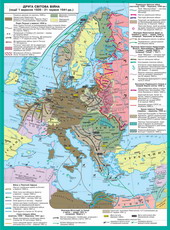
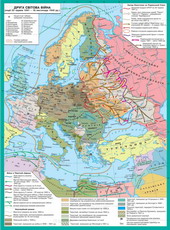
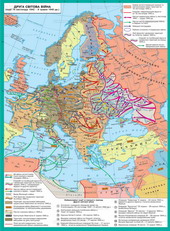
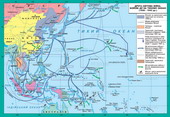
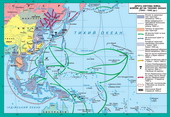
§5. Occupation regime in oppressed countries. Resistance Movement
1. Nazi"New order" in Europe. Japan's occupation policy
Occupationaggressive state of the vast territories in Europe, Asia, Africa, accompanied byestablishing a "new order". Its main content has been the ruleinvaders. This procedure was based on unrelenting terror and violence.
With Hitler's statements about the purpose of war
"We must destroy the population - is part of our mission of Germanpopulation. We will develop techniques depopulation. If I sendthe flower of the German nation in the hell of war, I have the right to destroy millions of peoplenyzchoyi race that multiply like worms? This is a war of attrition. OnEast violence is a boon for the future. Russians, Poles, Ukrainian, Belarusianshould disappear. They should be used for the benefit of the Reich. Someone to resettleAfrica, America? "
Occupied countries of Europe and Asiasuffered significant territorial changes. On the world map came newState: Slovakia (1939)Croatia (1941), Burma (1944), Indonesia (1945). Butindependence of these states has been discredited by cooperation with aggressors.
Nations such as Austria,Czechoslovakia, Poland, Yugoslavia, Luxembourg, Greece were eliminated. InOf Denmark, Norway, Belgium, Holland and France - came to power profashystski(Kolaboratsionistski) governments.
|
Collaboration - phenomenon, which is characteristic of the Second World War. The cooperation of governments, individuals with the invaders.
|
Allied Germany, Italy,Japan received substantial territorial acquisitions. Yes, Hungary has receivedCarpathian Ukraine, Transylvania, part of Slovakia and Yugoslavia, Romania -Transnistria, Bulgaria - South Dobrogea, Macedonia, Thrace, Finlandregained lost in 1940 territory.
Occupation policy inconquest of Eastern Europe and the USSR carried out under the plan "Ost".
Occupied Soviet territory weredivided into three parts. Tylovi areas of German armies groups were transferred undermanagement of military command and Compare pidporyadkovano "eastern ministries"led by Rosenberg i is divided into two reyhskomisariaty - "Ostland"(Baltic and larger part of Byelorussia) and Ukraine. Zahidnoukrayinski landwere affiliated to the Polish "governor-general."
The Nazis sought to createterritories conquered by them "living space for nimetskoyi nation. Localpopulation was to be converted to rabiv in fact, Intelligentsia eliminated. Onoccupied territory was planned to resettle about 10 million Germans. The local populationsupposed to leave about 14 million people. All others were subject to destruction. One ofThe first column of German immigrants created in the winery.
The principal means by which the Nazisutverdzhenni used in his rule, some have been hounding of Nations onand other physical extermination. These nations, like Gypsies, Jews were subject to fulldestruction.
In the occupied territories to Germanyi raw food were removed, other values of MATERIAL. Populationoccupied territories at all initially received nothing for their work,then was soldering mizerni get to work on the invaders. In appalling conditionswere 5.5 million Soviet military prisoners, 3,5 million of them died. Byperiod of 1941-1944 run away from enemy captivity 450 thousand Soviet soldiers andofficers, although much of it was captured, those who escaped, joined toResistance movement across Europe. Escape from captivity of such magnitude did not know any ofarmies of the world.
I wonder
Mortality of Englishmen and Americans in the Nazi campswas 4%, Soviet sodat - 50%. Mortality of Americans, Englishmen,Australians in Japanese camps was 27%. Died in Soviet captivity450 thousand Germans, returned home last 1,9 million Germanviyskovopolonenni returned to Germany in the mid 50's. 1.5 million ofthem worked on rebuilding damaged during the war. In Soviet captivityalso got about 640 thousand Japanese soldiers, of whichreturned to their homeland around 500 thousand
For use in low-cost Himechchynilabor performed deportation working population. Approximately 4.9 millionresidents of the occupied regions of the USSR were on chuzhyni in the difficult conditions of life andLabour (Ostarbaiter "), of which died in captivity 1,4 million total sacrificesoccupation began 10 million Soviet people (3180 thousand in Ukraine, 1360 in thousandsBelarus). Economy occupied countries became an appendage of the military machineGermany.
An important element in the plantations"New order" were the concentration camps, which were sent to alldissatisfied and those whom the Nazis considered dangerous to his regime. InEurope nalichuvalosya about 30 camps. The biggest of them - DahanBuchenwald, Majdanek Osventsim. It was a real factory of death. There wasdestroyed millions of people from different countries.

Crematorium furnaces toAuschwitz concentration camp area
Japan's occupation policy in the formwas somewhat different, but the essence kept the same. Aggressive ambitionsa cover slogan: "Creating a prosperous Asia," Asian Liberation of whitecolonizers. By occupying administrations formed sought to attractleaders of national liberation movements of oppressed peoples.
Such a policy would give the opportunitymake a conquest of European colonial possessions without significantresistance of local people. But the first months of Japanese occupation proved thatheld only change the colonialists. Japan shamelessly robbed seizedterritory.
After the introduction of "new orders"ponevoleni nations of Europe and Asia began to fight against the enemy.
2. Holocaust
Anti-Semitic policies thatconducted after the Nazis came to power in Germany in 1933 afterWorld War II has become even more vicious form. It beganorderly and systematic destruction by the Nazis and their Jewish manualsEuropean populations. This process is called "Holocaust." Since the Holocaust(1941-1945) killed 6 million Jews.
|
Holocaust (Translated from Greek - "burnt") - the systematic and organized destruction Jewish population during the Second World War. G. victims were six million Jews (In Ukraine - 1,4 million). It constituted about 63% of European and 36% of world Jewry. There is no single opinions on periodization G. Some researchers point to the period 1933-1945 biennium Others, in 1941-1945 he was - that a period of systematic mass destruction.
|
Immediately after the annexation of Poland, wherelived one of the largest Jewish communities, all the Jewish population wasresettled in specially created ghettos (separate from the world zrvnishnohosettlement with the minimum living conditions), and their property confiscated. Creationghetto pursued only one purpose - to further complete destruction of their inhabitants.
From the attack on the USSR by the Nazis cameto the "final solution" Jewish question ". Originally exterminatedsubject to the Jews living in the USSR, and later across Europe(About 11.5 million).
For the upcoming German Armymoved specially created four ayzatshrupy (two of them "C" and «D» operatedUkraine), who had to destroy "enemy elements", especially Jews. Already the firstmonths of the war marked by mass annihilation of Jews in Lithuania, Belarus,Ukraine. The symbol of this process was the tragedy of Babi Yar (September 29-301941). But the methods of mass murder, which used aynzatshrupy wereconsidered ineffective for the "final solution to the Jewish question."Aynzatshrupamy was destroyed about 750 thousand Jews. In January 1942natsyske management decides on a six in Polanddeath camps equipped with gas chambers and crematoria (Treblinka, Sobibur,Majdanek, Auschwitz, Belzhets).
In the death camps were not barracks forprisoners that existed in the concentration camps. Victims who came torailway station on the pretext of bringing itself into order directed atshowers. Then in the shower tabled a poisonous gas "Cyclone B" - and after 5 minutes2000 people were dead. The most mature technology destruction wascamp in Auschwitz, where a day znyschuvalosya 12 thousand people. In these camps for yearstheir existence was destroyed 2,5 million Jews.
Creating death camps accompaniedmass depopulation ghetto. In the USSR during1941-1942 biennium Were eliminated almost all ghetto, and their populations receiveto death camps or killed on the spot.
Such a policy could not Naziscause resistance in the Jewish population. He was a passive (spiritual resistanceescape, etc.), and armed. The first armed uprising took place in Vilniusghetto. Later in the ghetto in Minsk, Kaunas, Tudino, Mizachiv, Kremenets, LutskBrody, Lviv and others. Most of the uprising took place in the Warsaw ghetto(April - June 1943). Just over three months nerivnoyi fightrebellion was suppressed as a result of killing i sent to the campsdeath of 76 thousand people.
Reduced down to 25 000 Jews tookpart in the guerrilla movement in the USSR, 5 thousand - in France, 3 thousand - inYugoslavia, 2 thousand - in Greece, etc.
3. Resistance Movement
Occupation policy in Germany andJapan led the deployment of resistance movement. He appeared in all occupied countries, buthis swing was different. At the head of the Resistance movement were socialist, communist,radical and nationalist parties.
As a result of victories on the frontsantyhitlerivskoyi coalition troops is greatly enhanced resistance movement against the invadersin European countries. Many of them created partyzanski pens undergroundorganization. Resistance Movement united all that were not indifferent to the fate of itshomeland. But some who went on cooperation with the invaders, becomingcollaborators.
In France from Nazi occupation iMarshal Petena kolaboratsionistskym government troops and fought partyzanskipidpilni group ocholyuvani communists and Socialists. Established de Gaulleorganization "Free France" in the 1942-43 biennium control of theAfrican colonies of France. In November 1942 French undergroundconcluded with an agreement on de Gaulle by common action. In May next year wasestablished National Council of Resistance, uniting all the forces who foughtoccupiers. In June the French had established a national committee of Liberation,who declared themselves the government, led by de Gaulle.
Significant proportions camePeople's Liberation Movement in Yugoslavia. Since 1941 there was activeguerrilla action against the fascists. Partisan movement in Yugoslavia wassubmitted emigre government troops - chetniks (Commander D. M.)and the People's Liberation Army of Yugoslavia (NVAYU) under the leadership of the Communistled Broz Tito. In 1943, created a new government of Yugoslavia -National Committee for Liberation of Yugoslavia, headed by J. Broz Tito, the meetingAnti-Fascist People's Liberation assembly of Yugoslavia, which was recognizedcountries of the anti-Hitler coalition allies. Partyzanski army formedalso in Albania, Greece and Bulgaria. Significant role played in this processcommunists.

Josip Broz Tito(Right) was .1943
In Poland and its government emihrantskyyMission - "delehura" - led the fight zahoniv Army Executive.Communists opposed to them have created a nation guards.
Confidence strengthened antyfashystskii in Germany. Group officers and government bureaucrats try zdiysnylaoverthrowing the State to destroy the Nazi regime and stop war.July 20, 1944 Colonel Shtauffenberh left briefcase with a bombupovilnenoyi action in the premises where Hitler was. The bomb exploded, butHitler survived. Speech zakolotnykiv brutally suppressed.
In 1944 ryadi in Europecountries were held antyfashystski uprising. Defeat ended the uprising,pidnyate August 1, in Varshavi army Krajowa (commanding generalBoer-Komorowski). August 29 NATIONAL Slovak uprising began withSlovak army and guerrillas. Price not much effort Hitleritesoverwhelm him.
In the USSR people's struggle Vigilantereached a particularly large scale. On her forehead was the headquartersguerrilla movement. The main base was partisan Belarus. Herewere the greatest connection i partyzanski large areas. In Ukraine Centerguerrilla movement was in the northern areas. Constant relationship existed betweenpartisan bases i "mainland" Where partisans supplied weaponsoutfit? skilled military specialists. In 1942, Sovietguerrillas amounted to 125 thousand pers., in 1943 - 250 thousand FightingGermans were also troops of the Ukrainian Insurgent Army.
Partisan movement was asmilitary, so i type of political significance. Shyrokomasshtabni dyversiyni operationguerrillas vynyschuvalni raids made a significant contribution to the victory over the Nazis.Up extensive operations conducted partyzanski connection Kovpaka Fedorova Saburova,Naumov and others. Whole territory of the USSR was comprised of over 6 thousand guerrillazahoniv, which destroyed about 1 million hitlerivtsiv.
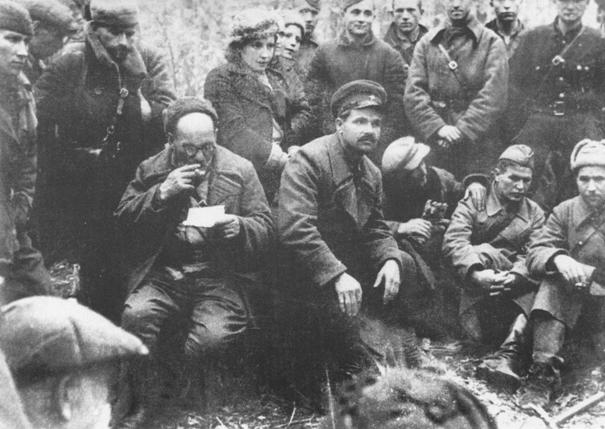

S. cap andS. Rudneva among partisans in the Bryansk Forest. 1942
The most shyrokomasshtabni dyversiyiwere in summer 1943 were carried during the Kursk battle under the name "RailWar began and in September 1943 under the name "Concert". The Nazis were for zmusheniof their komunikatsiy from partisans to keep their rear digit forces.
In general, to fight resistance movementGermany and her allies had to divert more than 10% of their forces.
The Japanese occupation also gave risedeployment of resistance movement. The biggest swing came in he Birmi, Malaya andPHILIPPINES IN UKRAINE, where acting in goals partyzanski army. Yaponski occupants were zmusheniBirmi to formal independence. In V'yetnami and Indonesia in the first stagesWar dominated pasyvni forms of struggle and only the final stage of the Resistance movementgained wide scale. Finally, the leaders of the national liberation movementproclaimed the independence of these states.
MovementResistance in Europe
|
Country
|
Organization, the armed movement forymuvannya Resistance
|
Highlights in the liberation struggle
|
|
France
|
External Resistance Movement: "Free French", "France is fighting, their successor - The French Committee of National Liberation (FKNV, 1943.).
Internal Resistance Movement: "Secret Army" (1942), National Council resistance (NRO, 1943), French internal forces (FFI, 1944)
All members of the Resistance movement recognized the general management FKNV led Sh.de Gaulle.
|
Armed resistance to foreign troops taking part in hostilities against German and Italian troops in North Africa and Western Europe in Allied stock.
Internal resistance used all the methods of dealing with invaders from underground to fight guerrilla actions (maki).
March 15, 1944 NRO adopted a program of movement: the overthrow zroyne the regime and the establishment of an interim government.
After landing in Normandy, Allied maki intensified action throughout in France. The largest rebellion flared in the area of Grenoble (south France).
August 18, 1944 Paris erupted in anti-fascist uprising. After 4 days the city was completely in the hands of the rebels.
|
|
Belgium
|
Front independence (1941) in 1943 created patryotychnu police. Emigre government subordinated "Secret Army".
|
Formation movement MDP using both passive and active methods against invaders (sabotage, sabotage, acts guerrilla groups, etc.).
|
|
Holland
|
Council of Resistance (1943), "fighting squads", "service order".
Single nerve center of resistance was not.
|
The above organizations have used all methods of struggle. Since 1944 emigre government tries to control the movement oorhanizatsiyamy Resistance.
|
|
Denmark
|
Liberty Council (1943), had a military commission and the army of 1925 ths.
|
Under pressure from the resistance movement kolaboratsionistskyy vidmovyvyvsya of government further cooperation with the invaders. Since April 1944 operations Resistance movement were subordinate Allied Headquarters.
|
|
Norway
|
Parts of the Norwegian army, do not lay down their arms, Guerillas, partisan groups. Single point of resistance did not exist.
|
1940-1941 biennium active armed struggle against the occupiers. 1942 slump resistance movement.
Since 1943 activation of the Resistance movement. Most high-profile event: the destruction of plant the production of heavy water for the German atomic bomb, the failure to mobilize Norwegian youth to the German army.
|
|
Italy
|
Committee of National Liberation. Guerillas haribaldiytsiv (formed Left and tsentryski party). In September 1943 King and Marshal Bodalo zmischayut Mussolini.
|
Since autumn 1943 deployment of mass guerrilla movement in the North Italy against the German occupation and the state of Salo, Mussolini headed. Creation "Partisan republics. Capture and execution of Mussolini and his partisans Petachchi mistress Carla (28 April 1945).
|
|
Poland
|
Force external resistance: armed groups in the USSR Army W. Anders (in 1942 the USSR was tips over in North Africa), Voysko Polish (was fighting with the Soviet Army).
Internal resistance forces: National Army (formed in 1939 representatives of right-wing and nationalist forces, subordinated emigre government). Guards formed communist nation. Peasant battalions.
Polish Committee of National Liberation (1944) held pro-Soviet positions.
|
Participation in combat with allies
(North Africa, western and eastern fronts of the Second World War). Participation in the assault on Berlin (Voysko Polish).
Internal resistance forces used all methods of struggle.
August 1944 anti-fascist uprising in Warsaw organized AK (Commander, General Bur-Komorowski) was suppressed after a month of fighting.
In 1943, in the Warsaw ghetto uprising took anti-fascist Jews, which was brutally suppressed.
|
|
Czech Republic and Slovakia
|
Resistance of external forces: the Czech brigade commanded by L. Liberty, which fought as part of the Soviet army. Emigrant government in London.
Forces internal resistance: the weakest in Europe (Czech Republic). There were some partisan groups and militants.
Guerrilla Army of Slovakia (65 thousand people.).
|
On the territory of the Czech resistance movement was limited mainly acts of sabotage.
Anti-fascist uprising in Prague (May 1945).
Slovak National Uprising (Autumn 1944). Suppressed German troops.
|
|
Yugoslavia
|
Chetniky (Royal Army of Yugoslavia in the homeland under the command of Dragoljub-pills Mikhailovich, formed in summer 1941), mostly Serbian.
People's Liberation Army of Yugoslavia (NOAYU), led by Communist led Broz Tito. Recognized allies.
|
Anti-fascist uprising in the summer of 1941 in Serbia and Montenegro. Suppressed.
Create a guerrilla army, the deployment of mass struggle. Prior NOAYU 1943, which consisted of 320 thousand soldiers, released 2 / 5 of the country. Decisive battle in the valley of the Neretva. German troops could not defeat NOAYU. In 1943 created a new government of Yugoslavia - National Committee for Liberation of Yugoslavia led by Josef Broz Tito, at a meeting of anti-fascist people's assembly Liberation of Yugoslavia, which was considered anti-Nazi allies countries coalition.
|
|
Albania
|
National Liberation Front (Memphis) and his National Liberation Army (Noah), led by Communists (E. Hodja).
Battalion Antonio Hramshy "Italian soldiers, who in 1943 passed guerrillas on its side.
|
Resistance Movement led a successful battle against Italian and from 1943 against German invaders. Noah themselves liberated the country from occupation.
|
|
Greece
|
In 1941 Communist Party of Greece, led by D. Satyasom created broad front of resistance (EAM) with its underground partisan Army (ELAS, commander Gen. S. Sarafis) - the largest and operationally (40 thousand people.).
|
By pyhodu British army (January 1944 released ELAS Greek territory from German troops and tried to establish its authority. In 1944 opened battles between British troops and ELAS (introduced by agreement between Churchill and Stalin), which caused her defeat.
|
4. Internalsituation in Germany, Japan, UK and U.S.
Facilities warring countries wasvoyenni transferred to rail. Production of military technique and equipment becameThe priority. Yes, in Germany, where the military industry more in 1932almost was not, during the war produced annually about 25 thousand combataircraft, tankiv 20 thousand, 50 thousand guns i minometiv. Since 1935hitlerivska Germany began to rebuild his military order of that economy.When the Second World War, Industry Reich worked on militaryneed to complete the power, letting one of the best tanks in the world, airplane,gun. Since 1943 German engineers began to activelydeveloping "miracle weapon" that would give Germany an opportunity to reverse the course of the war ontheir favor. These searches resulted in engineering a large varietymilitary equipment, weapons and technologies that were implemented in mass productionbut after World War II in the U.S. and the USSR. German industryhas established the world's first production jet aircraft, ballisticmissiles and more. However, this did not save the Nazi regime from collapse.
Production of military technique andweapons stimulated the development of heavy industry. Light industry muchvidstavala from heavy industriyi. In agriculture the mainproducers of commodity products were large landowners and farmers (Bauer).However, they did not cover the needs of Germany and its army in agricultural products.
Success is Nazi Germany ininitial stage of war made it possible to use economicalpotential of the conquered countries.
In 30-40-ies basis of economy of Germany was a military Industry. In1939 its share in gross production cost Universal was80%. Number of people engaged in industry for viyskoviy1939-1943 biennium has increased twice as i was five million people. Dyfitsyt in OfficeGermany syli covered by the forced labor of the military,million deported from occupied countries.
Despite Completemilitaryzatsiyu, nimetska economy was not fully meet the needs vzmoziFront. Since the end of 1943 Germany began Felt serious difficulties inof all sectors of the economy. Violated certain economic ties betweensystems, The basic fields of economy I feel a lack of raw materials, fuel,human resources, financial means. Since the second half of 1944industrial production sharply decreased. This was due to massive and strategicAllied bombing. In general allied bombing on Germantown lost one million German civilians. Were destroyed Hamburg, Cologne,Darmstadt, Leipzig and others.
Due to the decline of ruralEconomy shrunk posivni area decreased gross Fee grainpoholiv'ya cattle. Sharply decreased consumption of foodstuffs. DeficitBudget the Government tried likviduvaty by inflation. Sharply decreased welfarepopulation.
After Germany's economy has undergonecollapse. I could not endure a long rivalry with the economies of the United STATESJapanese economy and military, but helped transform Japan War began onIndustrial and agricultural state. The share of heavy industry in the manufacture of muchincreased. However, the war led to a worsening situation of the population: the coston war profits exceed four times. Inflation felt heavilyplechi on population. Living standards reached naynyschoho level in history. Frombeginning of the systematic bombing of U.S. strategic aviation, lossmajor sources of raw materials and foodstuffs Japan's economy has undergone a completecollapse. To ensure hoch somehow Japanese army weapons Japanese engineershave achieved excellence in the replacement of expensive materials for cheap. All equipmentproduced the lowest set of necessary equipment and parts. Mass beganproduced disposable aircraft for "kamikaze".
Soviet Union after the Naziaggression was in serious condition. Were lost important industrial andagricultural areas, leading to a fall in production in an environment whereFront demanded more weapons. Thanks to the heroic efforts of people at the end1941 situation could improve. Over the Urals was created powerfulindustrial base. Earned in 1360 evacuated enterprises.
I wonder
OnFall 1942 German troops and their allies occupied 1.8 million square meters. kmthe USSR (10% of the territory), where before the war lived 80 million people. (45%population), produced 60-70% of coal, iron, steel, railways ran 40%,there were half the livestock of cattle and I `acreage of which was about 45%grain.
In the worst situation has endedagriculture. In 1942, grains were collected 1 / 3 of the war. Bywith tight regulation and distribution could avoid starvation andprovide food to troops in the field.
Since 1942Soviet economy began to increase production, not only quantitatively but alsoqualitatively. Soviet-era weapons were not worse, and some even better thanhostile.
Dynamics of production of aircraft and tanks in the USSR
|
Years
|
Aircraft thousand
|
Tanks thousand
|
|
1942
|
21,7
|
24,4
|
|
1943
|
34,9
|
20
|
|
1944
|
40,9
|
29
|
I wonder
During the war years (since 1941) in the USSRcard system was introduced. For the first time card system in the USSRintroduced in 1928 Since January 1, 1935 canceled the card toflour, bread, cereals. From October 1 - for the remainder of food, and from January 1, 1936- On industrial goods. For cards issued not only products but also soap, clothing,shoes. Standards for all were different. Loss of cards put a man on the brink of starvationdeath.
Allowance on cards that were in the 1941-1947 biennium(In grams)
|
|
Bread
|
Sugar
|
Meat, fish
|
Fats
|
Cereals, pasta
|
|
|
On the day
|
Per month
|
|
Body workers and munition
|
880
|
800
|
2200
|
600
|
1500
|
|
Body workers and other plants
|
600
|
600
|
1800
|
400
|
1200
|
|
Employees
|
500
|
600
|
1200
|
300
|
800
|
|
Disabled (izhdyventsi)
|
400
|
400
|
500
|
200
|
600
|
|
Children under 12 years
|
400
|
400
|
400
|
300
|
800
|
England had endured a hostile threatinvasion masovani povitryani bombing, which piddavalys LondonBirminhem, Koventri Compare and cities, blockade nimetskymy navy shipskomunikatsiy, occupying several koloniy - Birmy, Sinhapuru, Malaya, big lossparts sales i Navy. Industrial production in the countrywar years, decreased by 5%. Sharply reduce production in sposterihalosvuhilniy industry (21%) in lehkiy, including cotton, more thandouble, vovnyaniy - 27%.
The costs of war were 25 billionpounds. To at least partially cover these costs, England raisedabout a third of its foreign kapitalovkladen, especially kolonialnyhcountries - India, Canada, Australia, South-African Union as well asLatin America and the USA. Public debt zbilshyvsya war three times over the years. InMany areas that were considered earlier sphere of influence of England, for example, countriesArab Union i South-East Asia, zakripyvsya American Capital,that penetrated reinforced in dominiony i koloniyi also English.
The burden of war is primarily affectedthe welfare population. Taxes per capita increased three times,cost of living - by 72%.
The war caused France occupying the isignificant zbytkiv that otsinyuvalys in 1.44 trillion. prewar frankiv. Lyudski victimsamounted to 1,1 million people. Industrial production declined to 30% oflevel of 1938, production agriculture - twice. Francei had no military trade flotiv. Current Foreign capitalscountry before 1945 decreased by half. In addition, France has lost itskoloniyi: Indokytay, uncooked, Livan, who won independence.
United States did notParticipation in the initial stage of war, but occupied clearly expressed antynimetskiposition. Introduction in the U.S. war against Japan and Germany forced the U.S. governmentpereoriyentuvaty economy to military order.
U.S. has not yet entered the war,provided in a loan or lease of weapons, ammunition, strategic raw materials,food and other resources MATERIAL countries to ally antyhitlerivskiycoalition (Lend-liz). He provided a massive sale of U.S. goods toforeign market, which contributed to maintaining a high level of production in the U.S..Amerykanski costs of operations by land-lizu exceeded 30.3billion.
During the years of war in the United States were introduced innew act of military industrial enterprises, valued at 25 billiondollars.
U.S. steel"Arsenal" of anti-Hitler coalition. In the year (1944) U.S.industry produced many planes as German for all the years of war.
Dynamics of production of aircraft and tanks in the U.S.
|
Years
|
Aircraft thousand
|
Tanks thousand
|
|
July
1940-December 1941.
|
23,2
|
4,3
|
|
1942
|
47,9
|
23,9
|
|
1943
|
85,9
|
29,5
|
|
1944
|
96,4
|
17,6
|
|
January-August 1945
|
43,2
|
11,2
|
U.S. was the only country where war is notworsened the well-being, but rather it grew. Was overcome unemployment.
III.Results
Since the Second World Warfascist bloc sought to not only defeat the enemy, and set the "new(World) order, which was to stand on violence, robbery and so on. Millionscivilians have become victims of aggressors (about 50% losses during the war).Most civilians znyschuvalas specifically: with the ideological, racial,political and other reasons. Such a policy is extremely znytsinyla human lifeputting to the people of the occupied territories dilemu: or die, orto arms. In occupied countries turned a mass resistance movement. Fromsuccess at the front of the anti-Hitler coalition, and grew mighty movementResistance. Forms and methods of struggle were different: from passive resistance to armedrevolts.
In World War II as inFirst solved the fate of war not only on the fronts, but in the rear. Softwaredepended on armies of economies. In rivalry eoknomik economiesfascist bloc suffered a complete collapse.
Questions and tasks:
1. What European countries were occupied by Nazis?
2. What is a Nazi "new order"?
3. What reasons prompted widespread occurrence of such phenomena as the collaboration?
4. Holocaust - is it?
5. As the Nazis attempted "Finallysolve the Jewish question "?
6. What factors most influence on the resistance movement in Europecountries?
7. In which European country resistance movement reached its zenith? Which countriesthemselves freed from Nazi oppression?
8. What provoked a split in the resistance movement? What political forces have played a majorrole in the resistance movement?
9. What is the impact war has had on economic development of the warring countries?
10. During the war years the Soviet economy has produced weapons in 2 times more thanGerman, but Soviet industrial capacity was several times smaller. Thatcontributed to the victory of the Soviet economy over the economy of Nazi Germany?
11. Why the U.S. called the "arsenal" of anti-Hitler coalition? Iswould be a victory over the fascist bloc countries without economic potentialU.S.?
12. What are the differences in domestic circumstances of countries and aggressorsanti-Hitler coalition?
 English
English