Home
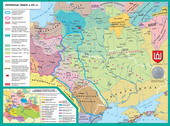
Lithuanian and Polish rule in Ukrainian lands
Plan presentation
- internal situation of Galicia-Volyn principality after the death of George II Boleslav.
- Entry Kyiv, Chernihiv-Sivershchyna, skirts to the Lithuanian state.
- Features social and political life of Ukrainian lands in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in the second half of XIV century.
- KREVO union.
- Galician and Volyn region after Krevsk Union.
Timeline
|
1340 |
Hike Polish king Casimir in Lviv. Start fighting for the Galician-Volyn land |
|
1340-1385 he |
reign in Volhynia Lubart Hedyminovycha |
|
1349 |
Hobby Polish king Casimir III the majority of lands of Galicia-Volyn Rus |
|
1362 |
Connect Kyiv, Chernihiv Pereyaslav and part-Sivershchyna to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania |
|
1363-1394 he |
Olgerdovich reign of Vladimir in Kiev |
|
1385 |
Conclusion Krevsk Union |
|
1387 |
final accession of Galicia to Polish Kingdom |
|
1392 |
signing of the Polish King Jagiello and Lithuanian prince Vytautas Ostrivs'ka Agreement |
|
1392-1430 he |
reign of Vytautas the Grand Duchy of Lithuania |
|
1434 |
Formation of Ruthenian region of Poland. The inclusion of Western Podolia to the Polish crown |
Persons
Liubard - son of Grand Duke of Lithuania Gedymin, after the death of George II in 1340 took the Galician-Volyn throne. Tue struggle for restoration of Galicia-Volyn principality.
Algirdas - son of Grand Duke of Lithuania Gedymin, Grand Duke of Lithuania (1345-1377 biennium). Reigned together with his younger brother Keystutom . After joining the majority of Ukrainian lands to Lithuania in Kiev planted autonomous ruler of his son Vladimir.
Keystut - son of Grand Duke of Lithuania Gedimin. Owned land in western Lithuania. 1345 Keystut expelled from Vilnius Yevnuta his brother and ruled the Grand Duchy of Lithuania along with older brother Olgerd.
Vytautas - Keystuta Hedyminovycha son, Grand Duke of Lithuania (1392-1430 biennium). Opposed conditions Krevsk Union, fought for political independence of Lithuania from Poland. According to the agreement signed in 1392 in jail, was found by Polish king Jagiello ruler for life Duchy of Lithuania.
Yahajlo - Olgerd Hedyminovycha son, Grand Duke of Lithuania (1377-1392 biennium) and king of Poland (1386-1434 biennium). After his father's death was Great-throne and began with his uncle Keystutom ruler of Lithuania. Soon the fighting broke out between them that resulted in death Keystuta. Krevsk Union signed in 1385 in 1387 and conquered Poland annexed to the Galician land. Founder of the Jagiellonian dynasty.
main presentation
1. The internal situation of Galicia-Volyn principality after the death of George II Boleslaw
Invitation to the Galician-Volyn table Lithuanian duke of Westminster
After the death of prince George II Boleslaw 1340 internal situation of Galicia-Volyn principality considerably worse.
-

 Due to the lack of successors to the princely family of boyars people there started looking elsewhere captain.
Due to the lack of successors to the princely family of boyars people there started looking elsewhere captain.
- choice fell on the Lithuanian duke of Westminster Hedyminovycha, who had a wife from a family of Galician-Volyn prince and how he felt, had a legal right to these lands.
Historians estimate - Board of Westminster in the Galician-Volyn land as a recovery state.
- However, their power could Liubard extend only to Volhynia, which was then virtually independent.
As for - Galicia , then Lubart power it was only a formality.
- real rulers of the earth was in Galician boyar Dmitry Dedko.
- He ruled in Galicia during 1340-1344 he on behalf of the Duke of Westminster. This state of affairs intends to change the Polish king, trying to connect the Galician land to seize it.
fight for the Galician-Volyn land between Lithuanian and Polish rulers
-

 Claims Polish kingdom in the land of Galicia were not new. Thus, the Polish king Casimir III , , the 1340 Lions attacked, just received the news of the death of Prince George.
Claims Polish kingdom in the land of Galicia were not new. Thus, the Polish king Casimir III , , the 1340 Lions attacked, just received the news of the death of Prince George.
- 's real war for land Galicia occurred in 1349
- Then the king of Poland with the support of their relatives - the Hungarian King Lajos (Ludwig) organized a big march in Galician-Volyn land, captured major cities, except for Luck, joined part of Galicia and Volhynia to the Polish state.
- Such developments seriously troubled Duke of Westminster, and he went to war against Casimir.
- War of the Galician-Volyn land waged with varying degrees of success. Yes, the 1352 Polish and Hungarian kings led army Belz, but could not take it and had to make peace.
- Liubard Hedyminovych next year, his vassals and allies continued their battle, won Galich and came to Poland. Later Poles again forced out of Westminster in Volyn.
-
 In 1366, during the new war, Belz withstood the siege of the Polish army, but the war consisted of Westminster to fail: he was forced to leave the Galician land, he lost much of Vladimir and Volyn.
In 1366, during the new war, Belz withstood the siege of the Polish army, but the war consisted of Westminster to fail: he was forced to leave the Galician land, he lost much of Vladimir and Volyn.
- died in 1370 Casimir III, became king of Poland and the Hungarian King Louis.
- Ukrainian territory, which would combat Casimir of Westminster, were ruled by Hungary.
- First Hungarian official ruled the earth, and with 1372 - a relative of Hungarian king Vladislav Opolsky sylezkyy prince, who called himself «master of the Rus land, and everlasting Didych autocrat » and coined their own money.
Meanwhile - Liubard was no weapon and in 1370 regained Vladimir. At the end of 1376 - At the beginning of 1377 troops led by Lubart Hedyminovychem came almost to Cracow. In early summer Vladislav Opolsky had to flee to Hungary.
In response - Louis gathered a large army and moved to Volhynia, circled Belz. After 7 weeks in autumn 1377, Belz land was annexed to the possessions of Vladislav Opole.
So long war ended because of Galicia and Kholmshchina Belz land came under protege of the Hungarian king, Volyn - under the authority of the Lithuanian dynasty.
2. The entry of Kyiv, Chernihiv-Sivershchyna, skirts to the Lithuanian State
-
 The only real force capable of resisting the progress of Lithuania in the Ukrainian lands was the Golden Horde. However, control over subordinates owned by the Mongol khans gradually lost stiffness: a giant felt given the size of the Horde and the internecine struggle that increasingly acute flashed in the Mongolian state.
The only real force capable of resisting the progress of Lithuania in the Ukrainian lands was the Golden Horde. However, control over subordinates owned by the Mongol khans gradually lost stiffness: a giant felt given the size of the Horde and the internecine struggle that increasingly acute flashed in the Mongolian state.
- Most Ukrainian lands were annexed to Lithuania during spivpravlinnya Princes brothers Olgerd and Keystuta Hedyminovychiv.
- affirm Lithuanian princes in the Kiev region, Chernigov-Siversky tail and some of the time source associated with the battle between wives and Lithuanian horde on the Water Blue that occurred in 1362 (now cyanosis river, left tributary of the Southern Bug).
joining lands of South-Western Rus turned Duchy of Lithuania to the large feudal state. the end of 14 century. it was a federation of land-principalities, including Ukrainian - Kyiv, Chernihiv-Seversky, Volyn, Podolski. Each of them is, as always, ruled autonomous prince, however, is no longer with the Rus dynasty Rurik dynasty, and a Lithuanian - Hedyminovychiv. Kyiv and Chernihiv-Sivers'kyi owners, in particular, were the sons of Grand Duke - Vladimir and Dimitri Olgerdovich Korbut. In Volyn reigned Olgerd Liubard younger brother, and after him - Lubart son Theodore, in Podolia ruled nephews Olgerd - Princes Koriatovychi. The new rulers quickly turned into Ukrainian Lithuanian dynasty rulers.
3. Features social and political life of Ukrainian lands in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in the second half of the 14 century.
- Most Ukrainian lands during the second half of the 14 century. joined the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
- Galicia appeared in the Polish Kingdom.
- is why historians call this period the Lithuanian-Polish era.
If - in Galicia remains Ukrainian nobility lost their power, in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania Rus princes and boyars retained their power law.
- Given the Belarusian and Ukrainian - the Russians, as if saying, terrain and conditions of their stay under the rule of Lithuanian Grand Dukes, who was called Lithuanian Lithuanian-Ruthenian state.
Stay Rus lands in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania was characterized by several features.
-
 Rusychi accounted for 90% of the population. Their culture had a significant impact on the Lithuanians.
Rusychi accounted for 90% of the population. Their culture had a significant impact on the Lithuanians.
- widespread among the Lithuanian nobility gained Ruthenian faith - so at first called on the Lithuanian Orthodox Christianity.
- Ruthenian language was the language of the grand court and state office.
- Therefore the Lithuanian Ruthenian population is not perceived as foreign.
- Ruthenian influence helped consolidate marriages Lithuanian princes of Rus Duchess.
But the salient feature of - stay Rus lands in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania was the fact that Lithuanians allowed local Ukrainian nobles hold the highest administrative positions.
- Rus princes and boyars became the service of the Grand Duke of Lithuania, for what for them fixing their ancestral land.
- remained on the ground all the previous management system. Save a traditional way of life carried out by the principle: «Old not break, and not introduce new ones.
- the end of 14 century. on our lands continue to be big and small separate principalities that personified the preservation and state traditions and the existence of state formations in our land.
- It lasted until the Lithuanian government has not changed his political orientation.
- beginning of the change was the conclusion by Lithuania Union (Union) with Poland.
- in 15 - early 16 th century. Grand Duchy of Lithuania had no "Lithuanian-Ruthenian" and became "Lithuanian-Polish".
Kiev principality of Vladimir Olgerdovich
-
 From 1363 in Kiev knyazyuvav Vladimir Olgerdovich .
From 1363 in Kiev knyazyuvav Vladimir Olgerdovich .
- mother baptized by the Orthodox rite, trained in customs and traditions of the Slavic, Lithuanian prince was seen in Kiev as a stranger and quickly porozumivsya the local boyars.
- He organized several trips to the south against the nomadic hordes.
- result of successful military operations ordyntsev was forced to the Black and Azov Seas.
This contributed to raising - fallen on hard times during the Mongol Kiev.
- evidenced by economic power and the desire to be free depending on Vladimir mint its own coins.
- Kyiv prince felt an independent ruler. This confirms the time and his title: in a few documents that survived from those times, Vladimir Olgerdovich imenuvav themselves «the grace of God Prince of Kiev» .
4. KREVO Union
-

 Changes in the position of Ukrainian lands in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania occurred with the advent of the Lithuanian Grand Duke Jagiello Olgerdovich, in its policy that began more than pay attention to Poland.
Changes in the position of Ukrainian lands in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania occurred with the advent of the Lithuanian Grand Duke Jagiello Olgerdovich, in its policy that began more than pay attention to Poland.
- affirm the new ruler of Lithuania took place under difficult circumstances, since inheritance Yahajlo Vilensky Great-table despite the generic principles of seniority: he was the youngest Olgerd.
- uncertain situation forced Jagiello actively searching for allies inside the country. Following the tradition spivpravlinnya it closer to his brother Skyrhayla.
- Soon Poles Jagiello offered to marry their queen Yadvyhoyu and, accordingly, the Polish crown.
- reason for the zealous solicitations on the part of Poland was a threat to both countries by the Teutonic Order.
- Yahajlo accepted the offer. result of his agreement was finalized between Lithuania and Poland in August 1385 in Kreva (now in Belarus) State and political union, known in history as Krevsk Union.
- Agreement between the Lithuanian and Polish princes powers that included a shift in Catholicism Jagiello, his relatives and all unbaptized Lithuanians marriage of Jadwiga and Jagiello Grand Duchy of Lithuania's accession to the Polish state.
- In February 1386 Yahajlo accepted Catholicism, taking the name W
-
 Soon to Catholicism were gathered and Lithuania. Boyars of Lithuania Catholics were urivnyano the rights of the Poles. Although complete agreement concluded in Kreva and ever connect all their lands, Lithuanian and Ruthenian, the Kingdom of Poland Yahajlo and failed, because the person Vytautas Keystutovycha found a keen advocate of state revival Lithuania.
Soon to Catholicism were gathered and Lithuania. Boyars of Lithuania Catholics were urivnyano the rights of the Poles. Although complete agreement concluded in Kreva and ever connect all their lands, Lithuanian and Ruthenian, the Kingdom of Poland Yahajlo and failed, because the person Vytautas Keystutovycha found a keen advocate of state revival Lithuania.
It was launched - Ostrivs'ka agreement in 1392, where Yahajlo had to recognize a life governor of Vytautas the Great Duchy of Lithuania, conquering all his power autonomous princes.
- Vytautas pleaded vassal of the Polish king.
5. Galician and Volyn region after Krevsk Union
With the death of Westminster - Volyn acknowledged supremacy of Lithuania.
- After 1382 it ceased to exist and the Polish-Hungarian union.
- lost support and the governor of Galicia Vladislav Opolsky .
- Polish-Lithuanian army, which came in the Galician lands in February 1387, almost no one did not resist.
- Przemysl and Lviv surrendered without a fight. Galician burghers defended, but when their palatine guarantee his possession, he also passed the city.
- Galician land was part of Poland.
- same time it was completed the conquest of Chelm and Belz principality.
- By 1434, these lands have remained autonomous holdings, managed by the Polish government - old age, judges and magistrates.
However, about - 1434 was formed Ruthenian Voivodeship as part of Lviv, Galician, Przemysl , Sanok and Chelm lands.
Immediately after the accession of Poland, Galicia to the Polish government set about opolyachuvaty Ukrainian forcibly enforce Catholicism: the existing closed, banned construction of new Orthodox churches and monasteries, the Orthodox forbidden to occupy high positions; planted disregard for the Ruthenian Orthodox faith and culture.
 English
English

 Due to the lack of successors to the princely family of boyars people there started looking elsewhere captain.
Due to the lack of successors to the princely family of boyars people there started looking elsewhere captain. 
 Claims Polish kingdom in the land of Galicia were not new. Thus, the Polish king Casimir III , , the 1340 Lions attacked, just received the news of the death of Prince George.
Claims Polish kingdom in the land of Galicia were not new. Thus, the Polish king Casimir III , , the 1340 Lions attacked, just received the news of the death of Prince George.  In 1366, during the new war, Belz withstood the siege of the Polish army, but the war consisted of Westminster to fail: he was forced to leave the Galician land, he lost much of Vladimir and Volyn.
In 1366, during the new war, Belz withstood the siege of the Polish army, but the war consisted of Westminster to fail: he was forced to leave the Galician land, he lost much of Vladimir and Volyn. 
 The only real force capable of resisting the progress of Lithuania in the Ukrainian lands was the Golden Horde. However, control over subordinates owned by the Mongol khans gradually lost stiffness: a giant felt given the size of the Horde and the internecine struggle that increasingly acute flashed in the Mongolian state.
The only real force capable of resisting the progress of Lithuania in the Ukrainian lands was the Golden Horde. However, control over subordinates owned by the Mongol khans gradually lost stiffness: a giant felt given the size of the Horde and the internecine struggle that increasingly acute flashed in the Mongolian state.  Rusychi accounted for 90% of the population. Their culture had a significant impact on the Lithuanians.
Rusychi accounted for 90% of the population. Their culture had a significant impact on the Lithuanians.  From 1363 in Kiev knyazyuvav Vladimir Olgerdovich .
From 1363 in Kiev knyazyuvav Vladimir Olgerdovich . 
 Changes in the position of Ukrainian lands in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania occurred with the advent of the Lithuanian Grand Duke Jagiello Olgerdovich, in its policy that began more than pay attention to Poland.
Changes in the position of Ukrainian lands in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania occurred with the advent of the Lithuanian Grand Duke Jagiello Olgerdovich, in its policy that began more than pay attention to Poland.  Soon to Catholicism were gathered and Lithuania. Boyars of Lithuania Catholics were urivnyano the rights of the Poles. Although complete agreement concluded in Kreva and ever connect all their lands, Lithuanian and Ruthenian, the Kingdom of Poland Yahajlo and failed, because the person Vytautas Keystutovycha found a keen advocate of state revival Lithuania.
Soon to Catholicism were gathered and Lithuania. Boyars of Lithuania Catholics were urivnyano the rights of the Poles. Although complete agreement concluded in Kreva and ever connect all their lands, Lithuanian and Ruthenian, the Kingdom of Poland Yahajlo and failed, because the person Vytautas Keystutovycha found a keen advocate of state revival Lithuania.