LIFE AND COMMERCIAL political system Left Bank Hetman and Sloboda UKRAINE In the second half XVII.
BACKGROUND
During the second half XVII. Russian kings intensified attack on Ukrainian statehood. This could not but affect the administrative-territorial structure. His authority in Hetman tsarist government carried through the Ambassador's commandment. During 1654-1662 he worked in his office stock of Little Russian affairs. In 1662-1722 he operated a special commandment of Little Russia. These institutions closely followed the activities of military and administrative authorities Hetmanate. Monastic Little Russia intervened in the election and the new Cossack Hetman, supporting some candidates and depriving the government of others; gathering information about the political situation in Ukraine, even resorting to such dirty methods as the denunciations; undertook direct management of rulers in Ukrainian cities, etc..
Colonization UKRAINIAN MASS Slobozhanshchina
- East of Hetman, on the border with Russia rozprostorylysya virgin land. Once those lands belonged to Chernihiv-Seversky Principality, were peopled and lived-in, but in the XIII century. suffered devastating invasions ordyntsev.
- Steppe invasions along rivers utoruvaly paths for their attack on Ukraine and Muscovy. That is why the rich land for a long time remained neglected and znelyudnilym. He was a kind of boundary between Muscovy and the Tatars.
- From the 1630's were here pinch rolls Ukrainian settlers who left their homes grace after failed uprisings, wars, exploitation of foreigners.
- Tsarism interested in zalyudnenni borderlands, strongly encouraged the Ukrainian migration, putting on them the protection of the borders of Moscow from the devastating blows of the steppe.
FOUNDATION Sloboda CITIES
- Mass Ukrainian migration fell to the mid XVII. Difficulty domestic situation with the National Liberation War, forced the family, and even entire villages to leave their homes and go into a dangerous path.
- Yes 1652 thousand Cossacks led by Colonel John Dzykovskoho with women and children came out of the gaff in Volhynia.
- near the Don river in a quiet pine tree, and Ostrohoschi, they founded the city Ostrohozk.
- Colonel Dzykovskyy brought with him all the regimental officers: ARCHITECTURE, secretary, captain and two priests.
- Settlers came from all farming, which made life easier in the new place.
- Another great group of settlers from Stavishche Bilotserkivskyi regiment led by Herasym Kondratyev same year founded the city of Sumy.
- in 1654 on the settlement, which merged Lopan River and Kiev, was founded in Kharkov.
- establishment had a similar history and cities like Saltiv, Murafa, Romney, Balakliya, raisins and more. Along with cities laid village.
- They usually settled small groups of immigrants from different lands of Ukraine.
- Since settlement there have been exempted from taxes, then they were called by the ancient Ukrainian tradition Sloboda . From here comes a title and land - Sloboda Ukraine , or Sloboda.
- left lived-in place and set out in the perilous journey mostly wealthy Cossack family. Encouraged by royal government, they received certain privileges.
- The main among them belonged to the right zaymanschyny. Each settler pryvlasnyuvav as land, forest, meadow, much as he could handle.
- busy land is not taxed. Similarly, no taxes were taken and commercial industries. Instead of paying taxes, Ukrainian immigrants were obligated to perform military service.
- The numerous settlers from the Left Bank and Right Bank attracted the right to self-Cossack, his royal government at the beginning of colonization remained in Ukrainian. Recognition of the settlers power of the king exposed oath.
- rights of Ukrainian settlers were tied to the king's brevet.
So during the second half XVII century. along with the Left-Bank Hetmanate put another Cossack region - Sloboda Ukraine.
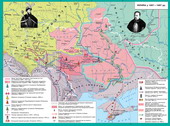
Administrative division of the Left Bank Hetman and Sloboda UKRAINE
Administrative division Hetmanate
remained unchanged since the National Liberation War. At the end of XVII century. the Left there 10 bands , who were both administrative and territorial units and the military.
Administrative division of Sloboda Ukraine
formed five Cossack regiments - Ostrohozkyy, Kharkov, Sumy, and Ohtirsky Izyumsky . These shelves, as in Hetman, were not only military but also the administrative and territorial units. The shelves were divided into hundreds. Colonel of the regiment led the regiment officers. Post colonel was elected . He headed the regiment administration, argued a court ruling handed settlers free land, and commanded the regiment during the campaigns.
colonels elected for life. In addition, Sloboda Ukraine happened often inherit the post of colonel. This stems from features colonization of new lands: Colonels were usually leaders of immigration groups. They had an extraordinary reputation for actually were the founders of the regiments, unlike Hetmanate.
power in the Left Bank Hetman and Sloboda UKRAINE
Hetman
- Place General Military Council was still hiding the Khmelnytsky officers' advice. It comprised the Hetman and the General Staff - ARCHITECTURE, clerk, two judges, two captain, Bunchuznyj, and 10 colonels. This established a council tax rates, rent, carried out the decisions on defense.
- direct solicitation relied on General Military Chancellery.
- highest official in Hetman Hetman was .
- In the second half XVII. narrow its elected officers' council, whose decision favored the Cossack army at the General Military Council.
- finally asserted Hetman king.
- Hetman's power was limited though kings, but in matters of domestic life remained significant left-bank Ukraine.
- Powers Hetman determined special article (conditions) , entered into by the hetman and the king.
- Getman, including the officers had a right to ownership of land for service, appoint.
- Hetman defined as areas of domestic policy Hetmanate conditions negotiations or correspondence with other governments.
- Rights Advisory Council of the hetman was the general foreman.
Sloboda Ukraine
- In Sloboda Ukraine Hetman position did not exist, and there was general foreman. This was another feature of the administrative and political structure Slobodian impose tsarist.
- Slobodskiy directly subordinate to Colonel Belgorod Province Governor.
- each regiment separately and at different times received the king's brevet in which determined his right to a Cossack system, free trade, tax exemptions for land etc..
- selected in the regiments of Colonels governor of Belgorod, where they were subject to military affairs, suggested to the king as ... Candidates for this position.
- The size of the Cossack regiments was not permanent.
List of all - Slobidsky regiments contained a list of Cossacks who had to perform military service.
Social status
When the National War Ukrainian society has undergone great changes.
Cossacks
- number of Cossacks grew, it became a privileged status.
- Cossacks names recorded in government registries and subject only Hetman government and officers.
- They have the right to freedom of residence in cities and villages, craft classes, trade, fisheries.
- preserved traditional Cossack Court.
- Cossacks were exempted from taxes, their main duty was military service.
- Cossacks was the leading state and Sloboda Ukraine.
- Cossacks owned land, worked on it for their own farms were allowed to trade freely, not paying taxes.
- Just as in Hetman, their main duty was military service.
- largest group of Cossacks were the garden - so called Cossacks, who lived in cities, towns, villages, hamlets Hetman Sloboda Ukraine, in contrast to the grassroots (Zaporozhye) Cossacks.
- In the second half XVII. from among the cossacks vyokremylas Cossack officers , which occupied the dominant place in society.
Ukrainian gentry
- kept in Hetmanate. It is increasingly mingled with Cossack leaders because of a petty rights and privileges.
Farmers
- Numerous Hetmanate stratum . After the National War changed their position. They gained the right to change domicile freely join the Cossack state (the only obstacle was the proprietary position for military service took place at their own expense).
- personal liberty save farmers and Sloboda Ukraine . Their difference from the Cossacks was that they had to pay tax to the king's treasury.
burghers
- Their situation in the second half XVII. has changed.
It was determined - royal letters Magdeburg law and norms.
Part - pokozachylasya urban residents (60-80%). Instead of townspeople to some farmers were recorded.
- burghers obtained the right to freely own land, they are limited in the crafts industry, and trade.
- They paid taxes and performed duties in favor of the state, which, however, were significantly lower than the Commonwealth.
- Many townspeople were among the settlers to Sloboda Ukraine. They, like farmers, lived more with agriculture, but not avoided and crafts, guild system in place similar to what existed in Hetmanate.
Clergy
- preferred Hetman state and Sloboda Ukraine.
- His position was determined by the fact that Orthodoxy had the status of state religion.
In the Orthodox Church - Hetman government laid a very important task - to be an ideological pillar of the independent Cossack state.
- no coincidence that all hetmans helped the church: whether financially supporting the monasteries, or the pursuit of improving the education of priests, and facilitating church books printed.
SUBORDINATION UKRAINIAN Orthodox Church Moscow Patriarchate
- execution core role of the Orthodox Church Ukrainian state troubled Russian kings, who sought the ultimate conquest of Ukraine.
- Royal officials believed that Orthodoxy in Ukraine has to justify their predatory policies of the Ukrainian lands.
- Meanwhile, the presence of independent Kiev Metropolis contrary to those beliefs.
Therefore - Moscow endeavored to fully subordinate Ukrainian Orthodox Church Moscow Patriarchate.
- After the death of Metropolitan Joseph Nelyubovych-Tukals'kyy (1675) through the intervention of Moscow's long postponed elections for a metropolitan department.
- Imperial Government sought to use the situation to achieve his goal: to bring the subordination of the Metropolis of Kiev Patriarch of Constantinople, by setting its supremacy over the Patriarch of Moscow.
- case subordination of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church Moscow Patriarchate could settle faster if this sympathetic Metropolitan of Kyiv. That is why the metropolitan department searched for an applicant, favorable Moscow. Finally, such a find (he was bishop of Lutsk Gideon Chetvertynsky) and June 19, 1684 council meeting.
With the support of Moscow - Bishop Gideon was elected metropolitan. In October of that year the newly elected Metropolitan went to Moscow, where Patriarch Joachim December 8, 1685 in the Assumption Cathedral was solemnly consecrated him.
- Meanwhile, Moscow's diplomacy was looking at the impact of the Patriarch of Constantinople, so he gave his consent to the transfer of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church Moscow Patriarchate in the submission.
- In May 1686 Patriarch of Constantinople under the pressure of the Turkish government agreed to a separation of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church of Constantinople to the throne. Thus, despite the religious laws, the Kyiv metropolitan was subordinated to the Moscow patriarch.
subordination of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church Moscow Patriarchate heavy defeat Ukrainian liberation movement - as of 1686 the church no longer provided ideological support in the struggle for national independence of Ukraine, and vice versa - has gradually become an obedient tool of aggression policy kings, becoming a means of Russification of Ukrainian, depriving them of the national public idea.
 English
English