§ 52. City of Rome and the lifeits inhabitants
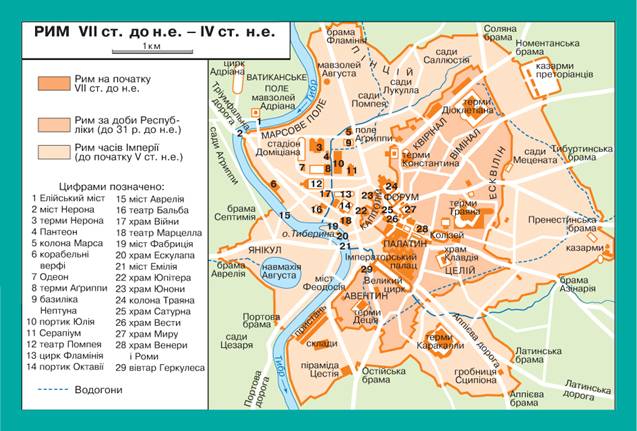
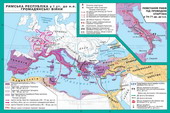
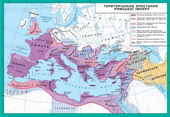
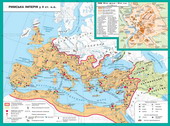
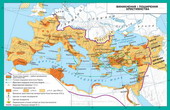
Rome VII art. BC - IVArt. BC
1. Eternal City
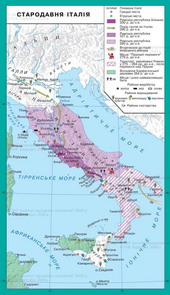
At the beginning of II century. BC Rome from a small village farmersturned into one of the largest cities of the ancient world. "Eternal City"Popularly known as Rome, situated on the banks of the River Tiber on seven hills. The mainof them is Capitol, Palatine,
Kvirinal. On top of Capitol Hill roseTemple of Jupiter. On Palatine Roman palaces wereemperors. Between the three hills extending central area of Rome - ForumRomanum. On both sides of the board at different times werebuilt temples devoted to gods and public buildings - the Basilica. Insidebasil held hearings concluded trade agreements. Onposts at different times establish monuments and sculptures. Forum was the placepublic meetings, so here towered platform for speeches and announcements of speakersgovernment decrees. From the Capitol Hill area approached to housepublic repository of documents - Tabulariy. This - the oldestbuilding of Rome, which remained until today. A little further down the slopetemples were located Concordia (Concord) and VespasianErected in an era of empire. In northwestern BoniForum II art. BC built the Basilica Emilia Consul(Basilica had addressed a political or public figure, the initiative whichtheir building). Along with her building housed the Senate. On the opposite sideforum were Julius Caesar's basilica, built in the first century. BCand temples dedicated to gods.
A sacred road passed through the forum, which combined Palatynskyyhill withCapitol. This road wastriumphal arch erected in honor of taking Tytom Jerusalem.

ArchEmperor Titus
Because of population growth between Capitoland Kvirinalom build additional forums. Onlargest of them - the forum of Trajan - located on the same line squareyard with equestrian statue of the emperor and the largest Roman basilica Ulpiya. Major public buildings of Rome - circuses,stadiums, amphitheatres built in the outskirts of the city.
From outside the city stretched Aqueduct, which provided it with water. Life-givingmoisture filed to 400 fountains, which served as pits.
The Romans created a new type of private accommodation - atrium. For heating homes and Romans used watersteam heating. Between empire built multi plebeianshouses - insulin, and for the rich - the palace,suburban villa.
2. The Rome community
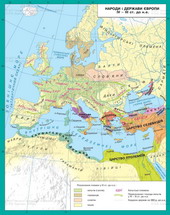
The structure of Roman society was complex. It was divided into patriciansand plebeians, free and slaves. Free is divided into kviryniv, Latin, perehryniv і freedman.Kviryny had title to landagreements, to vote in the national assembly and the right to hold office.Latina had limited rights. Perehryny - Foreigners -rightless were, but over time could be eligible if they were in the care kviryny. Freedman although considered Romancitizens, but only had the right to conclude trade agreements.
Slaves-slaves also were divided into groups. The worst was the situation of thosewho was taken prisoner in arms. Slaves allowed to participate in religiousrituals. There was a tradition of releasing slaves to freedom. But in general slavesconsidered "animals that are able to speak.
I wonder
During its peak in Romepopulation about 1 million people. To solve the transport problemoverpopulated cities, Julius Caesar banned citizens to use their owncarts. Rich people carried on stretchers or they moved topublic "taxi", which had a special counter for payment.
3. Daily LifeRomans
Day of the Romans to start at third (for our time at the ninth) in the morning. Romanhad breakfast with bread and wine, cheese and sometimes honey. Then went on their cases: the school,to court or to the Senate. Wealthy citizen took the poor, handing them foodand money, hoping that his support during the elections. Dinnercold and hot dishes, fish, bread, wine. In the afternoonrozpochynalasya siesta - the holidays. Work stopped in all institutions.Locked churches, merchants' shops. Exceptions were the only meeting of the Senate andCourt, People's Assembly. Sometimes slaves also continued to work in the field. After a siestaRomans played sports, went to term, trained at the Mars field. ThenRomans supper.
His favorite pastimes were fights Roman gladiators and chariot racing.Tens of thousands of Romans were going to the amphitheater to see how the gladiators,carted from different provinces, killing each other or fought with the predatoryanimals - lions, bears, bulls. Sometimes gladiatorial combat lasted forsix months. The fate of defeated gladiator decided by the audience. Thumbshowed that down meant death raised up - life. Having won manybattles, slave-gladiator could get nothing.
Roman House (Domus). Romans lived dependingof wealth or insulinOr in a palace, or inatrium. Atrium - a wealthy Roman house - had a courtyard, surrounded onfour sides of a covered colonnade (it was called relay).In relay among flowers and fountains family spenttheir free time. As part of the house were the library and Oikos - A large hall for receptions. In that building over time the floorbegan to cover the marble tiles, and then the mosaic. The walls were paintedfrescoes. Ceiling decorated with gold and ivory. Zaminyuvalosya andfurnished rooms: instead of the old oak furniture, wood furniture appearedvaluable species that zavozylasya from the East. Along with the wealthy household itemsRomans borrowed from Greece and the East as fashion and customs. Houses surroundedwalls. Outside the wall hung a bell, which notify owners about the comingvisitors. On the threshold of a mosaic was contained the word "savle"- "Farewell", and sometimes - mosaic image of the dog.
4. Roman and familyParenting
The right to create a family was one of the fundamental rights of Roman citizens.Marriages other population groups were considered illegal. If the father was a citizen,and have latynyankoyu, the child had the right of Roman citizenship.
At the head of household was the father. He had tremendous power. The law allowed himkill children for three years, and if they had physical disabilities or ill health,even older. Women in the Roman family respected mistress of the house. A husbandcould hurt her with his own will. With some guilt, he could only judge the wifetogether with relatives.
Childbirth was accompanied by many rites. During onewith ceremonies father took the child in his arms, thus recognizing it his.If the father did not recognize the child, then left her outside and she coulddie or become a slave. After recognition spovyvaly baby and laid in bed. On8 th or 9 th day of the birth of a small Roman given name and gave differentamulets: a sword with the name of father, mother, named axes, images of stars,animals that are worn on the neck of a child. Difficult was the election of the name. Childjust got the name of the genus, it dodavalosya personal name. They are inLatin, there were about 20. In addition, there is also a nickname.For example, the poet Ovid had a nickname Nazon - Nosy,Nick Cicero meant peas.
Family traditions changed over time. In Rome during the empire was widespreadadoption. Zmitsnyuvalasya independence of Roman women. Marriage practiced ina woman becomes subject to the power men have been possible divorce.
Questions and Tasks
1. When the town was founded Rome?
2. How many hills it is situated?
3. Describe the structure and the main buildings of Ancient Rome.
4. What was the structure of the Romancommunity? Which of the worst housing for city residents?
5. Make a description of the everyday life of the inhabitants of Rome.
 English
English