§ 9. Studies of Ancient PopulationEgypt
1. Irrigation farming
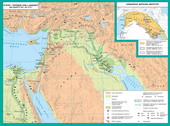
BasisEgyptian wealth was agriculture. But in hot climates andlack of rain (they dropped very rarely) Egyptian agricultureentirely dependent on the Nile spills. Gradually, the Egyptians have learned to raise the waterto plots of land in the years when the water level during flood was low. Ifwater were many and they threatened to flood the field, it took away. For thisEgyptians built the canals, which gave an opportunity to expand the area suitable foragriculture.
The firstinformation channels reach XXII-XXI century. BC The longest of them reached2 thousand km. Occupy the land in the desert Egyptians helped ramblingmechanisms.
HeightEgyptians in the Nile water was measured using «nilomiriv» – structures of stone,within which there were special devices.
Forlifting water from elevated areas XV. BC Egyptians beganuse «shaduf».
The device looked like a crane near the well in the Ukrainian villages. Shaduf looked like forked bearing with an attached longpole, one end of which was stoneon the other – skep water. In IV. toBC began to usespiral screws у cylinder thatraised water. Later thisdevice named "Archimedes screw. Then forused mechanical lifting water wheel.
I wonder
Year of the Egyptians divided into three seasons of four months. Flood season (19July - Mid November) - "ahet"then release the water season (mid November - mid March) - "Mo"And the season"shemu- Harvestingharvest (mid-March - 19 July).
Document
With prayers of ancient Egyptians to the Nile
... Thank you, NileThat comes in peace. To datelife of Egypt, ... waves spill on your gardens, which created the sun, youeverything quenches seeking heavenly moisture when you spustyshsya on the ground, her godgives the grain and simmer work in the workshops. You - the maker of wheat and barley,you hold the temples ...
Questions to the document
Why Egyptians sought the prayers to the Nileand called him "the creator of wheat and barley?
Cultivationland was important to the Egyptians so that plowing in November when the waterdecreased, began personally Pharaoh. Originally cultivated land primitive plow.Then it rozpushuvaly hoe and breast broken mallet. Hoesmade of wood, later - with the metal. In the delta of grain were sown directly inbar, then drove the cattle, which vtoptuvala it.
Harvestcollected in March and April by the sickle. Kolosky cut stems in the middleand tied in bundles. In the current animal (sheep or donkeys) hooves obmolochuvalyears. Part Threshed grain remained in those cultivated land, andanother for next year was kept in temples and royal granaries forfuture planting. Stocks used for food if the year was off.
Egyptianscultivated barley, flax, wheat, garlic, cucumbers. From wheat bread and bakedprepared beer.
CultivatedEgyptians also grapes and horticultural crops. Centers and Winewinemaking were Nile delta and oases. Manufacture of white and red Egyptianswine, which added honey and spices.
Tirelesswork of people, warm climate and Neil did breadbasket Egypt Ancient East.
2. Crafts
InAncient kingdoms day achieved significant development of handicrafts. This is evidencedPictures in Egyptian pyramids, which depict carpenters, masons, shoemakers,weavers, blacksmiths, potters and ceramics of ancient masters, later foundarcheologists.
Jobartisans was aimed at satisfying the everyday needs of both rich andpoor Egyptians.
Oldtype of craft was weaving. Informationabout it occur in Egyptmyths. It was believed that invented it and taught him the craft goddess people Isis. Weaving climax acquired during the period New Kingdom (1552-1069 years BC.AD).
In thiswhile the Egyptians learned to produce high quality fabrics of linen and paintthem. Clothes made of linen only. Other materials were considered unclean.Common colors were red, blue, green, but favorite colorremained white.
Highlevel reached in ancient Egypt pottery.Seized craft people started to merge nomivin one state. Originally potters clay mixed with water. Then they vymishuvalyher feet, adding strength to the straw and sand. Then come to clayon the potter's wheel.
Underskilful hands of craftsmen, it turned into bowls, cups, jugs and otheritems needed Egyptians in everyday life. Finished goods and decorated prosushuvalydrawings. Ended process of burning in brick kilns.
Egyptianscould well handle the stone, wood, glass manufacturing, were well aware of metallurgy and forging. Gradually they learned to smelt copper from ore andtin. The Egyptians also plavyly gold deposits which they opened in the Nubiandesert. Molded in metal ore in the furnace. In early ancient kingdom whichexisted in the era of copper and bronze and stone tools were gradually replacedcopper. Later, when the Egyptians uncovered the secret of making bronze and treatment,tools were mostly bronze. Crafts werevaried, but always simple. The most sophisticated carpentry and consideredcarpentry tools like axes, chisels, etc.. Blacksmiths in their workused hammers, tongs.
3. Hunting and fishing
UriznomanitnyuvalyEgyptian food by hunting. Depending on who huntedused various means. The most common was a big bow. To huntcrocodiles and hippos used pulls. Besides meat, valuable sourceEgyptian food was fish. In the waters of the Nile was known for some catfish, perch, mullet, carp,eel and so on. But in some nomah certain species of fish wereforbidden to eat, because they are considered sacred. Sometimes this led to militaryconflicts with nomamyWhere the fish used.
ForFisheries Nile Valley residents used various tools. In the tombimages showing scenes of fishing nets, conventional hooks, harpoons,moments. Harpoons made from bone. Used as rods with hooksof bone and bronze. Fishermen usually located on the banks of the Nile, butfished with boats. So Egyptians gradually mastering wealth Riverand learned to swim through it.
Egyptiansbuilt small boats from papyrus and large barges, carrying bouldersweighing several hundred tons. Over time, they are learning the art of building largeships moved by sails and oars, learned to swim in the openSea. Their journey, in particular, depicted in relief in the temple of Queen Hatshepsut in Deir el-Bahri.

Egyptian ship
Byboats using the river during the flood people get to towns and villages inislets. Neil was a way that combined all parts of the country and helpedcommunicate with neighbors.
Ship Pharaoh Cheops has a length of 43.3 m and width up to 5,6 m. The boat was the appointmentchenyy to transport the deceased pharaoh in zahrobtional life. Boat designperformed at nosingle nail - only the rope fastening.
Questionand objectives
1 What the natural characteristics of the Nile River usedyehyptyany in their favor?
2. Why is Egypt called the "gift of the Nile"?
3. Why the color of water in the Nile during the flood changed?
4. When in Egypt, the first farmers?
5. Describe how ancient Egyptians cultivated the land.
6. What devices are used for artificial irrigationfields?
7. What crafts were common in ancient Egypt?
8. Describe the work of the Egyptian potter.
9. Explain why the methods of cultivation land for the Egyptiansthousands of years were very simple (vtoptuvaly grain picked primitive plowsoil obmolochuvaly by animals, etc.).
 English
English