaction among the population.
To raise the prestige of his regimePol Pot fueling the conflict with Vietnam. In January, 1977 beginskirmishes on the border of Vietnam-kampuchiyskomu. Paul sweats idea was as follows:Vietnam provoked the offensive, then put counterfire, grabSouth Vietnam and kill people there. But this plan failed, raving, inJanuary 1979 v'yetnamski troops with the support of the insurgent populationoverthrew the regime of Pol sweats. Himself dictator disappears. In response, China carries out aggressionagainst Vietnam to "provide a lesson", but the position of the USSR and the defeat of Chinese forcesstop the aggression. In Kampuchea regime was installed prov'yetnamskyy.
Polpotivtsi not lay down their arms andbacked by China, from bases in Thailand launched artyzansku war. In the early 80's they joinedSleeping with the nationalists and supporters of Sana'a Norodom that provided them with supportthe U.S. and other Western countries.
At the end of 1987 startednegotiations between Norodom and pnompenskymSung Hun leader mediated by the UN, which resulted in the signing in October1991 The Paris agreement on an overall settlement in Cambodia.Under the agreement with the country's troops withdrawn and stopped v'yetnamskicivil war.
In 1994, Cambodia wasrestored monarchy. Norodom again became king. But "red Rouge does not stop armed struggle.This struggle continued until the late 90's, the death of Paul sweats.
4. New Industrialcountries ("Asian tigers" ("Dragon"))
In 60 and 70 years of the twentieth century.is the rapid growth the group of the Asia-Pacific regionleading to overall economic growth, which dramatically changedface of Asia. In the forefront of changes were South Korea (Republic of Korea), Taiwan,Hong Kong and Singapore, which was called "Asian tigers (Dragons).
The reasons for such changes frequently seen inpolitical patronage from the U.S. (particularly over South Korea and Taiwan) and otherof the West. In a "cold war" local elites declared themselvescommitment to ideas of democracy, market economy and anti-communism. But this is notprevented them from installing rigid authoritarian regimes (South Korea andTaiwan). U.S. regarded them as a strong point in the fight against communism in Asia.It directed the American aid, Western experts consulted inreforms, creation of industry, introduction of new technologiesetc.. In addition to these causes "economic miracle" can be described also as follows:cheapness, hardworking and disciplined workforce capacity of Asian markets.
Among the "tigers" special placeSouth Korea ranks. Its starting conditions were somewhat better than other"Tigers". She had developed agriculture, which eliminated foodproblem. But because of the war years 1950-1953 with North Koreaindustry of the country was completely destroyed. The first postwar governments soughtlead the country to ruin it due to agricultural development.However, the chosen strategy did not provide economic benefits over NorthKorea, that its development was guided by Soviet standards.
To prevent the penetration of ideasSocialism to the south with the tacit approval of U.S. 60-ies in the countryestablished a lasting military dictatorship of General Jeong Hee Park.The military regime installed the brutal crushing of any public appearances, butthus were given the full economic freedom that under U.S.help after some time began to give positive results.
In the period of Pak werelaid the foundation for rapid economic growth in Kazakhstan. The basis of economicdevelopment was taken Japanese model: develop export industries.Start a inductrialnoyi base was laid steel, creatingCompany Pasco, which now is second in the world. In those years the 70 Koreansi laid the basis for shipbuilding in the early 90's came in second place inworld. Koreans have achieved impressive of success in mikroelektronytsi. Company and SamsungLG has given way to seriously on the world market of the recognized leaders.
In the 90 yearsmanufacture of ships, electronics, chemicals, automobiles RepublicKorea surpassed even Japan (Japanese production of these goods is 2 / 3Korean exports).
During his intensive developmentSouth Korea hostile attitude toward foreign investment, imports of consumergoods, violent means oriented economy on exports. In60 70 years of growth of production was 10% in the period1987 1994rr - 8%. These phenomenal results achieved by the skillfulmobilization of national resources. Korea developed under the slogan: "Growth throughself-sacrifice. "
The working day was 12 hours perday during the six-day working week. Anyone who was not agree, freed orarrested. Labor disputes were handled by the army.
Authoritarianprofile and an educational system which was oriented to the needs of industry,ensure a constant flow of skilled and dedicated workforce. Incitizens actually withdrawn savings that were sent to developmentindustry.
Also, Korean leadership skillfullyused the nationalist slogan of Koreans prefer. The country wasthe goal: overtake Japan.
Over 30 years of agrarian reform Koreaturned into an industrial country. Output of only one companySamsung excess production capacity in Sweden. Gross national income percapita of 100 dollars in 1960 increased to 8500 dollars1994. In 1995, Korea has paid with his debts and has becomecreditor.
In the second half of the 70's in Koreaunfolding democratic movement, which became the main driving force for students. In1979 Pak Chang-Hee died and became the new dictator Chun Doo Hwan. For the periodwhose reign marked the main wave of student movement. Students beganreal war with the police on the streets of the capital. In 1987 went to warconcessions. New governor general became the country where Ro, which began to progressdemocratic reforms. The first democratic elections in 1993:Kim became president Ian himself. At the next election in 1997 wonKim Te Zhong. For the period of his presidency falls during the Asianeconomic crisis of the late 90 th century. With decisive action succeededprevent the devastating consequences of the crisis.
Example of "Asian tigers" becameattractive to other countries in the region. In the 70 years the "economic miracle" began toobserved and Thailand, Malaysia and Indonesia. Subsequently, this group of countriesjoined the Philippines, Brunei. In 80 years China and in 90 in Vietnam, Cambodia,Laos began to carry out reforms to ensure the dynamic development. Inresult of present day Asia-Pacific is the largest andmost dynamic markets.
For coordination between countriesSoutheast Asia even in 1967 established the Association ofSoutheast Asian Nations (ASEAN), which at present day unites all countriesregion and plays an important role in the deployment of integration processes.
I wonder
Philippines. In 1946 independence was declared the Philippines, but the U.S. underauthorities which were from the Philippines in 1898 here kept its militarybase and economic position. Long time internal situation in the country wasunstable because of numerous conflicts between different political factions,that often reached the armed opposition (Communists, Muslims).
In 70 years the country wasF. Marcus set up a dictatorship. Introduced martial law, anymanifestations of discontent prydushuvalys force. Such methods do not contribute to the Boardstabilization in the country: increased partisan and extremist movements.F. Marcus pryvlasnyuvav lot of public money. AdministrationU.S. zaplyuschuvala eye to such abuse because she was afraid that the Philippines canget in reach of the Soviet Union or China. Also guaranteed dictatorshippresence of U.S. bases on the islands. (U.S. bases have been the main source ofprofits dictatorship F. Marcus).
Changes in relations between the USSR and the USA, andalso in the attitude of the American administration to the dictator, led to changesauthorities in the Philippines. In the presidential election in 1986 to powercame the democratic opposition led by Corazon Aquino.
The new president launched a seriesradical change: a new constitution was started by landReform and modernization of the economy, the country withdrew U.S. troopsand eliminated Most Navy and Air Force baseU.S. Subic Bay. These reforms laid the foundation for rapid economicgrowth. But the political situation remains unstable in the country:held a series of failed military coups, continued guerrilla movement,Muslim extremists have resorted to terrorist attacks, capturehostages and so on.
Thailand. During World War II, Thailand was a supporter of Japan. But1944 Mount took the forces that pereoriyentuvaly foreign policy for the U.S.England. The political situation in the country after the war was unstable, twice inset by the country's military dictatorship (1957-1973 years,Years 1976-1977). After the restoration of constitutional order repeatedlyattempted coup took place. Despite military coupscountry remains a constitutional monarchy.
Since the late 70's beganof rapid economic development. Rapidly developing countryelectronics and electrical engineering, oil refining, chemical and automobileindustry. For 1991 Thailand took place in July by the level of per capitapopulation among the countries of East Asia (March 1990 dollars) and the ninth largest population(57 million people). Keeping this position till the present day. Such rapid growth of the economy has been achievedat the expense of cheap labor. But such an unreliable source of growth in thfuture is expected to slow the rapid economic development. A significantThailand became a factor in developing tourism, which invested huge funds.
In a country where incomeincreased the Thai government is trying to turn the country into regionalleader. Building a powerful army, air force and navy. This forces the neighboring countriesalso carry out modernization of armies, which resulted in the deployment of marine racing dog.
Results
After WorldWar in the national liberation movement in the region occupied dominant Communists.National Liberation Movement in the region was strong in the fight against the Japanese afterwar continued to unfold against the former colonialists, who triedrestore their power. May has a decade long bloody struggle with the French,English and Dutch colonizers. The gaining of independence has not broughtpeace in the region. Because it was one of the fronts of the Cold War, the confrontationbetween the USSR and China, local leaders under the influence of communist ideas have takenvarious experiments in building a brighter future and more.
Questions and tasks:
1. As there was a process of decolonization in Southeast Asia?
1. What reasons exist for a long timemilitary dictatorships in most of the PSA and Korea?
2. What impact had the cold war on the country's PSA and Korea?
3.
Fill in the table:"War in Vietnam"
|
Periods
|
Major developments Specifications
|
|
1945-1954 biennium
|
|
|
1960-1964 he
|
|
|
1964-1973 biennium
|
|
|
From 1973-1975 he
|
|
4.
What are the consequences of victoryIn the Vietnam War in the U.S.?
5.
6.Vyznachte impact of the war inIn Vietnam for: internal development of the country, international relations, the course of the ColdWar and the development of the United States.
6. What are the similarities and differences in `yetnamskoyi and the Afghan War? ReplyMake a table.
7. Identify the features of the "Khmer socialism".
8. Why the U.S. supported Pol Pot after the overthrow of his government, knowing itcrimes against their people?
9. What caused the war between China and in Vietnam in 1979?
10. What causes the rapid economic development of PSA in 70-90's? Whatresults and impact of this process?
 English
English