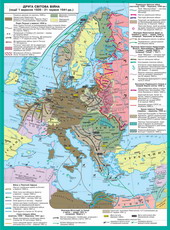
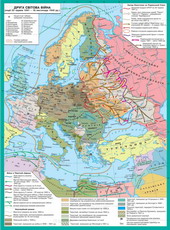
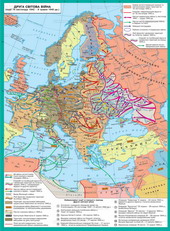
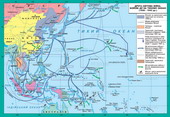
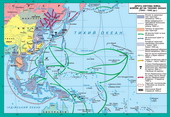
§4. Military actions in the second half of 1942 - 1943 рр.
1.Battle of Stalingrad
Battle of Stalingrad - one of thei largest major operations of World War II. Tentatively, it can bepodilyty into two parts. First - this attack German troops in summer 1942i withdrew them on the Volga and Northern Caucasus. Second - Soviet counteroffensiveTroops smash nimetsko i-Golf-Romanian-Hungarian army to Volzi.
The attack on troops nimetskyhStalingrad began on the distant approaches to it, when five well-armedi nimetskyh three armies army Italy, Romania and Hungary attacked withKharkiv direction? forsuvaly Siversky Donets i don.
6th army nimetska August 251942 reached the western outskirts of town Volzi. Besides it, advancing on Stalingradalso 4th Panzer Army. They resisted in 1938 weakened the Soviet Division.Eighteen of them were completed, the remaining, bleeding in previous battles,could be regarded as only nominally.
The ratio of forces at StalingradSeptember 1942
|
|
Soldiers
|
Tanks
|
Guns
|
|
Soviet troops
|
54 thousand people.
|
110
|
2000
|
|
German troops
|
100 thousand people.
|
500
|
900
|
Strategic and political importanceBattle of Stalingrad was correctly assessed the Soviet command. Itbecome a symbol of struggle totalitarnyh two regimes meet theirleaders. The list of personal ambitions, because the city was Tsaritsynrenamed Stalingrad in honor of "the leader of all peoples", which has in yearsCivil War on the task of Lenin overseen by defenseTsaritsyn.
October 14 German troops afterstrong aviation and artillery preparation went to storm the city. Begunbrutal street fighting. Both sides suffered heavy casualties. November 14 Germansbegan last storm the city, they managed to get to some sections of the Volgabut it was their last success.
After i bezplidnyh stubborn attemptsSturm reset radyanski troops in Volga, nimetske command in the middleOctober viddaty had to order the transition to defense.
At that time, military-strategiczminylasya situation in favor of the USSR. Viddaleni komunikatsiyi, stretched frontdemanded great efforts logistic services nimetskyh i economy. Totalnimobilizatsiyi znekrovyly nimetski enterprise, in place of skilledWorkers were "Ostarbaiter and peremischeni person from France, otheroccupied Europe. At the same time Soviet economy in the second half of 1942continuously enlarged its production of military products. Through the cruel discipline andoperation of the Stalin regime in the short term spromihsya establishactivity in the Urals powerful military-industrial complex. Starshi peoplewomen, children, that machine-tools mobilizovanyh zaminyly near the front Adult Workers,samoviddano worked zhurtovani slogan: "Everything for the front, everything for victory!"It yihnimy efforts in the second half of 1942 were produced 15.8 thousandcombat aircraft, 13,6 thousand tankiv, 15,6 thousand guns.
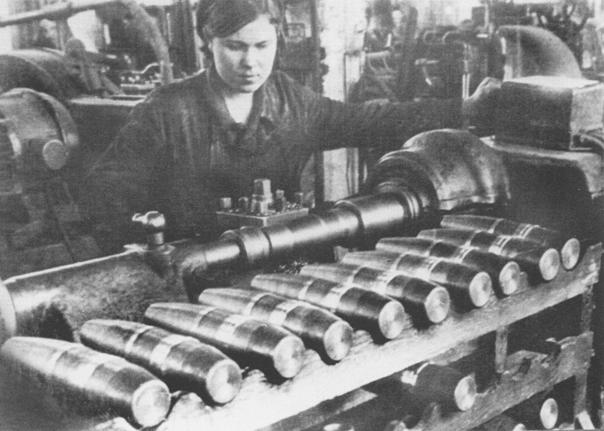

Productionshells on one of the Ural. 1942
At the end of autumn 1942prevailing conditions for the transition of Soviet troops in the offensive. Mainexpected to cause shock troops Kalinin and Western Fronts in theRzhev - Vyazma - Sychovky, toward the Gulf of Riga. There were two focusmillion soldiers, 3300 tanks, 1000 aircraft, 24 thousand guns and mortars. Itgroup was the offensive November 25, 1942
To provide the main shocksupposed to take six days earlier in the distracting blowStalingrad. In accordance with the plan "Uranium On 19 November1942 Soviet troops by three fronts - South West,Stalingrad and the Don - went to the counter-offensive, causing flank attacks.In the decisive Battle of Stalingrad point advantage in manpower and technology alreadywas on the side of the Soviet army.
Correlationforces before the Soviet counteroffensive
|
|
Soldiers
|
Tanks
|
Guns
|
Aircraft
|
|
Soviet troops
|
1103 thousand people.
|
1463
|
15500
|
1350
|
|
German troops
|
1011.5 thousand people.
|
675
|
10290
|
1216
|
November 23, 1942 Soviettroops locked ring around 330,000th enemy factions (22 divisions).Hitler ordered a last stand. It is forbidden to do with the army to breaki ordered environment wait deblokuyut its assault convoyGeneral Field Marshall Manshteyna. However, powerful tank strikes in December1942 in the region of Kotelnikov not succeed. They wererejected by Soviet troops. Manshteyn himself later wrote that the operation ofdeblokuvannyu 6 th Army Paulus could be successful if the joint impact ofmiddle and ring izzovni. German Aviation also proved unable tobring in the necessary quantity of cargo ring.
After refusing von Pauluscapitulate began destroying German forces surrounded, demoralized,exhausted by hunger and cold. Despite the ban Hitler, 30 January1943 Field Marshal Paulus (giving it the title, in a telegram to HitlerPaulus hinted that no German Field Marshal seemed in captivity) signed theAct on kapitulyatsiyu. February 2 last stop resistance surrounded hitlerivtsi: 100thousand from 330 thousand surrounded surrendered as prisoners, others killed (later from captivityreturned only 15 thousand people.). General loss of Nazis at Stalingradamounted to 1,5 million votes, almost 3,5 thousand tankiv i attack guns, 12 thousandi minometiv guns, 3 thousand airplanes. From this defeat nimetska army has notcould recovered. Initiative in eastern moved to the Soviet Union during WW II. In the secondWorld War there was a radical turn.
Historicalimportance of the Battle of Stalingrad:
|
·
It initiated a radical turn in During the Great Patriotic War and World War II;
|
|
·
defeat the enemy attacked the military machine of the Third Reich, the German army's prestige, morale Wehrmacht;
|
|
·
began a general offensive of Soviet troops from Leningrad to the Caucasus;
|
|
·
was attacked by fascist bloc general. Japan and Turkey refused to join the war against the USSR. Guide Romania and Italy (their army were among those who were crushed Stalingrad), and Hungary and Finland have started to look for exit War;
|
|
·
defeat the Nazis and their allies became a powerful impetus for anti-Nazi and national liberation movements, promoted consolidation of the anti-Hitler coalition forces.
|
While Stalingrad wasgaining a brilliant victory Rzhevs'ka Sychovska-operation has undergone a complete failure(Later she was named distracting to ensure success inStalingrad). For 23 days of fighting in this area Soviets lost215 thousand people killed and wounded.
ChronologyBattle of Stalingrad
|
Date
|
Event
|
|
July 17, 1942
|
Start the Battle of Stalingrad.
|
|
July 23 -
August 10, 1942
|
Fierce battles in turn Don.
|
|
August 23, 1942
|
Exit German troops to the Volga north of Stalingrad.
|
|
September 13, 1942
|
Start fighting in Stalingrad.
|
|
October 14, 1942
|
The beginning of the storming of the city German troops.
|
|
November 14
1942
|
Beginning last storm Stalingrad German troops. In some sections they managed to get to Volga.
|
|
September-November 1942
|
Developed under the direction of G. Zhukov and A. Wasilewski plan counterattack at Stalingrad.
|
|
November 19
1942
|
Start the Soviet counteroffensive Stalingrad (Operation Uranus ").
|
|
November 23
1942
|
Entourage 22 German divisions (Over 300 thousand people.).
|
|
12-20 December
1942
|
Attempt and fail Manshteyna deblokuvaty surrounded by German troops.
|
|
January 10, 1943
|
Begin Operation Ring "on surrounded by the destruction of German communities.
|
|
February 2, 1943
|
Capitulation Army Field Marshal Paulus. Completion of the Battle of Stalingrad.
|
2. Kurskbattle
In January 1943 SovietMore troops have made one significant success - was prorvano Leninhradu blockade,and in the west to the Red Army pidiyshla Smolensk.
12 cichnya 1943 troops undercommand of General Holikova attacked from under the Voronezh in generaltowards Kharkov. February 7 was released Kursk, 9 - Belgorod. Troops undercommand of General Vatutina mastered cake i have threatened environmentGreat German groups in the Kharkov. February 16 left the enemyindustrialne great city.
In the second half of February the situationchanged. Fearing the threat environment of troops from the Caucasus and vidiyshly Kubaniunder i to Rostov Basin, nimetske command caused a powerful retaliation inflank of the stretched troops and Holikova Vatutina. Kharkov, Belgorod and numberother cities again passed into the hands of the enemy. Formed a great Orel-Kurskarc.
In spring 1943Soviet-nimetskyy Leninhrada from front and to the Black Sea stabilizuvavsya.Both sides gathered forces for a summer offensive. Industrycontinuously enlarged edition of all kinds of weapons.
Interestingknow
From 1 January 1943 in the RedArmy shoots were introduced for soldiers, sergeants, officers, generals, and marshals.Tea soon became known as the Soviet army. The emergence of the Soviet soldier shootssometimes ambiguously perceived population that were occupiedterritory.
Spring 1943 GermanHigh Command has decided to seize the initiative again. According toPlan Citadel Nazi leadership was aimed routSoviet troops and deploy speech Kursk offensive on Moscow. Forattack created new designs weapons (tanks - "Tiger""Panther", self-propelled guns -
"Ferdinand", etc.), which should provide the Germanforces technical advantage.
The Soviet command had received accurateinformation about preparing to attack the Germans. And though this time the Red forcesArmy has dominated the Wehrmacht forces, it was decided to "intentionallydefense "to the military potential obezkrovyty Germans and cause themretaliation.
To make a breakthrough on both kintsivOrel-Kursk speech nimetske command concentrated in the Eagle 7tank, two motorized infantry Division and 9, and in the region of Belgorod - 10tank, a motorized and 7 pihotnyh Division. Total German group 'counted 900 thousand people., 10 thousand guns and mortars, 2700 tanks and assaultguns, 2050 aircraft. But the Soviet side has created a powerful performance in the region ofgroup. In Summer 1943 in the Soviet army was 6,6 millionvotes, 105 thousand guns i minometiv about 2.2 thousand military installationsrocket artillery, over 10 thousand tankiv i mobile artilleryunits (SAU), 10.3 thousand combat aircraft. The advantage of this time was on the sideSoviet troops.
The attack nimetskyh armies of under-Belgorod and from the Eagle in the direction of Kursk began on July 5. Sovietcommand in time trends identified enemy offensive operations icarefully to pidhotuvalosya vidsichi. Percussion German group couldmove forward with heavy losses at 12 km inland location armiesCentral Front (commander - K. Rokossovsky), and 40 km to the region of VoronezhFront (commander - M. Vatutin). At the time when the enemy has not yet vydohsyatime to go on the offensive and defensive Soviet troops moved Bryansk,Steppe and South-Western frontiv. It is necessary for them attackedCentral and Voronezh Fronts.
July 12 took place during Prohorivkoyuthe largest tank battle of the Second World War. Both sides took part in it1200 self-propelled guns tankiv i (800 and 400 Soviet-German). Germantroops in one day lost hundreds of tanks and 10 thousand soldiers. On the same dayzminyvsya character all the Kursk battle, the troops moved in radyanski stronglyoffensive. Breaking the resistance of the enemy, they released August 5 Eagle (Operation Kutuzov)and Belgorod, August 23, broke to Kharkov (Operation Rumyantsev.)
I wonder
August 5, 1943 in honor of the victories the Red Army,liberation of Orel and Belgorod in Moscow was the first place artillerysalute. Later, Moscow 347 times saluted the soldiers of the Soviet Army forliberation and capture cities, some days 4-5 times.
Battle of Kursk showed thatinitiative wholly owned Soviet troops. It marked the completionradical turn in the Second World War. The victory at Kursk wasachieved a price: the Soviet losses were 863 thousand Pers., 6000tanks and 1600 planes. At the same time with 50 days of continuous fighting the German armylost 30 divisions: 500 thousand people., 1300 tanks, 3 thousand guns, 1000 aircraft.Despite considerable losses, the Soviet army had considerable reserves, whilepower was undermined by the Wehrmacht.
Historic Battle of Kursk:
|
·
Nazis defeated the best divisions;
|
|
·
ceded the strategic initiative the Soviet army began a general offensive of Soviet troops throughout the front;
|
|
·
resulted in a radical turn in the second World War II;
|
|
·
conditions were established to Anglo-American landing troops and the collapse of the German block.
|
3. Battle forDnipro
Developing the offensive, Soviet troopsthe end of September 1943 went to the Dnieper. Here, the German commandcreated a so-called "East shaft. Germancommand tried to use the river flowing from the high right bank asnatural reinforcement. Population zhanyalos with a 300-kilometer strip alongDnieper. Much of the city - Kiev, Kremenchug, Poltava - wasbroke and burnt. The Dnipro slopes Nazis styahly Army Group Centre inpart of 62 divisions. At the end of September 1943 The Soviet army controlled700 kilometers on the left bank of the Dnieper.
Spividnoshennya forces before the Battle of the Dnieper
|
|
Soldiers
|
Tanks
|
Guns
|
Aircraft
|
|
Soviet troops
|
2633 thousand people.
|
2400
|
51200
|
2850
|
|
German troops
|
1240 thousand people.
|
2100
|
12600
|
2100
|
The advantage of the Soviet army wasinsignificant. In terms of operations autumn 1943 primary task was to capturebridgehead on the right riverbank, there consolidation and deployment of offensiveOperations on the Right Bank. Battle of the Dnieper opened from Loyeva to Zaporozhye.
Soviet troops byPartisans at the end of September 1943 in very difficult conditions forsuvalyDnieper and established bridgeheads on the north and south of Kyiv, a total of 23.The main breakthrough was supposed to make Bukrynskoho springboard, but allattempts proved futile, the enemy stubbornly defended.
All the October Soviet commandled the preparation for storming the Dnieper. Seeking to raise the morale of troops, whichoutput in Ukraine replenished mainly by locals bidrenamed Voronezh, Steppe, South-West and Southern Frontsaccording to the First, Second, Third and Fourth Ukrainian fronts.
After unsuccessful attempts at Bukryn(Died 250 thousand Soviet soldiers), the main forces of Soviet troopsinvisible to the enemy focused on Lyutizkomu beachhead (150 thousand people.,1500 guns and mortars, 800 tanks).
In the early days began in Novemberdecisive battle for Kyiv. Stalin gave the order to take Kyiv anniversary of the Octoberrevolution. This order was executed. November 6, 1943 was releasedCapital of Ukraine - Kyiv. For successful forcing of the Dnieper River in 2438 to Soviet soldierswas awarded the title Hero of the Soviet Union, received about 10 thousand combatorders.
Sturm accompanied Dniproextremely large and often unacceptable sacrifices. Tens and tens of thousandsrecruits, the so-called "jackets" - unarmed, undisciplined young men, hastilymobilized At the regions of Ukraine, were victims of assault. Their bodiescovered bridgeheads on the Right Bank. Explained by the fact that in the attitudes of seniorSoviet leaders and military commanders felt distrustliberated from the Nazis citizens of Ukraine. It often expands into rancor,desire to make the inhabitants of the Republic "blood atonement" their stay inoccupation. It was one of the manifestations of violence of war, which at pomnozhuvalasyacruelty and injustice of the totalitarian regime, which led military action.
As a result, forcing the heroicDnipro significant price losses (according to different estimates of 417 thousand to 1 millionpeople.), Soviet troops liberated Kiev October 14, October 25 -Kiev, November 6 - Kyiv.
Thus, late autumn1943 Soviet troops came to the right bank of the Dnieper, entrenched there,German troops repelled a counter attack in the region of Zhytomyr and prepared the conditions forattack and subsequent liberation of Soviet territory.
4. Nativefracture in combat in North Africa. Capitulation of Italy
In October-November 1942 inNorthern Afrytsi also held a radical turn in favor of Anglo-Americanallies. A decisive battle took place near the town of El Alamein (Egypt). InOctober 1942 British troops, with a significant military advantage inby General B. Montgomery caused the Germans and Italians defeat. Latestwere forced to hastily depart to the west. In November 1942 oppositethe North Africa (Morocco, Algeria) American troops began landingunder the command of D. Eisenhower (Operation Torch (Torch).

Dwight Eisenhower,outstanding military leader, Major General U.S. Army
during the Second World War, and later -U.S. President
German and Italian troopscaught in a trap at the seaside in Tunisia. Their desperate resistance andeven some progress on the left flank of American troops have not changed the overalldisposition of resources and May 13, 1943 they capitulated.
Table.: Spividnoshennya forces partiesBattle of El Alamein
|
|
Soldiers
|
Tanks
|
Guns
|
Aircraft
|
|
English troops
|
230 thousand people.
|
1440
|
2311
|
1500
|
|
Italo-German troops
|
80 thousand people.
|
540
|
1219
|
350
|
Serious defeats, which were in1943 the country's fascist bloc, contributed to its collapse. The firsttrying to get out of the war Italy.
Digit losses in lyudskiy syli andtehnitsi that they were state "oci" in Tunici (about 130 thousand onlyprisoners of war), contributed successfully to the allied troops landed on the island. Sytsyliya. Hebegan in July 1943 planting and marine parashutystiv pihoty(Operation "husky"). It should be on transport ships arrived Division 7 thAmerican and 8 th of English armies under the command of Patton and Manthomeri.Overall management of seizing these windows Sytsyliyi zdiysnyuvav AmericanGeneral D. Eisenhower. After long battles that were fought for pereminnym success,nimetskyh remains evacuated parts of Appeninskyy pivostriv and the soldiersMonthomeri Patton and cleared the last line of defense the Germans on Sytsyliyi - portMessinu.
I wonder
Patton received kapitulyatsiyu cities, notwaiting for arrival of English representative there. This he calleddissatisfaction ally and seriously complicated the relationship with Englishcommand. In total, Patton was quite scandalous reputation, hedirect statements that often led to scandal.
Under the influence of lesions on 25 July inItaly held a coup with King Victor Emmanuel andMarshal Badolyo. Mussolini was arrested. King was declaredcommander and Badolyo headed the government and became Minister of Foreign Affairs.September 8, 1943 new government signed an armistice with the Allies.
Approximately pivtora months afterimprisonment of Mussolini villi in rocks Abrutskyh mountains there for a specialvkazivkoyu Fuhrer came under the command zahin esesivtsiv O. Skortseni i zvilnyvdemoralizovanoho Duce.
A delay Eisenhower, notadjusted instantly landing troops on Golf toe boot "and all requiredfrom Badolyo unconditional kapitulyatsiyi, the Allies could not usefavorable conditions. Hitler Marshal Kesselrinhu viddav order to moveDivision to the South Golf pivostriv i occupy. Allied troops hadovercome strong resistance region of Germans in Salerno, Naples and other southernitaliyskyh cities ("Gustav Line"). Operations here became protracted.Northern part of Italy's fascist troops detained under the command ofRommel. There, was delivered and emancipated Duce. He headed marionetkovyymode, which utilizes only nimetskyh bayonets (State Salo).
U. Cherchill pidhanyav GeneralG. Alexander, who led the campaign after Eisenhower Golf to a possiblequickly took Rome. But Kesselrinh, though i was a general aviation, vmiloestablished a defense. Only the June 4, 1944 Rome was taken alliedtroops. Further, they could not move. Defence strategic quadrangleItaly Turin - Milan - Genoa - Bologna with its military-industrial mohutnimcomplex continued until April 1945 ("Gothic Line").
5. TeheranConference
Critical events that determined the outcome of the war, certainlytook place at the front, but for the further fate of the world and human civilizationhad an important event in the diplomatic sphere. As the morechytkishe vymalovuvalysya prospects for the war, before the leadersanti-Hitler coalition faced more acutely the question of postwarsettlement. Consultations on this issue began with the beginning of 1943The first serious discussions took place at the Moscow Ministerial ConferenceForeign Affairs of the USSR, USA, England, held from 19 to 30 October1943 The main objective of the conference was to prepare a meeting betweenState and Government of the USSR, the USA and England - "Big Three".
In the ministers had a few issues. Yes, it wasreached a preliminary agreement on opening a second front in France in the spring1944 It was agreed establishing the European AdvisoryCommission to "study European problems related to the end of the war.Important was the approval of the Declaration of general security ", which statedthe necessity of establishing the post-war general international organization forpeace and security, which would be based on principles of sovereignty andequality of all peaceful nations. Besides Moscow conference1943 Foreign Ministers of the USSR, U.S. and UK took"Declaration on Austria", indicating that the Federal State does not recognizeconquest of Austria and want to see it restored, free and independent. InThe Declaration of Italy "was that" fascism and all its negative effectsshould be removed, and the Italian people should be given the opportunitycreate the government and other institutions based on democratic principles. " Alsopublished statement of responsibility Nazis for their crimes.Main supposed to punish criminals according to the joint decisions of governmentscountries.
At the same time, the conference identified key issues and thatcaused the differences between the anti-Hitler coalition allies: the question of bordersand political regimes in liberated countries.
Great work done by diplomats allowed us to performsummit meeting between Stalin, F. Roosevelt, Winston Churchill, which enteredhistory as the Teheran Conference (28 November - 1 December 1943),because the event took place in the capital Tehran, Iran. During the meetingfurther warfare and post-war world order. As a resultdiscussions, despite the controversy that arose between the leaders of the UnionStates (Churchill suggested opening a second front in the Balkans, Stalin -in northern France, where the shortest path to the opened bordersGermany), the USSR has made it necessary for the solution of key issues:
- Was a final decision on landing in FranceMay 1944 Allied forces;
- Moving the boundaries of Poland to the west to the Oder andrecognition of the future eastern border on the "Curzon Line";
- Recognition of Soviet claims to Konigsberg;
- Recognizing the Soviet annexation of Baltic statesUnion.
Stalin agreed to the USSR in the war with Japan afterthe defeat of Nazi Germany.
In discussing the problem postwar world consensuswas not reached and the discussion was postponed.
Teheran Conference (28 November - 1 December1943) with the participation of Winston Churchill, Stalin, F. Roosevelt
|
The problem of the Second Front
|
The Polish question
|
The German Question
|
Iranian issue
|
Japanese issue
|
|
W. Churchill and F. Roosevelt promised to make intrusion through the English Channel (that is to open second front) in May 1944
|
The Soviet Union insisted on the expansion of the territory Poland by foreign (German) lands on the establishment of Western border country along the rivers Oder and Neisse. Eastern border - on the "Curzon Line".
|
Discovered important differences: F. Roosevelt advocated dismemberment of Germany; W. Uerchill - in exchange for the Danube federation which had come in and part of German lands, Stalin - for the preservation of unity Germany.
|
The decision to assist Iran and output Allied troops from its territory by the end of the war.
|
Supposed to deprive Japan of its colonial possessions, to convey China's Manchuria and Taiwan to independence of Korea.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

Roosevelt, ChurchillStalin and celebrate the day
birthChurchill in Tehran. 1943
The historic significance Tehran Conference:
·
This was the first meeting"Big Three".
·
Despite the fact thatSome key issues between the parties and the differences were no agreement was reached, the factConference leaders of the USSR, the USA, Britain strengthened Antyhitlerivskucoalition.
·
Showed their rishuchysend of Nazism in Europe.
·
Discussed the keyissue of post-war system of `party found out for himself outside of concessions andcompromises in the future.
III.Results
Victory of Soviet troops inBattle of Stalingrad (early radical turn in WWII), allied troops inBattle of El Alamein in North Africa, in a sea battle near Mururoa Miduyeyand in the struggle for Fr. Guadalcanal showed a fracture in the Second WorldWar in favor of the anti-Hitler coalition. The victory at Kursk andthen in the battle for Dnipro completed a radical turn in the Great Patriotic War.Expulsion Italian-German forces in North Africa (May 1943),stabilization of the situation in the Atlantic and Pacific Ocean, stopping Japanese troopsnear the borders of India, witnessed the completion of a radical turn in the SecondWorld War II in general. The determining factors are the events in Soviet-Germanfront - the home front, armed struggle against Germany and its allies.Offensive strategy of Germany suffered a final defeat. To the end1943 at war with the Axis countries, there were 37 countries. Startedcollapse of the fascist bloc (capitulation of Italy).
Questions and tasks:
1. Describe the progress of major events of the war in 1942 - 1943 рр.
2. What is the role of Stalingrad and Kursk battles in the defeat of Germany?
3. Identify the historical significance of the Battle of Sky?
4. Describe the fighting in North Africa in 1942-1943 biennium
5. What was determined by the Allied landing in Italy, not in France?
6. Can you believe the Allies landed in Sicily and Italy in the openingSecond Front?
7. As events evolved on the Italian front?
8. Identify the interdependence of events on the fronts of the Second svitvoyi war. Zapovnistsinhronistychnu table
|
Soviet-German front
|
Battleground in North Africa and the basin Mediterranean
|
Pacific theater of war
|
|
|
|
|
9. What are the main decision Tehran Conference? Can I call thisconference a success? With `yasuyte its historical significance.
10. Give the definition of - "a radical turn. What battles have become crucialin World War II?
 English
English