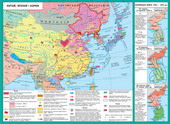
§ 31. China
1. Completion of civil war. Proclamation of China
China was the first country towere attacked by hostile countries (Japan 1931). World War IIsomewhat consolidated various political forces in the fight against Japaneseaggression over time were each armed struggle.The end of World War sharpened the differences between the CPC andhomindanom в Combat
for power.
The Government of Chiang Kai-shek (homindan) longtime supported the USSR, USA, UK. He was one of the founders of the UN.China was considered one of the great powers. Homindan controlled a large China's territory and made a significant contribution todefeat of Japan. August 14, 1945 between the USSR and China signed a treatyof friendship and cooperation, also a series of agreements.
The main rival in homindanupower struggle was the CCP (Chinese Communist Party) and its paramilitariesPLA (National Liberation Army of China). CCP and PLA made a significant contribution toagainst Japanese aggression and, unlike homindanu, brought her consistentlyquite successfully. During the struggle with Japan, PDA, PLA suffered from attacksHomindanu.
Introduction of the Soviet Union in waragainst Japan, the defeat of the Kwantung Army, the establishment of Soviet controlSouth-east China, the beginning of the confrontation between the USSR and the West have made changes inarrangement of forces in China. Friction between the West and the USSR led to a change of tacticsSoviet Union.
Spring 1946 Soviettroops withdrew from Manchuria and the control of the territory wastransferred PLA, which also got a lot of Japanese trophyweapons.
October 10, 1945 between the CPC andHomindanom the Agreement on peace and national revival. But actuallythe agreement was before the truce decisive phase of the struggle for power.
Output Soviet forces unleashedHomindanu hand to extend its authority in Southeast China. In citieswhere Chiang Kai-shek troops entered likvidovuvalys local authorities createdPDA. Such actions have caused clashes between the army and the PLA Homindanu. In their actions ChanKai-shek relied on U.S. support, which ozbroyily his army. But the rapid successwas unable to achieve, and the fighting resulted in the long-running civil war.
After a year of brutal fighting PLAstopped homindanivskyh strategic offensive forces and went into counterattack(July 1947). In August 1948 - January 1949 PLA receivedvictory in three major battles: Lyaoshy-Shenyang, Huayhayskiy,Beytin-Tyantszinskiy. In April 1949 PLA forsuvala Yangtze, therebyChiang Kai-shek regime was put to the brink of defeat. Remains homindanivskyh troopswere evacuated to the island of Taiwan.
In liberated territory PDAcarried out agrarian reform, which provided support to farmers in the CCPcivil war. June 30, 1950 a law on agriculturalreform: likvidovuvalos landlordism, land handed over inproperty to farmers. But this led to division of land into small plots thatimpeded the modernization of agriculture. Realizing this, the Communists at once
after the start cooperating land distribution, which wascompleted in 1956
Proceeded nationalization of largeindustrial enterprises, banks, railways, foreign capital ownership. It washave a monopoly of foreign trade and controlling imports of foreigngoods. But the economy remained multistructural, not communists confiscatedproperty of those who supported them. Since 1956, through the purchase ofprivate sector has turned into the state.
October 1, 1949 Mao Zedong onTiananmen Square in Beijing announced the formation of the People's Republic(PRC). Established diplomatic relations with many European andAsian countries. In December 1949 Mao Zedong visited the USSR. February 141950 signed an agreement of friendship, alliance and mutual assistance. Westdid not recognize the new state - a place it held before the UN in 1971Homindanu representatives.

Mao Dzedun
In 1950, all continentalpart of China except Tibet, was released from Chiang Kai-shek troops whowere evacuated at about. Taiwan under the protection of U.S. and Burma. This was the beginningsplit China. Mainland China and the island went separate wayseconomic, social and ideological development.
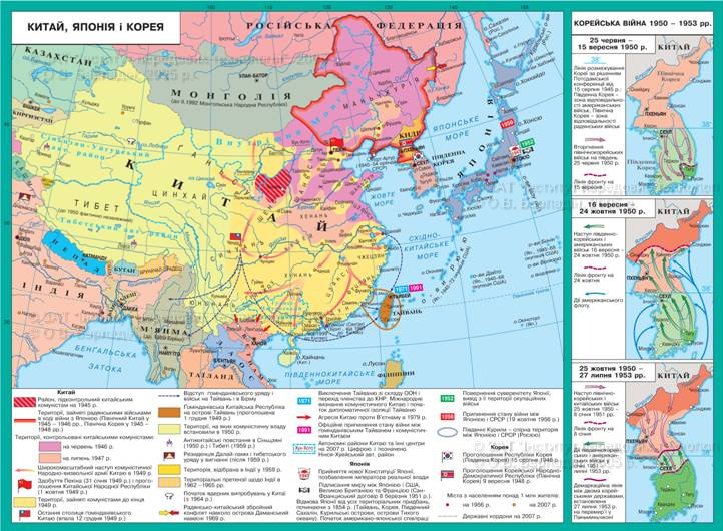
October 25, 1950 China armyenter the war in Korea, thus saved from the defeat of President Kim Il Sung regimeprice of 1 million Chinese soldiers.
2. The beginning of socialist construction. "Great Leap"
Since 1953 China was takencourse of industrialization and nationalization of private property, which wascompleted by the end of 1955 First Five Year Plan was successfully implemented(1953-1957 years). China provided significant assistance to the USSR. An 250 enterprisesand trained 20 thousand specialists.

Chinese posterera "Great Leap"
In February, 1957 Mao madespeech on the correct resolution of contradictions among the people ", where thebalanced set of proposals on China's socialist path. Butin mid-1958 Mao, building on progress made with the first five-yearinitiative to speed up economic development and make a "bigleap "towards a communist society. Before and afterdeclaration of policy "big jump" opened wide companyagainst "right-leaning (some figures accused in cpccommitment to the capitalist path of development for which were subjected to repression). Mainmeans of building a brighter future was to become communist, that isfree labor under the slogan "Three years of hard work - 10 thousand yearshappiness. "Instead, agricultural cooperatives were created"People's communes, which brings together 20 thousand peasants. In these communes everything, including homesteadususpilnyuvalos area, introduced the principle of egalitarian distribution. Life peasantswas strictly regulated: they paradego to work, ate together indining room.
In industry, it was decidedaccelerate industrialization. The country was expanded by increasing the mass movementproduction of iron and steel. The whole country was covered with primitive clay"Blast furnace".
At the same time were greatly influencedmade in foreign policy. Seeking to accelerate the development of China, Mao Zedongfelt the need to accelerate the worldwide revolution. He believed that the forcesSocialism is enough for an attack on capitalism and for its destruction can bedonate millions of people. Such a foreign policy led toPDA polemics with the CPSU and, ultimately, the gap between the USSR and China. Both sidesaccused the other of departure from Marxism-Leninism.
Meanwhile, the "bigjump "collapsed. Industrial and agricultural productiondecreased. There was a great shortage of essential goods, people livedfrom hand to mouth. In 1959 Mao heard the criticism.
Since 1960 by 1965 inChina followed the process of elimination devastating consequences "big jump".The country returned to normal
gradual development of the economy. But Mao saw the termination of the greatjump "just breaking and insisted on the correctness of his course. Incountry and the party have a real opposition to his course. At this time Maoreturns to the idea of strengthening the class struggle in the way of building socialism.This is the basis for deployment the country's "Great ProletarianCultural Revolution.
"Great Leap"
|
Measures "big jump"
|
Results of the "great leap"
|
|
Ideological fight "right-leaning" in the party.
Free work under the slogan "Three years of hard work - 10 thousand years good luck.
Instead of agricultural cooperatives were created "people's communes" which brings together 20 thousand peasants. In these communes everything, including homestead ususpilnyuvalos area, introduced the principle of egalitarian distribution. Life peasants was strictly regulated: they parade went to work, ate together in the cafeteria.
Acceleration industrialization. The country was expanded by increasing the mass movement production of iron and steel. The whole country was covered with primitive clay "Blast furnace".
"Push" "Acceleration" of world revolution. The deterioration of Soviet-Chinese relations.
|
Beginning political repression.
Breakdown agriculture and industry.
Disorganization economic life.
Ideological confrontation between China and the USSR, which later led to the break.
Distribution in Third World Maoist communist parties that are deployed armed struggle against the existing regimes.
The split in socialist camp.
|
3. "Cultural Revolution"
In 1957 Mao Zedong put forwardidea of class struggle in socialist society. In 1962 heput forward the idea of sharpening class struggle and the continuation of the revolutiondictatorship of the proletariat. The main enemy was proclaimed a national and internationalrevisionism (view Marxist-Leninist doctrine to its vyholoschennyarevolutionary). To combat revisionism in 1965 Mao called for"Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution. "CulturalRevolution, which started in 1966 was focused on what to remove fromParty and state leadership of all who disagree with the policies of Mao, China to imposescheme of "barrack communism" (spread the slogan: "throughoutcountry to learn from the army ").
Group has been established in cases"Cultural revolution" (GOR): Chen Boda - secretary of Mao Zedong, Jiang Qing -Mao's wife, Zhang Chuntsyao - Secretary of the Shanghai City Committee, Kang Sheng - SecretaryCPC Central Committee, oversaw the state security organs. Developing personality cult of Mao Zedong.
In the struggle with the opposition, which hadconsiderable support in the party and state apparatus, Mao relied on the youthassault troops hunveybiniv (Red Guards).
With cards hunveybiniv (1966)
"In alltheaters, cinemas, bookshops etc. should be placed portraits of MaoTszeduna1
Old habits must die!
It is necessary to eliminate high-class restaurants!
The slogan should write the red, not gold letters!
Studying Mao Zedong's works should begin in childhoodgardens!
Intellectuals should go work in the village!
It should eat together and restore morality firstPeople's Commune in 1958!
Should stop using perfumes, jewelry,cosmetics and clothing non-proletarian character!
It should eliminate first-class railway carriages andsaloon car!
Do not make photos that promote so-called femininebeauty!
It should deal with an old painting that abusednon-political topics, pictures of bamboo trees! Not be allowedthat picture did not correspond to the ideas of Mao Zedong! "
Classes at schools and universities werestopped, persecution of intellectuals began, members of the party committee. Inprimarily hunveybiny defeated Beijing University. Behind it beganpogroms and these universities. With special hatred hunveybiny treatedteachers and all the other "ochkarykiv. They were beaten, taunted them over. At the Schoolfoci were arranged with the bourgeois "books, records, fashion and cultural itemsvalues. Hnodminnym attribute hunveybina was a small book with Scarletquotations from Mao's speech. They all wore the same paramilitary uniforms.On the 9 th eighth plenum of the CPC Central Committee called for the convening of Mao against'Bourgeois headquarters, asked to completely defeat orparalyze the activities of senior centers and local party organizations PDAsPeople's Committees mass organizationsworkers, and create a new revolutionary government. And the challengecope hunveybiny and similar things tszaofaniv groups (rebels) to facilitate"Cultural revolution" in the working environment. Early1967 Company expands to seize power and hunveybinamytszaofanyamy. Such actions gave rise to chaos and mass
violence. Having achieved his Mao to calm turmoil in late 1967was uses against hunveybiniv andtszaofaniv army. As a result, 10 million young people were sent tore in the village. However, the win was not complete. Mao wastyahotitysya influence longtime ally of Lin Biao, who was appointedsuccessor to the leader. Attempts to remove him from power led to attemptsBiao supporters to stage a coup. But the coup failed and the conspiratorskilled in plane crash (September 13, 1971) in Mongolia(MNR).
Getting rid of the opposition party andpublic management, Mao decided to take control of the army. Thatneutralize the effect of Mao begins to restore the party and state bodiesevidence of departure from the original ideas of "cultural revolution". All that was achieved in the fight Mao consolidatedin the Constitution. Were rehabilitated some party figures who were subjected topersecution, among them was the future architect of Chinese reforms Deng Xiaoping. The country seemed returned tonormal.
However, not all that comfortable with.Mao's wife Jiang Qing and forms a group of his supporters - the "Gang of Four",as it was later called, an attempt to continue the policy of "cultural revolution"They opposed the moderate leaders of the party headed by Hua Hofenom. After Mao's death (9September 1976) broke acute power struggle in which victoryHua took Hofen.
Thus ended the tragic periodChinese history, whose victims were 100 million people.
4. Policy ReformsChina
At the Plenum of the CPC Central Committee in December1978 were taken from the course, called "fourmodernization: restructuring and transfer to the new base industryagriculture, military, science and technology. The ideological foundations of reformThe following principles are: socialist path of development, democratic dictatorshippeople, the leadership of the Communist Party, Marxism-Leninism and Mao Zedong's ideas. Reformsstarted in agriculture, and then were extended toindustry.
Policy reforms in China
|
The industry
|
In agriculture economy
|
|
·
to enterprises introduced self-financing and economic incentives to work;
·
encouraged individual labor;
·
created small private Enterprises in trade in services and light industry;
·
was introduced service in the industry.
·
to attract foreign investment to modernize Chinese industry, introduction new technologies and training of qualified personnel created free economic zones.
|
·
land communities equally divided between peasant families and transferred them to the property;
·
created family row;
·
since 1984 Villagers allowed to sell products on the market remains after state order;
·
increased public prices;
·
A network of small agricultural product processing enterprises and utility industries.
|
Economic reforms have givensignificant increase in production (8-10% per year). China holds superiority incement, coal, cotton, grain and meat. In the consumer marketThere are countless numbers of products that were previously absent. China becameone of the largest exporters. Improved living standards. Bygross national product China yielded only the U.S. but withper capita is in last place.
Feature of Chinesereforms is that they have affected the political sphere. In China, remains in powerCommunist Party. Attempts to raise the question of the democratic forces of politicalreforms culminated in the bloody tragedy in Tiananmen Square in 1989,when it was dispersed in the bloody battles of students (about 2 thousand people diedpeople.).
An important event in the developmentChina was the transfer of power of the older generation younger managers thattook place in 2003 The new leaders of China are: President of China - HuJintao, President of the National Assembly of China - In Bangui, Head of the State Council - Wen Jiabao

Chinese Architect reforms Deng Xiaoping
Since Deng Xiaoping's opening speech at the gathering XII PDA (1 September 1982)
"80-years -most important period in the historical development of our Party and state.The acceleration of socialist modernization, reunification,including unification with Taiwan, the struggle against hegemony, for the preservation of peacearound the world - the following three major tasks facing the Chinese peoplein the 80's. The basis of these three problems is economic construction, itkey to resolving the external and internal problems of the country. There was a longtime, at least during the last 20 years the present century, weneed without weakening efforts to complete the four cases: the restructuring of the governingStaff and reform the economic system revolyutsionizuvannya, rejuvenation andarmament general and specialized knowledge workers staff numbers,construction of socialist spiritual culture, cessation of criminal activitieseconomic and other areas that undermine socialism; orderingstyle of party and party organizations in-depth study of a newCharter Party. In this most important key to upholding the socialistway and mobilize all forces to carry out modernization.
In an interview Deng Xiaoping (6 October 1984)
Revive the economy before we startedall from the village. For here live 80% of Chinese population. The stability of the Chinesesociety and the development of China's economy primarily depends on the developmentvillage and improve the lives of peasants. Increased annual production of 4times depend primarily on the fact whether those 80% of the population achieve this increase. As is now cleara number of new approaches to the village brought success, the effect they give fast,visible results. Previously the village had to tight. Now we can say thatlarge majority of the rural population eats plenty and dressed better,living conditions are much improved. Effectiveness of policy towards the villageinspired us to increase gross national product to 4 times, strengthenedour confidence. "
5. Foreign policy in China
The coming to power in China the CCP wasimpossible without the support of the Soviet Union. This gave Stalin a pretext to considerChina as its puppet in the cold war. Participation of Chinese troopsthe war in Korea is closely tied to the Soviet Foreign Chinacourse. Moreover, Stalin treated condescendingly Chinese leaders (in terms of their"Friends" he called Mao Zedong "margarine Marxist"for his views on the peasantry as a driving force of the socialist revolution).
Nothing new, but deteriorationrelations in dealing with China, is introduced and Khrushchev, who considered China as"Little brother". The first misunderstanding between Mao and Khrushchev emergedafter Khrushchev's report at the XX Party Congress, where the latter denounced the personality cultStalin. Second - following a meeting of communist parties in 1960, where the Communist Partywas proclaimed vanguard of the communist movement. These and other misconceptionsgradually led to the aggravation of interstate relations.
Sino-Soviet negotiationsBorder issues have come into a angle. From1964 started escalating military confrontation between the two countries.Confidence Chinese leadership provided by Chinese scientistsatomic bomb (October 1964) and their advantage in manpower.
In 1964, held in the USSRchange in leadership. But relations with China continued to escalate. In1966 between the USSR and Mongolia, signed the agreement on friendship andcooperation. According to him were introduced in Mongolia of Soviet troops. Chinaresponded by increasing forces in the north (in 1967 in Manchuriawas concentrated 400 thousand groupsChinese troops). The crucial moment came in 1968 when the Chineseleadership was worried about a repetition of Czechoslovakoption "against him by the USSR. intensively China began to prepare forWar the Soviet-Chinese borderall the time there were armed clashes. The most dangerous place on the islandDamanskyy (June 13, 1969) and near the town Zhalanashkol (Kazakhstan 1913August 1969 r). Clashes on the border of the USSR General Staff urged to developplan preventive strike on nuclear facilities in China. But realism took the hill andpolitical conflict has been repaired by peaceful means. Between the USSR and Chinabegan negotiations that continued intermittently for 80 years.
At the end of 70 years, China and the USSRagain faced a threat of war, which was caused by Vietnam-Chinaconflict over Cambodia. In 1979, China carries out the attack on Vietnam inVietnam's lesson to give leadership. In response to the USSR its pidtyahnuv Chinese troops to the border, as part ofknocked over in Vietnam. Chinese troops were defeated, and conflict aroundCambodia was repaired by peaceful means.
In confrontation with the Soviet Union Chinafinds support from the U.S.. January 1, 1979 between China and the U.S. wererestored diplomatic relations and established trade links.
After years of mutualhostilities and military confrontations (ozbroyuvaly U.S. government and supported Chiang Kai-shek,in 1958 threatened to use nuclear weapons against China, transmittingpolicy between the two Chinas) early 80's American-Chinese Relationsthe road of rapid improvement. In the military-political field they are,relatively short time transformed into a strategic interaction. United States, rejectingideological biases, went on cooperation to gain extra,strong trump card in the confrontation with the USSR. Similar motives and run by Chinesemanagement, considering the USSR as enemy number 1.
In 1982 China refuses tothe policy of confrontation with the USSR. And the USSR in 1983 announced its intentionnormalize relations with China. The Chinese government set a number ofpreconditions: the withdrawal of Soviet troops from Afghanistan and Mongolia;Vietnam withdraw its troops from Cambodia.
In 1989 these obstacles wereeliminated and the visit of Gorbachev to China. Between the USSR and China wereconcluded a new agreement on border, but not eliminated all conflicts betweenparties on this issue.
Important role in productionChina's foreign policy played a theory of Mao Zedong's "worldRevolution "and" three worlds ", spread 60-70 years in Maoistparties in different countries, especially least developed, which startedarmed struggle against the existing regimes in these countries.
Now China, being a constantUN Security Council and "nuclear club", plays an important role inglobal politics, especially in the Asia-Pacific region. Importantachievements of Chinese foreign policy was decolonization in China(Hong Kong (1997), Macao, 1999), the country'sWorld Trade Organization (WTO). One of the main goals of foreignChinese policies - is to gain accession Taiwan Island and providestable economic development.
China is the second Russiantrade partner of Ukraine. This causes great Ukrainian-Chinese relations.In 1995, 2003 China paid an official visit PresidentUkraine. During the visit, were outlined long-term plans of development of relationsbetween countries and signed several agreements. Repeatedly came to UkraineChinese delegation.
6. Taiwan
The emergence of the issue of Taiwan is closelyis due to the "cold war" and fighting the Communists for power.
I wonder
Taiwan - an island in East AsiaTaiwan separated from mainland (Formozkoyu) Strait. BySymonosekskym contract in 1895 China, after losing the war, gaveisland under the jurisdiction of Japan. During the Second World War in 1943 wasKairskoe signed, and in 1945 - Potsdam Declaration on returnIsland of China. May 25, 1945 Taiwan was officially incorporated into theChina.
Having suffered defeat in the CivilWar remains homindanivtsiv (650 thousand people.) entrenched on the island of Taiwan andadjacent islands under the protection of U.S. Navy and Air Force. The split of Chinaby ideological principle causes tension in the Asia-Pacificregion to date.
In December 1954 signedTaiwan-US joint defense agreement. Crisis of 1958 inrelations between China was the most dangerous. She has been involvedlarge state and there was a threat of nuclear war. By the early 70's between the twowere carried out by the low-intensity warfare in which took part in the mainair force and navy.
Leaders homindanu, being inFr. Taiwan and come to terms with the loss of opportunity to restore its power incontinent, focused on building their own state on the island. To1971 Taiwan held China's UN seat, which gave the opportunity to influenceworld politics and the public. But with the loss of seats in the UN was in Taiwaninternational isolation. In addition, in December 1978 U.S. had toaccept the three principles put forward by China establishing diplomaticrelations. These include breaking diplomatic relations with Taiwan; cancelTreaty on the common defense and the withdrawal of American troops from the island. OfficialTaiwan has diplomatic relations only with some countries: South Africa, Chile, Israelet al. This reflected the international status of Taiwan and domestic life. Incountry was established one-party system - Homindanu Party, headed bycontinued to remain until his death on Chiang Kai-shek. Dominant in the countryplayed by the military. In the early years of Taiwan States United States provided itsubstantial assistance, but once the island's importance in the global confrontation with theUSSR fell, Taiwan was in a quandary. This was theeconomic reforms aimed at developing export industries. The State shallcontributed to the development industry - built large metallurgical,metalworking industry has been developing shipbuilding, etc. Throughattracting Japanese experience and technology began rapid development of electronicindustry and household appliances. Economic growth reached 10%year. Taiwan along with the Republic of Korea, Hong Kong (China became a member in1997), Singapore was one of the most developed countries of the region thatcalled "Asian tigers". According to its economic development theyeven outperformed some European countries. Income per capita in Taiwan onTop 90's was 13 thousand dollars.
In early 1996 Taiwanwere held the first democratic presidential election. They became Denhuey Lee.On the eve of the elections took place deteriorating relations with China.Mainland China has decided to make pressure on Taiwan and thusaffect the results. However, this did not help. Because it talks aboutassociation of the two Chinas were interrupted and not restored to the present day.
90 years in developing countriescharacterized by viewing the entire foreign and domestic policy. Dominanthave views about the refusal of ambitious plans and their independentRepublic of Taiwan. In elections in 1999 not the first time elected "presidentChina, as it was before, and the president of Taiwan. In this election winnerRepresentative of the Democratic Progressive Party (PPP) Chen Shui-bian, supporterindependence.
May 20, 2004 Taiwanheld new presidential elections and the first ever referendum. Voterswere asked two questions: 1) whether to purchase a new air defense system to counterChinese missile threat, and 2) whether to enter into negotiations with China.
In the election of Chen won again, andthe referendum was declared invalid because of low turnout.
Results
Completion of the Second World Warbrought peace to the territory of China. In a country with a bang erupted civilwar that ended in the early 50's ended with the victory of Communists,but led to the separation of Taiwan, where authorities kept Homindan. Communistsbeating on mainland China resorted to communist transformations.Gradual did not work for the country's leadership headed by Mao, they startedspeed up processes. Experiments with the construction of communism ("The Great Leap""Cultural Revolution") costs of the country: hundreds of millions of people, almostruination of the country. Since the late 70's China's leadership understoodprevious errors come from a radical economic reform, which gavephenomenal results.
Questions and tasks:
1. When was the proclamation of the PRC? What contributed to the victory of Communists in the civilwar?
2. What were the first measures of communists?
3. Why politics "great leap" has collapsed?
4. What is the purpose of "cultural revolution"? Whether she has it?
5. What impact has "cultural revolution"?
6. What caused the implementation of policy reforms in the late 70 th century.?What tasks has set itself the Chinese leadership since the reform?
7. What reforms have been undertaken with agriculture?
8. Describe the results of reforms?
9.
Fill in the table: China's Foreign Policy
10. What is the problem of Taiwan?
 English
English