§ 10. StructureEgyptian society
Egyptiansperceived the person as a small part that holds its own clearly defined place inlarge public body. Farmers provide foodentire country. Craftsmen produced items of everyday life, the workers workedthe construction of temples and pyramids. Pystsi considering the size and Harvestdetermined taxes. Pharaohmilitary officers and priests led the entire state system. Belonging to the residentor other groups determinedwork he performed. But even the farmer or artisan, having the abilityhis education could become pystsem, officials and priests.
Terms and Notions
Tax - Cash orpayment for the maintenance of natural state.
Stratum (Orsocial status) of the population - of people with clearly defined rights andresponsibilities.
Hierarchy - Division of societyin groups (social conditions) and the situation of subordination insociety - higher.
1. Pharaoh and officials
OnPharaoh was the head of state. Below the pharaoh position in the social hierarchyoccupied policymakers. Typically, Pharaoh appointed to these positions and their sonsdaughters or other relatives. Among the distinguished principal officials "Minister" – chat. He held the highest administrative position in the country andreported only to Pharaoh. Here were the rulers nomiv.On their shoulders all implies a very complex system of construction managementpyramids, canals, irrigation systems, the overall life of communities that were part of nomiv. Host led military leaders.
2. Priests
AlmostEgypt every city having its own gods. They built temples honor thatcare of priests. The highest position was considered a High priest – servantsgod. Him often was Pharaoh himself. The next step occupied priest who ruledtemples. High priests obeyed the so-called lower priests – uabu. They performed daily rituals, care ofAs the church and the needs of the gods. Among uabustand out: the priests-astronomers who observed the stars and tried toprophesy the future, priests who followed the daily routine of the temple; readers thatprohovoryuvaly holy prayers; papyrus scribe; economic executives whocare of agricultural land, libraries and others.
3. Pystsi
Validofficials were pystsi. They had many duties: recorded decisionsadopted by the Pharaoh, defined level of water in the Nile during the flood and in reservoirs.Also pystsi had to check the fields beyond the river after the spill,harvest accounted for monitoring the number of cattle, wine, etc..Sometimes they made the agreement, wrote private letters, recorded ritual wordsand prayers. On their shoulders were going to identify and collect taxes.
Situationman who knew how to write in society was high because it was literatebit, and writing was very difficult. Pystsi always carried with him supplieswriting: wooden planks with paint, a vessel with water for their breeding andcane sticks, and that nakreslyuvaly characters.
4. Peasants and artisans
The vastinhabitants of ancient Egypt was free to farmers. They are unitedfor soil "slogan, construction and use of irrigation systemscreating agricultural communities. That farmers cast a large number of shaftsmandatory work: built pyramids, palaces, tombs. Another theirduty to the State Department was in the army of Pharaoh. An important link in publiclife were craftsmen who provided the people of Egypt with all necessary.
Document
Biography swept
[Heritage received Swept.] It was given to himestate of his father InpuemanhaJudges and pystsya: no(No) grains, (no) assets of every home, as were men and flocks.
[Career swept.] He was appointed first secretary of food storage,Property chief food storage ... was nomarchBovine tionAfter (a) a judge of bovinehim ... was appointed head of all royal linen, it wasappointed governor of ... settlements, the ruler of the great fortifications ... nomarch Sayisa...
Questions fordocument
What could be achieved in ancient Egypt and pystsya descendant of a judge? Give youropinion.
Terms and Notions
Army - Militaryorganization that served to protect the borders of the country from enemies and attacksto capture new territories.
Trophy - Property andprisoners captured in war.
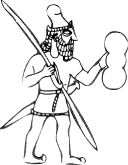
5. Warriors of Egypt
ArmyAncient Egypt was composed of infantry and combat chariots. Army of Pharaohscollected as needed. Sometimes the army consisted of several thousand people, and sometimesreached tens of thousands. The army recruited from the peasants. It coming in one ofhundred adult males. Army commanded by senior officers. The main tasktroops were guarding the borders of the country.
Byduring the New Kingdom became a professional army, its soldiers were based, whichbeen in military battles and skirmishes. For their service they received slavestrophies, plots of land. Often the Egyptian army posylyuvalosya mercenariessuch as the Nubians, who lived in the south of the country.
EgyptianInfantry was the basis for war. During the New Kingdom it consisted ofeasy- and man- soldiers.The first skill oruduvaly bow and arrow. Second ozbroyuvalysya slight crescent orheavy straight sword. Widespread were short spears and javelins for throwing – darts.But the weapon remained bow. Egyptian infantry had protective armor thatconsisted of a sack, which wrapped the body, leather or bronzehelmets. Body protecting shield which had a rounded top. Infantry was divided intolarger and smaller units – number 250 and 50.

Egyptian troops
Chariotappeared in Egypt during the New Kingdom. they were made of wood, and they were extremelylight. Chariot weighed only 34 kg. Thus, it could raise even oneman.
Onchariots were two soldiers. One managed it, the second – destroy enemiesshooting with the bow, throwing darts or applying during dogfightcrescent sword or ax. On the right hand of a trooper was assigned shield thatand defended him, and warrior. Cabbie had a helmet and long coat with bronzepads. A warrior was bound to the chariot leather belts, and so bothhis hands were left free to warfare. Sometimes bright chariotdecorated. The most luxurious was always Hieroglyph Chariot CombatPharaoh. its bright colors painted on a gold background.
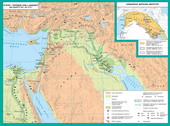
Forborder security of the country built the fortress, but only in the north and the south.From the west and east of Egypt was protected by rocks and deserts. EgyptianFortress had a circle, square or rectangle and defended trenches. Nearwith walls built tower with a ground for soldiers.
Oneexample of engineering art of ancient Egypt is a fortress Abydosin Upper Egypt. It was rectangular in shape with sides 125 and 1968 m. Height of wallsreached 11 m,and the thickness is 2 pm
6. Slaves
Servants havecalled "living dead" or "live for the murder." The name suggests thatinitially they were prisoners of war. Slaves could also become impoverished farmers bydebts on time, and criminals. Most slaves used on heavyworks in agriculture, mines, military. Slavery was not always lifetime. Rabi-mast foreigners get freedom, enteringto the army. Egyptian peasants, who are in slavery for debt, became free,vidpratsyuvavshy them.
Questions and Tasks
1. What in ancient Egypt werepriests?
2. Tell us about the main dutiespystsya.
3. Describe a day in the lifeEgyptian farmer.
4. What are the parts includedEgyptian army?
5. Using text describe ancient Egyptian fortress.
6. Why ancient Egyptian societyThe Society would be able to without Pharaoh priests pystsiv,officials, soldiers, peasants?
 English
English