FORMATION OF UKRAINIAN COSSACK STATE - Hetman
Principal PROCEEDINGS
- main achievement of the National Liberation War - the establishment of the Ukrainian state - Hetman.
- feature of the Cossack state was its military. He explained by a need to fight for independence and traditions Zaporizhia Army.
- during summer - autumn of 1648 liberated the Ukrainian lands was established Ukrainian central and local government, judicial institutions, introduced a new principle of territorial-administrative division, gradually formed a new socio-economic structure.
- to participate in building the country were involved in various segments of contemporary Ukrainian society (Cossacks, Ukrainian Orthodox nobles, burghers and the clergy).
BODIES OF STATE POWER
| |
|
General Council - the general council of all troops, the highest legislative body of state | |
|
| |
|
officers' council - general officers and colonels - considered all the issues of international policy, including peace and war, the city asserted privileges and executions, etc. | |
|
|
General Government (General Staff) led by Hetman
Hetman
-
implemented legislative, executive and judicial power;
-
called General and the officer council;
-
issued proclamations;
-
was chief of the armed forces;
-
involved in legal proceedings (acting hetman of general court-martial);
-
supervised financial system;
-
by the Board started the war;
-
led peace talks;
-
led diplomatic relations with other states and intelligence services. |
Administrative division
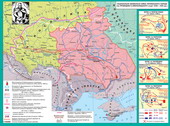
- territory of the Cossack state under the terms of the contract Zborivsky consisted of the former lands of Kiev, Chernigov and Bratslav provinces and held 200 thousand square meters. km. - From the river Slutch Moscow in the west to the east and the border of the Pripyat Basin in the north to the steppe zone in the south.
- capital and residence of the hetman was pm Chigirin.
In the liberated lands - skasovuvavsya Polish administrative system. It eliminated the province, district, and instead created shelves of their territorial division. In 1649 the entire territory of the Ukrainian state was divided into 16 bands (on the Right Bank - 9, of the Left - 7 bands).
- Center regiment was one of the great cities of the regimental area.
- Each regiment was headed by Colonel, who was elected to the Council or appointed regimental hetman. Colonel concentrated in the hands of military, judicial and administrative authority in the regiment, that was not only a military leader but also had authority over all inhabitants of the regiment.
- Territory regiment was divided into 10-20 and even more hundred . Hundreds, like shelves, area and population variation. Administrative centers were hundreds of cities, towns and large villages.
- military-administrative authority in the hundreds conducted hundreds .
- Cities had Magdeburg Law (Kyiv, Nizhyn Chernigov, Pereyaslav, Starodub, deaf, Poltava, Baturin et al.) directing magistrates led by log. In rural affairs dark age, which selected the peasant community and Cossack affairs - their elected atamans.
- Zaporizhzhya Sich was a separate state in the subdivision.
ESTABLISHMENT OF UKRAINIAN ARMY
- Hetman state was one of the strongest armies in Europe at that time, which was created by Bogdan Khmelnitsky and Cossack officers experienced in the first year of the war the union of disparate peasant and Cossack troops.
- People's Liberation Army consisted of over 100 thousand soldiers and was organized by regiment centesimal-territorial principle: a certain area exhibited several hundred Cossacks, which joined the regiment.
- army consisted of representatives from various groups. Most were peasants and commoners pokozachene. However, the core of the army were Registered and Zaporozhye Cossacks.
- structuring forces, its logistical support, training and personnel policies as implemented by tradition Zaporizhia Army.
- basis Cossack troops was infantry . On the initiative of Hetman during the National War created the Cossack cavalry , which has successfully resisted in 1649 the enemy. In the field army units also included intelligence, fortifications and border guard services, Guard units. Special units provided arms, ammunition, food.
fellow campaigner Bogdan Khmelnitsky
- Bogdan Khmelnitsky was able to attract talented Cossack army commanders. They came from different social conditions, but all of them united extraordinary commitment to national liberation war and personally Brussels.
- Philo Jalali, Theodore Veshnyak John poise, Nestorenko Maxim, Maxim Sergeant, Tymish proboscis monkey, take Vyhovski, Nechai, Ivan Bohun, Ostap Gogol (Gogol ancestor), Anton Zhdanovich, Martin Nebaba were closest getmansku environment. For example, Theodore Veshnyaka advisor called Khmelnytsky and of Philo Dzhalaliya contemporaries wrote that he was at nevidluchno hetman.
- Many originated from the Cossack nobility. In particular, Kyiv Colonel Mikhail Krichevsky , who participated in the battles of 1648 - the first half of 1649, born in Brest Ukrainian gentry. Old generation Ukrainian Orthodox nobles Gulyanitskii gave Ukraine three colonels - Gregory, John and Cyril.
- Natives of the nobility, becoming the Cossacks, often arriving at the General Office, for the most part had a good education, know the laws and diplomatic etiquette.
- were among the Cossack officers and representatives of the burghers and peasants. Former Korostyshev burgher and then Chernihiv colonel Nebaba Martin foreign diplomats consider one of the best colonels Khmelnytsky.
FINANCIAL SYSTEM
- organization of state apparatus, the maintenance of troops, diplomatic activity requiring a lot of money. Financial matters within the Cossack Bohdan Khmelnytsky directly supervised.
- There were multiple sources of income military treasure, and above all - the land that came into use Treasure, agricultural industries (mills, breweries, etc.) and charge them rent.
- lot of money came from trade (with fees and trading fairs, border fees, etc.).
- existed in the state and general taxes.
Features - payments and income taxes were determined Getmanov universals. Unit of taxation was set to court, ie the economy.
- with bank notes in circulation were the most common Polish coins, then Moscow and Turkish money. According to contemporaries, in late 1649 began minting coins of the state, however, those coins were found.
PROCEEDINGS
- Cossack state was acting in its own system of justice. It consisted of the General Court, and centesimal regimental courts.
- highest judicial institution was General Military Court at the hetman. He considered the appeal of the case and centesimal regimental courts, and some things with which applicants applied directly to the hetman.
- The General Court consisted of two judges and the general court clerk.
- Courts on the ground led by colonels or captains personally. Cossack courts were subject not only to the Cossacks, but also the commoners and peasants.
- In cities of Magdeburg city courts were right. In addition, Ukraine has functioned and church courts, which extended the validity of the internal affairs of the clergy.
changes in socio-economic life COSSACK UKRAINE
- promotion of the Ukrainian Cossack state - Hetman - took place against the backdrop of profound changes in economic and social life.
- was eliminated and a large secular middle tenure filvarkovo panschynnu-system management, serfdom.
Instead - formed Cossacks, peasants, and public ownership of land.
- In this connection, changed the social structure of society. Were forced to leave Ukraine Polish magnates and Catholic nobles, Catholic clergy - those groups that were holding in their hands the power to the National Liberation War.
- leading role in society has to play a Cossack state.
- government and the main wealth concentrated in the hands of the Cossack.
- Cossack officers formed of representatives of different social classes.
- absolute conquest of the Cossack state was the personal freedom of the vast majority of peasants and townspeople, who, moreover, could easily join the Cossack.
The vast majority of peasants - pokozachylasya, started to hold free Cossack economy.
- burghers polipshuvalosya situation also because the cities were eliminated the dominance of foreigners and to remove national and religious barriers to employment in handicrafts, fisheries, trade, to participate in governance.
 English
English